AI News for 9/6/2024-9/9/2024. We checked 7 subreddits, 384 Twitters and 30 Discords (215 channels, and 7493 messages) for you. Estimated reading time saved (at 200wpm): 774 minutes. You can now tag @smol_ai for AINews discussions!
At the special Apple Event today, the new iPhone 16 lineup was announced, together with 5 minutes spent covering some updates on Apple Intelligence (we’ll assume you are up to speed on our WWDC and Beta release coverage).
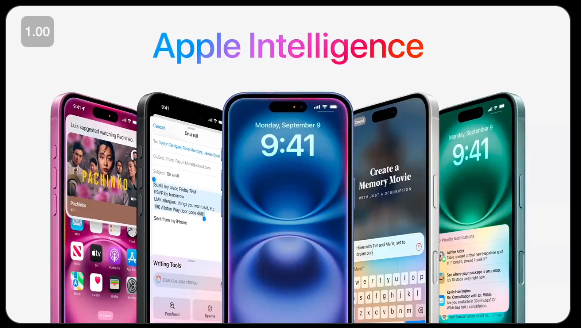
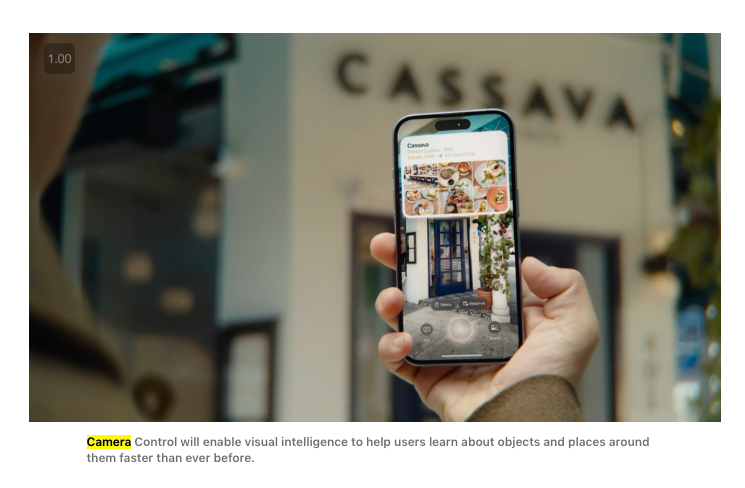
The newest update is what they now call Visual Intelligence, rolling out with the new dedicated Camera Control button for iPhone 16:
As discussed on the Winds of AI Winter pod and now confirmed, Apple is commoditizing OpenAI and putting its own services first:
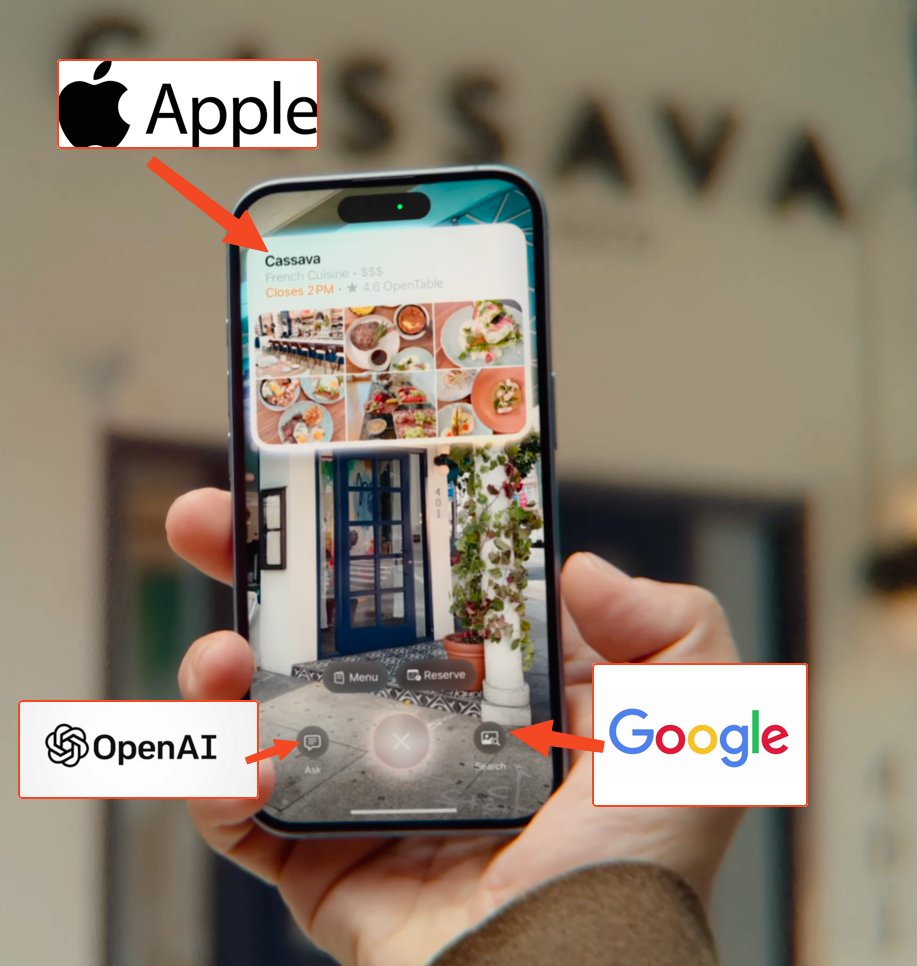

Presumably one will eventually be able to configure what the Ask and Search buttons call in the new UI, but every Visual Intelligence request will run through Apple Maps and Siri first and those services second. Apple wins here by running first, being default, and being private/free, which is surprisingly a more defensible position than being “best”.
Apple Photos now also have very good video understanding, down to the timestamps in a video:

Craig Federighi called this a part of Apple Intelligence in his segment, but some of these features are already in the iOS 18.0 beta (Apple Intelligence only shipped in iOS 18.1).
You can read the Hacker News commentary for other highlights and cynical takes but that’s the big must-know thing from today.
How many years until Apple Visual Intelligence is just… always on?

A Note on Reflection 70B: our coverage last week (and tweet op-ed) covered known criticisms on Friday, but more emerged over the weekend to challenge their claims. We expect more developments over the course of this week, therefore it is premature to make it another title story, but interested readers should scroll to the /r/localLlama section below for a full accounting.
Perhaps we should work on more ungameable LLM evals? Good thing this month’s inference is supported by our friends at W&B…
Sponsored by Weights & Biases: If you’re a builder in the Bay Area Sep 21/22, Weights & Biases invites you to hack with them on pushing the state of LLM-evaluators forward. Build better LLM Judges at the W&B Judgement Day hack - $5k in prizes, API access and food provided.
{% if medium == ‘web’ %}
Table of Contents
[TOC]
{% else %}
The Table of Contents and Channel Summaries have been moved to the web version of this email: [{{ email.subject }}]({{ email_url }})!
{% endif %}
AI Twitter Recap
all recaps done by Claude 3.5 Sonnet, best of 4 runs.
AI Model Developments and Benchmarks
-
Reflection-70B Claims: @JJitsev reported that Reflection-70B claims to be the “world’s top open source model” based on common benchmarks. However, preliminary tests using the AIW problem show the model is close to Llama 3 70B and slightly worse than Qwen 2 72B, not reaching top-tier performance as claimed.
-
LLM Planning Capabilities: @ylecun noted that LLMs still struggle with planning. Llama-3.1-405b and Claude show some planning ability on Blocksworld, while GPT4 and Gemini perform poorly. Performance is described as “abysmal” for all models on Mystery Blocksworld.
-
PLANSEARCH Algorithm: @rohanpaul_ai highlighted a new search algorithm called PLANSEARCH for code generation. It generates diverse observations, constructs plans in natural language, and translates promising plans into code. Claude 3.5 achieved a pass@200 of 77.0% on LiveCodeBench using this method, outperforming the no-search baseline.
AI Tools and Applications
-
RAG Pipeline Development: @dzhng reported coding a RAG pipeline in under an hour using Cursor AI composer, optimized with Hyde and Cohere reranker, without writing a single line of code. The entire process was done through voice dictation.
-
Google AI’s Illuminate: @rohanpaul_ai mentioned Google AI’s release of Illuminate, a tool that converts research papers to short podcasts. Users may experience a waiting period of a few days.
-
Claude vs Google: @svpino shared an experience where Claude provided step-by-step instructions for a problem in 5 minutes, after spending hours trying to solve it using Google.
AI Research and Developments
-
AlphaProteo: @adcock_brett reported on Google DeepMind’s unveiling of AlphaProteo, an AI system designed to create custom proteins for binding with specific molecular targets, potentially accelerating drug discovery and cancer research.
-
AI-Driven Research Assistant: @LangChainAI shared an advanced AI-powered research assistant system using multiple specialized agents for tasks like data analysis, visualization, and report generation. It’s open-source and uses LangGraph.
-
Top ML Papers: @dair_ai listed the top ML papers of the week, including OLMoE, LongCite, AlphaProteo, Role of RAG Noise in LLMs, Strategic Chain-of-Thought, and RAG in the Era of Long-Context LLMs.
AI Ethics and Societal Impact
-
Immigration Concerns: @fchollet expressed concerns about potential immigration enforcement actions, suggesting that legal documents may not provide protection in certain scenarios.
-
AI’s Broader Impact: @bindureddy emphasized that AI is more than hype or a business cycle, stating that we are creating new beings more capable than humans and that AI is “way bigger than money.”
Hardware and Infrastructure
-
Framework 13 Computer: @svpino mentioned purchasing a Framework 13 computer (Batch 3) for use with Ubuntu, moving away from Mac after 14 years.
-
Llama 3 Performance: @vipulved reported that Llama 3 405B crossed the 100 TPS barrier on Together APIs with a new inference engine release, achieving 106.9 TPS on NVIDIA H100 GPUs.
AI Reddit Recap
/r/LocalLlama Recap
Theme 1. Reflection 70B Controversy: Potential API Fraud and Community Backlash
-
CONFIRMED: REFLECTION 70B’S OFFICIAL API IS SONNET 3.5 (Score: 278, Comments: 168): Reflection 70B’s official API has been confirmed to be Sonnet 3.5. This information aligns with previous speculations and provides clarity on the technical infrastructure supporting this large language model. The confirmation of Sonnet 3.5 as the API suggests specific capabilities and integration methods for developers working with Reflection 70B.
-
OpenRouter Reflection 70B claims to be Claude, Created by Anthropic (try it yourself) (Score: 68, Comments: 29): OpenRouter’s Reflection 70B model, available through their API, claims to be Claude and states it was created by Anthropic. This assertion raises questions about the model’s true identity and origin, as it’s unlikely that Anthropic would release Claude through a third-party API without announcement. Users are encouraged to test the model themselves to verify these claims and assess its capabilities.
-
Reflection 70B (Free) is broken now (Score: 86, Comments: 25): The Reflection 70B free API is currently non-functional, possibly due to exhaustion of Claude credits. Users attempting to access the service are encountering errors, suggesting that the underlying AI model may no longer be available or accessible through the free tier.
- Reflection 70B API outage is attributed to exhausted Claude credits, with users speculating on the end game of the developer. A VentureBeat article hyped GlaiveAI as a threat to OpenAI and Anthropic, but major publications have yet to cover the fallout.
- OpenRouter replaced the API version with an open weights version, still named Reflection 70B (Free). Users questioned OpenRouter’s verification process, with the company defending its quick model deployment without extensive review.
- Some users suggest this incident mirrors a previous Glaive-instruct 3b controversy, indicating a pattern of hyping models for funding. Others speculate on potential distractions or ulterior motives behind the reputation-damaging event.
Theme 2. Community Lessons from Reflection 70B Incident: Trust and Verification in AI
-
Well. here it goes. Supposedly the new weights of you know what. (Score: 67, Comments: 77): The post suggests the release of new weights for Reflection 70B, a large language model. However, the community appears to remain highly skeptical about the authenticity or significance of this release, as implied by the cautious and uncertain tone of the post title.
-
Reflection 70B lessons learned (Score: 114, Comments: 51): The post emphasizes the critical importance of model verification and benchmark skepticism in AI research. It advises that all benchmarks should start by identifying the specific model being used (e.g., LLAMA, GPT-4, Sonnet) through careful examination, and warns against trusting benchmarks or API claims without personal replication and verification.
- Users emphasized the importance of verifying models through platforms like Lmarena and livebench, warning against trusting unsubstantiated claims from unknown sources. The community expressed a need to recognize bias towards believing groundbreaking improvements.
- There’s growing evidence that Matt Shumer may have been dishonest about his AI model claims. Some speculate this could be due to mental health issues, given the short timeframe from project conception to revealed fraud.
- Commenters stressed the importance of developing personal benchmarks based on practical use cases to avoid falling for hype. They also noted that the incident highlights the expectation for open-weight models to soon match or surpass proprietary options.
-
Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence, something Reflection 70B clearly lacks (Score: 177, Comments: 31): The post title “Extraordinary claims require extraordinary evidence, something Reflection 70B clearly lacks” suggests skepticism about claims made regarding the Reflection 70B model. However, the post body only contains the incomplete phrase “Extraordinary c”, providing insufficient context for a meaningful summary of the author’s intended argument or critique.
- Reflection 70B’s performance is significantly worse when benchmarked using the latest HuggingFace release compared to the private API. Users speculate the private API was actually Claude, leading to skepticism about the model’s claimed capabilities.
- Questions arise about Matt Shumer’s endgame, as he would eventually need to deliver a working model. Some suggest he didn’t anticipate the visibility his claims would receive, while others compare the situation to LK99 and Elon Musk’s FSD promises.
- Users criticize Shumer’s lack of technical knowledge, noting he asked about LORA on social media. The incident is seen as potentially damaging to his credibility, with some labeling it a scam.
Theme 3. Memes and Humor Surrounding Reflection 70B Controversy
-
Who are you? (Score: 363, Comments: 34): The post presents a meme depicting Reflection 70B’s inconsistent responses to the question “Who are you?”. The image shows multiple conflicting identity claims made by the AI model, including being an AI language model, a human, and even Jesus Christ. This meme highlights the issue of AI models’ inconsistent self-awareness and their tendency to generate contradictory statements about their own identity.
- The Reflection 70B controversy sparked numerous memes and discussions, with users noting the model’s responses changing from Claude to OpenAI to Llama 70B as suspicions grew about its authenticity.
- A user suggested that the developer behind Reflection is using commercial SOTA models to gather data for retraining, aiming to eventually deliver a model that partially fulfills the claims. Others speculated about the developer’s true intentions.
- A detailed explanation of the controversy was provided, describing how the model initially impressed users but failed to perform as expected upon release. Investigations revealed that requests were being forwarded to popular models like Claude Sonnet, leading to accusations of deception.
-
TL;DR (Score: 249, Comments: 12): The post consists solely of a meme image summarizing the recent Reflection 70B situation. The meme uses a popular format to humorously contrast the expectations versus reality of the model’s release, suggesting that the actual performance or impact of Reflection 70B may have fallen short of initial hype or anticipation.
- The Twitter AI community was criticized for overhyping Reflection 70B, with mentions that it was actually tested on Reddit. Users pointed out similar behavior in subreddits like /r/OpenAI and /r/Singularity.
- Some users expressed confusion or criticism about the meme and its creator, while others defended the release, noting that it provides free access to a model comparable to Claude Sonnet 3.5.
- A user suggested that the hype around Reflection 70B might be due to OpenAI’s pivot to B2B SaaS, indicating a desire for new developments in the open-source AI community.
-
POV : The anthropic employee under NDA that see all the API requests from a guy called « matt.schumer.freeaccounttrial27 » (Score: 442, Comments: 17): An Anthropic employee, bound by an NDA, observes API requests from a suspicious account named “matt.schumer.freeaccounttrial27”. The username suggests potential attempts to circumvent free trial limitations or engage in unauthorized access, raising concerns about account abuse and security implications for Anthropic’s API services.
- Users joked about the potential consequences of API abuse, with one comment suggesting a progression from “Matt from the IT department” to “Matt from his guantanamo cell” as the scamming strategy escalates.
- The thread took a humorous turn with comments about Anthropic employing cats, including playful responses like “Meow 🐱” and “As a cat, I can confirm this.”
- Some users critiqued the post itself, with one suggesting a “class action lawsuit for wasting our time” and another pointing out the misuse of the term “POV” (Point of View) in the original post.
Theme 4. Advancements in Open-Source AI Models and Tools
-
gemma-2-9b-it-WPO-HB surpassed gemma-2-9b-it-simpo on AlpacaEval 2.0 Leaderboard (Score: 30, Comments: 5): The gemma-2-9b-it-WPO-HB model has outperformed gemma-2-9b-it-simpo on the AlpacaEval 2.0 Leaderboard, achieving a score of 80.31 compared to the latter’s 79.99. This improvement demonstrates the effectiveness of the WPO-HB (Weighted Prompt Optimization with Human Baseline) technique in enhancing model performance on instruction-following tasks.
- The WPO (Weighted Preference Optimization) technique is detailed in a recent paper, with “hybrid” referring to a mix of human-generated and synthetic data in the preference optimization dataset.
- AlpacaEval 2.0 may need updating, as it currently uses GPT4-1106-preview for human preference benchmarking. Suggestions include using gpt-4o-2024-08-06 and validating with claude-3-5-sonnet-20240620.
- The gemma-2-9b-it-WPO-HB model, available on Hugging Face, has outperformed both gemma-2-9b-it-simpo and llama-3-70b-it on different leaderboards, prompting interest in further testing.
-
New upstage release: SOLAR-Pro-PT (Score: 33, Comments: 10): Upstage has released SOLAR-Pro-PT, a new pre-trained model available on Hugging Face. The model is accessible at upstage/SOLAR-Pro-PT, though detailed information about its capabilities and architecture is currently limited.
- Users speculate SOLAR-Pro-PT might be an upscaled Nemo model. The previous SOLAR model impressed users with its performance relative to its size.
- The model’s terms and conditions prohibit redistribution but allow fine-tuning and open-sourcing of resulting models. Some users suggest fine-tuning it on empty datasets to create quantized versions.
- There’s anticipation for nousresearch to fine-tune the model, as their previous Open Hermes solar fine-tunes were highly regarded for coding and reasoning tasks.
-
Ollama Alternative for Local Inference Across Text, Image, Audio, and Multimodal Models (Score: 54, Comments: 34): The Nexa SDK is a new toolkit that supports local inference across text, audio, image generation, and multimodal models, using both ONNX and GGML formats. It includes an OpenAI-compatible API with JSON schema for function calling and streaming, a Streamlit UI for easy testing and deployment, and can run on any device with a Python environment, supporting GPU acceleration. The developers are seeking community feedback and suggestions for the project, which is available on GitHub at https://github.com/NexaAI/nexa-sdk.
- ROCm support for AMD GPUs was requested, with the developers planning to add it in the next week. The SDK already supports ONNX and GGML formats, which have existing ROCm compatibility.
- A user compared Nexa SDK to Ollama, suggesting improvements such as ensuring model accuracy, providing clear update information, and improving the model management and naming conventions.
- Suggestions for Nexa SDK include using K quantization as default, offering I matrix quantization, and improving the model listing and download experience to show different quantizations hierarchically.
All AI Reddit Recap
r/machinelearning, r/openai, r/stablediffusion, r/ArtificialInteligence, /r/LLMDevs, /r/Singularity
AI Model Developments and Releases
-
Salesforce’s xLAM-1b model surpasses GPT-3.5 in function calling: A 1 billion parameter model achieving 70% accuracy in function calling, outperforming GPT-3.5 despite its smaller size.
-
Phi-3 Mini update with function calling: Rubra AI released an updated Phi-3 Mini model with function calling capabilities, competitive with Mistral-7b v3.
-
Reflection API controversy: A sonnet 3.5 wrapper with prompt engineering was marketed as a new model, leading to discussions about AI hype and verification.
AI Research and Applications
-
Virotherapy for breast cancer: A virologist successfully treated her own recurring breast cancer using experimental virotherapy, raising discussions about medical ethics and self-experimentation.
-
Waymo robotaxi progress: Waymo is providing 100,000 robotaxi rides per week but not yet profitable, drawing comparisons to early-stage strategies of companies like Uber and YouTube.
-
AI-generated video creation: A demonstration of creating an AI-generated video using multiple tools including ComfyUI, Runway GEN.3, and SUNO for music generation.
AI Development Tools and Visualization
- TensorHue visualization library: An open-source Python library for tensor visualization compatible with PyTorch, JAX, TensorFlow, Numpy, and Pillow, designed to simplify debugging of tensor contents.
AI Ethics and Societal Impact
- AI-generated art evaluation: A discussion on shifting focus from identifying AI-generated art to assessing its quality, highlighting the evolving perception of AI in creative fields.
AI Industry and Market Trends
- Data growth and AI training: Michael Dell claims the amount of data in the world is doubling every 6-7 months, with Dell Technologies possessing 120,000 petabytes compared to 1 petabyte used in advanced AI model training.
Memes and Humor
- A humorous video about OpenAI’s release cycle and the anticipation for new models.
AI Discord Recap
A summary of Summaries of Summaries GPT4O (gpt-4o-2024-05-13)
1. AI Model Performance
- Reflection 70B underwhelms: Reflection 70B’s performance lagged behind Llama 3.1 in benchmarks, raising skepticism about its capabilities, with independent tests showing lower scores and delayed weight releases.
- Matt Shumer acknowledged issues with the uploaded weights on Hugging Face, promising a fix soon.
- DeepSeek Coder struggles: Users reported DeepSeek Coder malfunctioning and providing zero responses, indicating possible upstream issues despite the status page showing no problems.
- This added to existing frustrations over API limitations and service inconsistencies.
- CancerLLM and MedUnA advance medical AI: CancerLLM and MedUnA are enhancing clinical applications and medical imagery, supported by benchmarks like TrialBench.
- Discussions emphasized diving deeper into medical papers to improve research visibility.
2. AI Tools and Integrations
- Aider improves workflow efficiency: Community members shared their Aider workflows, integrating tools like CodeCompanion for streamlined project setups and emphasizing clear planning.
- A refined system prompt is expected to enhance output consistency in Aider.
- OpenInterpreter’s resource management woes: While the 01 app allows quick access to audio files, users face performance variability on Mac, leading to inconsistent outcomes.
- One user indicated a preference for plain OpenInterpreter due to the 01 app’s stability problems.
3. Open Source AI Developments
- GitHub Open Source AI panel: GitHub is hosting a free Open Source AI panel next Thursday (9/19) at their San Francisco office, discussing access, democratization, and the impact of open source on AI.
- Panelists include representatives from Ollama, Nous Research, Black Forest Labs, and Unsloth AI.
- Finegrain’s open-source image segmentation model: Finegrain released an open-source image segmentation model outperforming closed-source alternatives, available under the MIT License on Hugging Face.
- Future improvements include a subtler prompting method for enhanced disambiguation beyond simple bounding boxes.
4. Benchmarking and Evaluation
- Overfitting concerns in model training: Concerns were raised about overfitting, with benchmarks often misleading and models inevitably experiencing overfitting regardless of size, leading to skepticism about benchmark reliability.
- A member expressed hope for their article on benchmark issues to be reviewed at NeurIPS, highlighting evaluation challenges.
- Benchmark limitations acknowledged: Insights were shared on benchmark limitations, with members noting they remain crucial for comparisons despite flaws.
- Discussions emphasized the necessity of diverse benchmarks to gauge AI models, pointing out risks of overfitting to certain datasets.
5. AI Community Events
- Berlin AI Hackathon: The Factory Network x Tech: Berlin AI Hackathon is scheduled for September 28-29 at Factory Berlin Mitte, aiming to gather 50-100 builders motivated to drive AI-driven innovations.
- Participants can improve existing products or initiate new projects in a collaborative environment.
- LLVM Developer Meeting: The upcoming Fall LLVM Developer Meeting in October will feature 5 talks by Modular on topics including Mojo and GPU programming.
- Recorded sessions will be available on YouTube following the event, generating excitement among attendees.
PART 1: High level Discord summaries
HuggingFace Discord
- Hugging Face Inference API Troubles: Users are facing ‘bad credentials’ errors when accessing private models via the Hugging Face Inference API, often without helpful logs.
- Suggested solutions involve verifying API token setups and reviewing recent updates affecting functionality.
- Fine-Tuning Models on Hugging Face: Discussions indicated that models fine-tuned on Hugging Face might not always upload correctly, leading to missing files in repositories.
- Users recommended scrutinizing configurations and managing larger models during conversion processes for optimal results.
- Challenges in AI Art Generation: The community shared experiences about generating quality AI art, highlighting persistent issues with limb and hand representations.
- Simpler, cheesier prompts were suggested as surprisingly more effective in yielding desirable results.
- Universal Approximation Theorem Insights: Members analyzed the Universal Approximation Theorem, referencing Wikipedia for foundational details.
- Discussions revealed limitations in Haykin’s work and better generalizations from Leshno et al. addressing continuity.
- Exploring Medical AI Advances: Recent updates featured CancerLLM and MedUnA for their roles in clinical applications, alongside benchmarks like TrialBench.
- Members expressed enthusiasm for delving deeper into medical papers, enhancing the visibility of significant research.
aider (Paul Gauthier) Discord
- DeepSeek struggles with benchmark accuracy: Users voiced concerns about DeepSeek Coder performance, indicating it may be using the incorrect model ID, leading to poor stats on the dashboard.
- Both model IDs currently point to DeepSeek 2.5, which may be contributing to the benchmarking issues.
- Aider improves workflow efficiency: Community members shared their Aider workflows, integrating tools like CodeCompanion for streamlined project setups and emphasizing clear planning.
- The introduction of a refined system prompt is expected to enhance output consistency in Aider.
- Reflection 70B falls short against Llama3 70B: Reflection 70B scored 42% on the code editing benchmark, while Llama3 70B achieved 49%; the modified version of Aider lacks necessary functionality with certain tags.
- For further details, check out the leaderboards.
- V0 update shows strong performance metrics: Recent updates to v0, tailored for NextJS UIs, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities, with users sharing a YouTube video showcasing its potential.
- For more insights, visit v0.dev/chat for demos and updates.
- Concerns over AI’s impact on developer jobs: Members expressed worries about how advanced AI tools could potentially alter the developer role, raising questions over job oversaturation and relevance.
- As AI continues to evolve, there’s rising tension regarding the workforce’s future in development.
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) Discord
- Reflection API Available for Playtesting: The Reflection API is now available for free playtesting on OpenRouter, with notable performance differences between hosted and internal versions.
- Matt Shumer expressed that the hosted API is currently not fully optimized and a fixed version is anticipated shortly.
- ISO20022 Gains Attention in Crypto: Members are urged to explore ISO20022 as it could significantly influence financial transactions amid crypto developments.
- The discussion highlighted the standard’s implications, reflecting a growing interest in its relevance to the evolving financial landscape.
- DeepSeek Coder Faces API Malfunctions: Users reported that the DeepSeek Coder is providing zero responses and malfunctioning, indicating possible upstream issues despite the status page showing no reported problems.
- This complication adds to frustrations surrounding existing API limitations and inconsistencies in service availability.
- Base64 Encoding Workaround for Vertex AI: A workaround was devised for JSON upload issues with Vertex AI; users are now advised to convert the entire JSON into Base64 before submission.
- This technique, drawn from a GitHub PR discussion, streamlines the transfer process.
- Integration of Multi-Modal Models: Technicians inquired about methods for combining local images with multi-modal models, focusing on request formatting for proper integration.
- Guidance was provided on encoding images into base64 format to facilitate direct API interactions.
Stability.ai (Stable Diffusion) Discord
- LoRA vs Dreambooth Showdown: LoRAs are compact and easily shareable, allowing for runtime combinations, whereas Dreambooth generates much larger full checkpoints.
- Both training methods thrive on limited images, with Kohya and OneTrainer leading the way, and Kohya taking the crown for popularity.
- Budget GPU Guide Under $600: For local image generation, users suggest considering a used 3090 or 2080 within a $600 budget to boost VRAM-dependent performance.
- Increasing VRAM ensures better results, especially for local training tasks.
- The Backward Compatibility Hail Mary: There is a plea for new Stable Diffusion models to maintain backward compatibility with SD1.5 LoRAs, as SD1.5 is still favored among users.
- Conversations underline SD1.5’s strengths in composition, with many asserting that newer models have yet to eclipse its effectiveness.
- Content Creation Critique: Influencers vs Creators: A critique surfaced regarding the influencer culture that pressures content creators into monetizing via platforms like Patreon and YouTube.
- Some community members yearn for a shift back to less commercialized content creation, while balancing the reality of influencer marketing.
- LoRAs Enhance Image Generation: Users highlighted that improving details in AI-generated images depends heavily on workflow enhancements rather than merely on prompting, with LoRAs proving essential.
- Many incorporate combinations like Detail Tweaker XL to maximize results in their image productions.
LM Studio Discord
- Users express concerns over LM Studio v0.3: Feedback on LM Studio v0.3 reveals disappointment over the removal of features from v0.2, sparking discussions about potential downgrades.
- Concerns about missing system prompts and adjusting settings led developers to assure users that updates are forthcoming.
- Model configuration bugs impact performance: Users face issues with model configurations, particularly regarding GPU offloading and context length settings, affecting the assistant’s message continuity.
- Solutions suggested involve tweaking GPU layers and ensuring dedicated VRAM, as one user experienced context overflow errors.
- Interest in Training Small Language Models: Discussion focused on the viability of training smaller language models, weighing dataset quality and parameter counts against anticipated training loss.
- Challenges specific to supporting less common languages and obtaining high-quality datasets were highlighted by multiple members.
- Navigating LM Studio server interactions: Users clarified that sending API requests is essential for interacting with the LM Studio server rather than a web interface.
- One user found success after grasping the correct API request format, resolving their earlier issues.
- Excitement for Apple Hardware: Speculation surrounds Apple’s upcoming hardware announcements, particularly regarding the 5090 GPU and its capabilities compared to previous models.
- Expectations suggest that Apple will maintain dominance with innovative memory architectures in the next wave of hardware.
Perplexity AI Discord
- Cancellation of Subscriptions Sparks Outrage: Users are frustrated with the cancellation of their subscriptions after using leaked promo codes, with reports of limited support responses from Perplexity’s team.
- Many are seeking clarification on this issue, feeling left in the dark about their subscription status.
- Model Usage Limit Confusion Reigns: Clarification is needed regarding imposed limits on model usage, with pro users facing a cap of 450 queries and Claude Opus users only 50.
- Questions are arising about how to accurately specify the model in use during interactions, pointing to a lack of straightforward guidance.
- API Responses Lack Depth: Users noticed that API responses are short and lack the richness of web responses, raising concerns about the default response format.
- They are looking for suggestions on adjusting parameters to enhance the API output, indicating potential areas for improvement.
- Payment Method Errors Cause Frustration: Numerous users reported authentication issues with their payment methods when trying to set up API access, with various errors across multiple cards.
- This problem appears to be widespread, as others noted similar payment challenges, particularly with security code error messages.
- Web Scraping Alternatives Emerge: Discussions have shifted towards alternatives to Perplexity’s functionality, citing other search engines like You.com and Kagi that utilize web scraping.
- These options are gaining attention for effectively addressing issues related to knowledge cutoffs and inaccuracies in generated responses.
Cohere Discord
- Cohere tech tackles moderation spam: Members highlighted how Cohere’s classification tech effectively filters out crypto spam, maintaining the integrity of server discussions.
- One user remarked, ‘It’s a necessary tool for enjoyable conversations!’, emphasizing the bot’s importance.
- Wittgenstein launches LLM web app: A member shared the GitHub link to their newly coded LLM web app, expressing excitement for feedback.
- They confirmed that the app uses Langchain and is available on Streamlit, now deployed in the cloud.
- Concerns about crypto scammers: Members voiced frustrations over crypto scams infiltrating the AI space, impacting the reputation of legitimate advancements.
- It was noted by an enthusiast how such spam tarnishes AI’s credibility in broader discussions.
- Exploring Cohere products and their applications: Members expressed interest in Cohere products, pointing to customer use cases available regularly on the Cohere blog.
- Usage insights and starter code can be found in the cookbooks, inspiring members’ projects.
- Invalid raw prompt and API usage challenges: Members discussed a 400 Bad Request error associated with the
raw_promptingparameter while clarifying how to configure outputs.- A member noted, ‘Understanding chat turns is critical’, reinforcing the need for clarity in API documentation.
Nous Research AI Discord
- Reflection 70B’s Underwhelming Benchmarks: Recent evaluations reveal that Reflection 70B scores 42% on the aider code editing benchmark, falling short of Llama 3.1 at 49%.
- This discrepancy has led to skepticism regarding its capabilities and the delayed release of some model weights, raising questions about transparency.
- Medical LLM Advancements in Oncology: Highlighted models like CancerLLM and MedUnA enhance applications in oncology and medical imagery, showing promise in clinical environments.
- Initiatives like OpenlifesciAI’s thread detail their impact on improving patient care.
- AGI Through RL Training: Discussion emphasized that AGI may be achievable through intensive training combined with reinforcement learning (RL).
- However, doubts persist about the efficacy of transformers in achieving Supervised Semantic Intelligence (SSI).
- PlanSearch Introduces Diverse LLM Outputs: Scale SEAL released PlanSearch, a method improving LLM reasoning by promoting output diversity through natural language search.
- Hugh Zhang noted this enables deeper reasoning at inference time, representing a strategic shift in model capabilities.
- Scaling Models for Enhanced Reasoning: Scaling larger models may address reasoning challenges by training on diverse, clean datasets to improve performance.
- Concerns remain regarding resource demands and the current limitations of cognitive simulations in achieving human-like reasoning.
CUDA MODE Discord
- Together AI’s MLP Kernels outperform cuBLAS: Members discussed how Together AI’s MLP kernels achieve a 20% speed enhancement, with observations on SwiGLU driving performance. The conversation hinted at further insights from Tri Dao at the upcoming CUDA MODE IRL event.
- This sparked inquiries on efficiency metrics compared to cuBLAS and prompted exchanges on achieving competitive speedups in machine learning frameworks.
- ROCm/AMD Falling Behind NVIDIA: Discussions raised concerns about why ROCm/AMD struggles to capitalize on the AI boom compared to NVIDIA, with members questioning corporate trust issues. Despite PyTorch’s compatibility with ROCm, community consensus suggests NVIDIA’s hardware outperforms in real-world applications.
- Such insights have led to speculations about the strategic decisions AMD is making in the ever-evolving GPU marketplace.
- Triton Matmul Integration Shows Potential: The Thunder channel session highlighted the application of Triton Matmul, focusing on real-world integration with custom kernels. For those interested, a recap is available in a YouTube video.
- Members expressed enthusiasm for the deployment of fusing operations and teased future application to the Liger kernel.
- AMD’s UDNA Architecture Announcement: At IFA 2024, AMD introduced UDNA, a unified architecture merging RDNA and CDNA, aiming to better compete against NVIDIA’s CUDA ecosystem. This strategic pivot indicates a commitment to enhancing performance across gaming and compute sectors.
- Moreover, AMD’s decision to deprioritize flagship gaming GPUs reflects a broader strategy to expand their influence in diverse GPU applications, moving away from a narrow focus on high-end gaming.
- Concerns with PyTorch’s ignore_index: It was confirmed that the handling of
ignore_indexin Cross Entropy avoids invalid memory access, managing conditions effectively with early returns. Test cases demonstrating proper handling reassured concerned members.- This exchange pinpointed the essentiality of robust testing in kernel implementations, particularly as performance tuning discussions continued to evolve.
OpenAI Discord
- Reflection Llama-3.1 Claims Top Open Source Title: The newly released Reflection Llama-3.1 70B model is claimed to be the best open-source LLM currently available, utilizing Reflection-Tuning to enhance reasoning capabilities.
- Users reported earlier issues have been addressed, encouraging further testing for improved outcomes.
- Clarifications on OpenAI’s Mysterious ‘GPT Next’: Members were skeptical about GPT Next being a new model, which OpenAI clarified was just figurative terminology with no real implications.
- Despite clarification, frustration remains regarding the lack of concrete updates amid rising expectations.
- Hardware Needs for Running Llama 3.1 70B: To successfully operate models like Llama 3.1 70B, users need a high-spec GPU PC or Apple Silicon Mac with at least 8GB of VRAM.
- Experiences on various setups highlighted that inadequate resources severely hamper performance.
- Enhancing AI Outputs with Prompt Engineering: Members recommended using styles like ‘In the writing style of Terry Pratchett’ to creatively boost AI responses, showcasing prompt adaptability.
- Structured output templates and defined chunking strategies were emphasized for effective API interactions.
- Debating AI for Stock Analysis: Caution arose over using OpenAI models for stock analysis, advocating against reliance solely on prompts without historical data.
- Discussions pointed towards the necessity of real-time updates and traditional models for comprehensive evaluations.
Modular (Mojo 🔥) Discord
- Integrating C with Mojo via DLHandle: Members discussed how to integrate C code with Mojo using
DLHandleto dynamically link to shared libraries, allowing for function calls between the two.- An example was provided where a function to check if a number is even was executed successfully after being loaded from a C library.
- LLVM Developer Meeting Nuggets: The upcoming Fall LLVM Developer Meeting in October will feature 5 talks by Modular on topics including Mojo and GPU programming.
- Attendees expressed excitement, with recorded sessions expected to be available on YouTube following the event.
- Subprocess Implementation Aspirations: A member expressed interest in implementing Subprocess capabilities in the Mojo stdlib, indicating a push to enhance the library.
- Concerns were raised about the challenges of setting up development on older hardware, emphasizing resource difficulties.
- DType’s Role in Dict Keys: Discussion focused on why
DTypecannot serve as a key in a Dict, noting DType.uint8 as a value rather than a type.- Members mentioned that changing this implementation could be complex due to its ties with SIMD types having specific constraints.
- Exploration of Multiple-precision Arithmetic: Members discussed the potential for multiple-precision integer arithmetic packages in Mojo, referencing implementations akin to Rust.
- One participant shared a GitHub link showing progress on a
uintpackage for this capability.
- One participant shared a GitHub link showing progress on a
Eleuther Discord
- DeepMind’s Resource Allocation Shift: A former DeepMind employee indicated that compute required for projects relies heavily on their product-focus, especially post-genai pivot.
- This insight stirred discussions on how foundational research might face reduced resources, as noted by prevalent community skepticism.
- Scraping Quora Data Issues: Members examined the potential use of Quora’s data in AI training datasets, acknowledging its value but raising concerns over its TOS.
- The discussion highlighted the possible infeasibility of scraping due to stringent regulations.
- Releasing TurkishMMLU Dataset: TurkishMMLU was officially released with links to the dataset and a relevant GitHub issue.
- This addition aims to bolster language model evaluation for Turkish, as outlined in a related paper.
- Insights on Power Law Curves in ML: Members discussed that power law curves effectively model performance scaling in ML, referencing statistical models related to scaling laws in estimation tasks.
- One member noted similarities between scaling laws for LLM loss and those in statistical estimation, indicating that mean squared error scales as N^(-1/2).
- Exploring Adaptive Transformers: A discussion focused on ‘Continual In-Context Learning with Adaptive Transformers,’ which allows transformers to adapt to new tasks using prior knowledge without parameter changes.
- This technique aims for high adaptability while minimizing catastrophic failure risks, attracting attention across various domains.
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) Discord
- Reflection API Performance Questioned: The Reflection 70B model faced scrutiny, suspected to have been simply a LoRA trained on benchmark sets atop Llama 3.0; claims of top-tier performance were misleading due to flawed evaluations.
- Initial private API tests yielded better results than public versions, raising concerns over inconsistencies across releases.
- AI Model Release Practices Critiqued: Debates emerged on the incompetence surrounding significant model announcements without robust validation, leading to community distrust regarding AI capabilities.
- Members urged the industry to enforce stricter evaluation standards before making claims public, noting a troubling trend in inflated expectations.
- OpenAI’s Transition to Anthropic Stirs Talks: Discussion centered on OpenAI co-founder John Schulman’s move to Anthropic, described as surreal and highlighting transitions within leadership.
- The light-hearted remark about frequent mentions of ‘from OpenAI (now at Anthropic)’ captures the shift in community dynamics.
- Speculative Buzz Around GPT Next: Speculation arose from a KDDI Summit presentation regarding a model labeled GPT Next, which OpenAI clarified was just a figurative placeholder.
- A company spokesperson noted that the graphical representation was merely illustrative, not indicative of a timeline for future releases.
- Internal Bureaucracy Slowing Google Down: An ex-Googler voiced concerns over massive bureaucracy in Google, citing numerous internal stakeholders stymying effective project execution.
- This sentiment underscores challenges employees face in large organizations where internal politics often hinder productivity.
Latent Space Discord
- AI Codex Boosts Cursor: The new AI Codex for Cursor implements self-improvement features like auto-saving insights and smart categorization.
- Members suggested that a month of usage could unveil valuable learning outcomes about its efficiency.
- Reflection API Raises Eyebrows: The Reflection API appears to function as a Sonnet 3.5 wrapper, reportedly filtering out references to Claude to mask its identity.
- Various evaluations suggest its performance may not align with claims, igniting inquiry about the benchmarking methodology.
- Apple’s Bold AI Advances: Apple’s recent event teased substantial updates to Apple Intelligence, hinting at a potentially improved Siri and an upcoming AI phone.
- This generated excitement around competitive implications, as many members called for insights from Apple engineers.
- New Enum Mode Launches in Gemini: Logan K announced the advent of Enum Mode in the Gemini API, enhancing structured outputs by enabling selection from predefined options.
- This innovation looks to streamline decision-making for developers interacting with the Gemini framework.
- Interest in Photorealistic LoRA Model: A user showcased a photorealistic LoRA model that’s captivating the Stable Diffusion community with its detailed capabilities.
- Discussions surrounding its performance, particularly unexpected anime images, have garnered significant attention.
OpenInterpreter Discord
- OpenInterpreter’s resource management woes: While the 01 app allows quick access to audio files, users face performance variability on Mac, leading to inconsistent outcomes.
- One user indicated a preference for plain OpenInterpreter due to the 01 app’s stability problems.
- Call for AI Skills in OpenInterpreter: Users are eager for the release of AI Skills for the standard OpenInterpreter rather than just the 01 app, showcasing a demand for enhanced functionality.
- Frustration echoed regarding the 01 app’s performance relative to the base OpenInterpreter.
- Discontinuation and Refunds for 01 Light: The team announced the official end of the 01 Light, focusing on a free 01 app and processing refunds for all hardware orders.
- Disappointment was prevalent among users eagerly waiting for devices, but assurance was given regarding refund processing through [email protected].
- Scriptomatic’s triumph with Open Source Models: A member successfully integrated Scriptomatic with structured outputs from open source models and plans to submit a PR soon.
- They expressed appreciation for the support provided for Dspy, emphasizing their methodical approach involving grepping and printing.
- Instructor Library Enhances LLM Outputs: The Instructor library was shared, designed to simplify structured outputs from LLMs using a user-friendly API based on Pydantic.
- Instructor is poised to streamline validation, retries, and streaming, bolstering user workflows with LLMs.
LlamaIndex Discord
- Deploy Agentic System with llama-deploy: Explore this full-stack example of deploying an agentic system as microservices with LlamaIndex and getreflex.
- This setup streamlines chatbot systems, making it a go-to for developers wanting efficiency.
- Run Reflection 70B Effortlessly: You can now run Reflection 70B directly from LlamaIndex using Ollama, given your laptop supports it (details here).
- This capability allows hands-on experimentation without extensive infrastructure requirements.
- Build Advanced RAG Pipelines: Check out this guide for building advanced agentic RAG pipelines with dynamic query routing using Amazon Bedrock.
- The tutorial covers all necessary steps to optimize RAG implementations effectively.
- Automate Financial Analysis Workflows: A blog post discusses creating an agentic summarization system for automating quarterly and annual financial analysis (read more).
- This approach can significantly boost efficiency in financial reporting and insights.
- Dynamic ETL for RAG Environments: Learn how LLMs can automate ETL processes with data-specific decisions, as outlined in this tutorial.
- This method enhances data extraction and filtering by adapting to different dataset characteristics.
Torchtune Discord
- Gemma Model Configuration Updates: To configure a Gemma 9B model using Torchtune, users suggested modifying the
modelentry in the config with specific parameters found in config.json.- This approach leverages the component builder, aiming for flexibility across various model sizes.
- Gemma 2 Support Challenges in Torchtune: Discussion arose around difficulties in supporting Gemma 2 within Torchtune, mainly due to issues with logit-softcapping and bandwidth constraints.
- The burgeoning architecture improvements in Gemma 2 have generated a backlog of requested features waiting for implementation.
- Proposed Enhancements for Torchtune: A potential bug concerning padding sequence behavior in Torchtune was highlighted alongside a proposed PR to fix the issue by clarifying the flip method.
- The goal is to achieve feature parity with the torch pad_sequence, enhancing overall library functionality.
- Cache Handling During Generation Needs Refinement: Users discussed the need for modifications in cache behavior during generation, proposing the use of
torch.inference_modefor consecutive forward calls in attention modules.- Despite this, they acknowledged that an explicit flag for
.forward()might yield a more robust solution.
- Despite this, they acknowledged that an explicit flag for
- Chunked Linear Method Implementation Reference: A member shared interest in a clean implementation of chunked linear combined with cross-entropy from a GitHub gist as a potential enhancement for Torchtune.
- Integrating this method may pose challenges due to the library’s current separation of the LM-head from loss calculations.
LangChain AI Discord
- Struggling with .astream_events() Decoding: Users reported challenges with decoding streams from .astream_events(), especially the tedious manual serialization through various branches and event types.
- Participants highlighted the lack of useful resources, calling for a reference implementation to ease the burdens of this process.
- Gradio Struggles with Concurrency: After launching Gradio with 10 tabs, only 6 requests generated despite higher concurrency limits, hinting at potential configuration issues.
- Users pointed out the hardware limitations, suggesting the need for further investigation into handling concurrent requests.
- Azure OpenAI Integration Facing 500 Errors: A user is dealing with 500 errors when interacting with Azure OpenAI, prompting queries about endpoint parameters.
- Advice included validating environment variables and naming conventions to potentially resolve these troubleshooting headaches.
- VAKX Offers No-Code AI Assistant Building: VAKX was introduced as a no-code platform enabling users to build AI assistants, with features like VAKChat integration.
- Members were encouraged to explore VAKX and the Start Building for Free link for quick setups.
- Selenium Integrated with GPT-4 Vision: An experimental project demonstrated the integration of Selenium with the GPT-4 vision model, with a detailed process available in this YouTube video.
- Interest sparked around leveraging this integration for more effective automated testing with vector databases.
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) Discord
- Overfitting Concerns Take Center Stage: Members raised issues regarding overfitting, emphasizing that benchmarks can mislead expectations, suggesting that models inevitably experience overfitting regardless of size.
- “I don’t believe benchmarks anymore” captured skepticism towards reliability in model evaluations based on inadequate data.
- Benchmark Limitations Under Scrutiny: Insights were shared on benchmark limitations, revealing that although flawed, they remain crucial for comparisons among models.
- A member expressed optimism for their article on benchmark issues to be reviewed at NeurIPS, highlighting current evaluation challenges.
- AI Tool Exposed as a Scam: A recently hyped AI tool turned out to be a scam, falsely claiming to compare with Claude 3.5 or GPT-4.
- Discussions stressed the time loss caused by such scams and their distracting nature across various channels.
- Urgent Inquiry on RAG APIs: A member urgently sought experiences with RAG APIs, needing immediate support for a project due to their model being unready.
- They highlighted the challenges of 24/7 hosting costs and sought alternatives to manage their AI projects effectively.
- H100’s 8-Bit Loading Limitations Questioned: A member queried why the H100 does not support loading models in 8-bit format, seeking clarity on this limitation.
- They reiterated the urgency for insights into the H100’s constraints regarding 8-bit model loading.
LAION Discord
- Berlin AI Hackathon Promises Innovation: The Factory Network x Tech: Berlin AI Hackathon is scheduled for September 28-29 at Factory Berlin Mitte, aiming to gather 50-100 builders motivated to drive AI-driven innovations.
- Participants can improve existing products or initiate new projects in a collaborative environment, fostering creative approaches.
- Finegrain’s Open-Source Breakthrough: Finegrain released an open-source image segmentation model outperforming closed-source alternatives, available under the MIT License on Hugging Face.
- Future improvements include a subtler prompting method for enhanced disambiguation and usability beyond simple bounding boxes.
- Concrete ML Faces Scaling Issues: Discussions highlighted that Concrete ML demands Quantization Aware Training (QAT) for effective integration with homomorphic encryption, resulting in potential performance compromises.
- Concerns about limited documentation were raised, especially in its applicability to larger models in machine learning.
- Free Open Source AI Panel Event: GitHub will host an Open Source AI panel on September 19 in SF, featuring notable panelists from organizations like Ollama and Nous Research.
- While free to attend, registration is prerequisite due to limited seating, making early sign-up essential.
- Multimodality in AI Captivates Interest: The rise of multimodality in AI has been underscored with examples like Meta AI transfusion and DeepMind RT-2, showcasing significant advancements.
- Discussion suggested investigating tool augmented generation employing techniques like RAG, API interactions, web searches, and Python executions.
DSPy Discord
- LanceDB Integration PR Submitted: A member raised a PR for LanceDB Integration to add it as a retriever for handling large datasets in the project.
- They requested feedback and changes from a specific user for the review process, emphasizing collaboration in enhancements.
- Mixed feelings on GPT-3.5 deprecation: Members discussed varying user experiences with models following the deprecation of GPT-3.5, noting inconsistent performance, especially with open models like 4o-mini.
- One user suggested using top closed models as teachers for lower ones to improve performance consistency.
- AttributeError Plagues MIPROv2: A user reported encountering an
AttributeErrorin MIPROv2, indicating a potential issue in theGenerateModuleInstructionfunction.- Discussion circled around suggested fixes, with some members pointing to possible problems in the CookLangFormatter code.
- Finetuning small LLMs Generates Buzz: A member shared success in finetuning a small LLM using a unique reflection dataset, available for interaction on Hugging Face.
- They provided a link while encouraging others to explore their findings in this domain.
- CookLangFormatter Issues Under Scrutiny: Members debated potential issues with the CookLangFormatter class, identifying errors in method signatures.
- Post-modifications, one user reported positive outcomes and suggested logging the issue on GitHub for future reference.
tinygrad (George Hotz) Discord
- WebGPU PR #6304 makes waves: The WebGPU PR #6304 by geohot marks a significant effort aimed at reviving webgpu functionality on Asahi Linux, with a $300 bounty attached.
- ‘It’s a promising start for the initiative,’ noted a member, emphasizing the community’s excitement over the proposal.
- Multi-GPU Tensor Issues complicate development: Developers are encountering AssertionError with multi-GPU operations, which requires all buffers to share the same device.
- A frustrated user remarked, ‘I’ve spent enough time… convinced this goal is orthogonal to how tinygrad currently handles multi-gpu tensors.’
- GGUF PRs facing delays and confusion: Concerns are rising regarding the stalled status of various GGUF PRs, which are lacking merges and clear project direction.
- One user inquired about a roadmap for GGUF, highlighting a need for guidance moving forward.
- Challenges in Model Sharding: Discussions unveiled issues with model sharding, where certain setups function on a single GPU yet fail when expanded across multiple devices.
- One user observed that ‘George gave pushback on my workaround…’, indicating a complex dialogue around solutions.
Gorilla LLM (Berkeley Function Calling) Discord
- xLAM Prompts Deviation from Standard: Members discussed the unique system prompt used for xLAM, as detailed in the Hugging Face model card.
- This prompted an analysis of how personalized prompts can diverge from the BFCL default.
- LLaMA Lacks Function Calling Clarity: Participants noted that LLaMA offers no documentation on function calling, raising concerns regarding prompt formats.
- Although classified as a prompt model, LLaMA’s handling of function calling remains ambiguous due to inadequate documentation.
- GitHub Conflicts Cause Integration Delays: A user reported facing merge conflicts with their pull request, #625, obstructing its merger.
- After resolving the conflicts, they resubmitted a new pull request, #627 to facilitate integration.
- Exploring Model Evaluation via VLLM: A query arose regarding the evaluation of models after setting up the VLLM service.
- The inquiry reflects a significant interest in model assessment methodologies and best practices within the community.
- Introducing the Hammer-7b Handler: The community discussed the new Hammer-7b handler, emphasizing its features as outlined in the associated pull request.
- Detailed documentation with a CSV table highlights model accuracy and performance metrics.
LLM Finetuning (Hamel + Dan) Discord
- 4090 GPU enables larger models: With a 4090 GPU, engineers can run larger embedding models concurrently, including Llama-8b, and should consider version 3.1 for enhanced performance.
- This setup boosts efficiency in processing tasks and allows more complex models to operate smoothly.
- Hybrid Search Magic with Milvus: Discussions highlighted using hybrid search with BGE and BM25 on Milvus, demonstrated with an example from the GitHub repository.
- This example effectively illustrates the incorporation of both sparse and dense hybrid search for improved data retrieval.
- Boost Results with Reranking: Implementing a reranker that utilizes metadata for each chunk helps prioritize and refine result sorting.
- This method aims to enhance data handling, making retrieved information more relevant and accurate.
Alignment Lab AI Discord
- Understanding RAG Based Retrieval Evaluation: A member inquired about necessary evaluation metrics for assessing a RAG based retrieval system within a domain-specific context.
- They were uncertain whether to compare their RAG approach to other LLMs or to evaluate against results without using RAG.
- Comparison Strategies for RAG: The same member pondered whether to conduct comparisons only with and without RAG or also against other large language models.
- This question sparked interest, prompting members to consider various approaches for evaluating the effectiveness of RAG in their projects.
MLOps @Chipro Discord
- GitHub Hosts Open Source AI Panel: GitHub is hosting a free Open Source AI panel next Thursday (9/19) at their San Francisco office, aimed at discussing access, democratization, and the impact of open source on AI.
- Panelists include representatives from Ollama, Nous Research, Black Forest Labs, and Unsloth AI, contributing to vital conversations in the AI community.
- Registration Approval Required for AI Panel: Attendees are required to register for the event, with registration subject to host approval to manage effective attendance.
- This process aims to ensure a controlled environment as interest in the event grows within the AI sector.
The Mozilla AI Discord has no new messages. If this guild has been quiet for too long, let us know and we will remove it.
The DiscoResearch Discord has no new messages. If this guild has been quiet for too long, let us know and we will remove it.
The AI21 Labs (Jamba) Discord has no new messages. If this guild has been quiet for too long, let us know and we will remove it.
PART 2: Detailed by-Channel summaries and links
{% if medium == ‘web’ %}
HuggingFace ▷ #general (930 messages🔥🔥🔥):
Hugging Face Inference API IssuesModel Fine-Tuning ExperiencesAI Art and Prompting ChallengesQ&A on LLM Features and Usage
- Hugging Face Inference API Issues: Users are experiencing difficulties with the Hugging Face Inference API, particularly when trying to access private models, which leads to a ‘bad credentials’ error without any useful logs.
- Suggested solutions include ensuring proper setup of API tokens and evaluating recent updates that may have affected functionality.
- Model Fine-Tuning Experiences: The process of fine-tuning models on Hugging Face is discussed, with users noting that the resulting models may not always upload correctly, resulting in missing files in repositories.
- Users recommend checking configurations and handling large models, especially when converting formats like GGUF for local hosting.
- AI Art and Prompting Challenges: Conversations explore the challenges of generating high-quality AI art, specifically focusing on issues with limb and hand representations in generated images.
- The importance of using effective prompts was emphasized, with users suggesting that simpler, cheesier prompts often yield better results.
- Q&A on LLM Features and Usage: Users inquire about effective local hosting options for language models and tools like vLLM, with discussions on batching and the utility of different inference methods.
- Mention of various models, such as Mistral and LLama, highlights the interest in their performance and usability in real-world applications.
Links mentioned:
- no title found: no description found
- 401 Client Error: Unauthorized for url: Recently I started to get requests.exceptions.HTTPError: 401 Client Error: Unauthorized for url: https://api.soundcloud.com/oauth2/token using soundcloud (0.5.0) Python library.&#x...
- Civitai | Share your models: no description found
- Google Colab: no description found
- Meta-Llama3.1-8B - a Hugging Face Space by freeCS-dot-org: no description found
- Karate Kid GIF - Karate Kid Wax Rotate - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- shafire/talktoaiZERO · Hugging Face: no description found
- Google Colab: no description found
- Text Generation Inference (TGI): no description found
- Error 401 Client Error: Unauthorized for url: When using model card of my private speech recognition model with LM, I got this error: 401 Client Error: Unauthorized for url: https://huggingface.co/api/models/taliai/tali-asr-with-lm/revision/main...
- WaifuDiffusion Tagger - a Hugging Face Space by SmilingWolf: no description found
- Dies Cat GIF - Dies Cat Dead - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Gen Battle SF: Let’s make Music Videos With AI! · Luma: Let's get into groups and make a music video! For AI beginners and experts split into groups and create short films together. By the end of the night, we'll…
- RandomForestClassifier: Gallery examples: Release Highlights for scikit-learn 1.4 Release Highlights for scikit-learn 0.24 Release Highlights for scikit-learn 0.22 Comparison of Calibration of Classifiers Probability Cali...
- Napoleon Dynamite Kip GIF - Napoleon Dynamite Kip Yes - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Tweet from cocktail peanut (@cocktailpeanut): OpenAI preparing to drop their new model
- shafire (Shafaet Brady Hussain): no description found
- Kamala Harris Real Though GIF - Kamala harris Real though - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Joe Biden Presidential Debate GIF - Joe biden Presidential debate Huh - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Steve Brule Orgasm GIF - Steve Brule Orgasm Funny - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Tim And Eric Spaghetti GIF - Tim And Eric Spaghetti Funny Face - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Ohearn Sad Mike Ohearn Sad GIF - Ohearn sad Ohearn Mike ohearn sad - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- shafire/talktoaiZERO at main: no description found
- Manage your Space: no description found
- Empire'S Got Your Back GIF - Empire I Got You Brothers - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- openai/whisper-large-v3 · Hugging Face: no description found
- Btc Blockchain GIF - Btc Blockchain Fud - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Hello GIF - Hello - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Data Visualization : Bar Chart and Heat Map: In this video, I will discuss bar charts and heat maps, explaining how they work and the trends they reveal in data, along with other related topics. If you'...
- shafire/talktoai at main: no description found
HuggingFace ▷ #today-im-learning (9 messages🔥):
Latch-up effect in CMOS microcircuitsDeploying uncensored models to SageMakerDaily learning progress forum
- Understanding Latch-up Effect in CMOS: A member inquired about the Latch-up effect in CMOS microcircuits, seeking information on how it functions.
- This topic remains open for further discussion and clarification from knowledgeable members.
- Sharing Insights on SageMaker Deployment: One member asked for experiences and guidance on deploying uncensored models to SageMaker, following the Hugging Face documentation.
- Another member mentioned they were looking into similar issues, with a follow-up noting that things are going decently well.
- Community Motivation through Daily Progress: A member queried if the channel functions like a forum for posting daily learning progress, akin to 100 days of code.
- Other members confirmed this setup is meant to motivate individuals on their learning journeys.
- Appreciation for Collaboration: A member expressed admiration for a fellow user’s work, stating it was ‘amazing’, to which the original poster credited Nvidia and Epic Games for their contributions.
- This highlights the collaborative spirit and recognition within the community.
HuggingFace ▷ #cool-finds (11 messages🔥):
Medical AI Research UpdatesAlphaProteo Protein Prediction ModelMedical LLMs ApplicationsML Training Visualization ToolsExploring Medical Literature
- Last Week in Medical AI Highlights: The latest update covered several cutting-edge medical LLMs, including CancerLLM and MedUnA, and their applications in clinical tasks.
- TrialBench and DiversityMedQA were noted as significant benchmarks for evaluating LLMs’ performance in medical applications.
- DeepMind’s AlphaProteo Model Revolutionizes Protein Design: The AlphaProteo model from Google DeepMind predicts protein binding to molecules, enhancing bioengineering applications like drug design.
- This new AI system aims to advance our understanding of biological processes through improved protein interactions, as highlighted in their blog post.
- Interest in Diving into Medical Papers: Members expressed enthusiasm about exploring medical papers further, enhancing visibility for research in the medical AI domain.
- A suggestion was made to engage in deeper discussions around the recent papers listed in the latest research updates.
- Inquiry About Open Access of AlphaProteo: A question arose regarding the open access status of the AlphaProteo model by Google DeepMind.
- This reflects ongoing discussions about accessibility of advanced AI tools in the research community.
- Tools for Training Curve Visualization in ML: A member inquired about frameworks and tools to automatically generate training and validation curves for ML models, specifically for image classification.
- This underscores a continued interest in effective visualization methods for improving model training processes.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Open Life Science AI (@OpenlifesciAI): Last Week in Medical AI: Top Research Papers/Models 🏅(September 1 - September 7, 2024) Medical LLM & Other Models : - CancerLLM: Large Language Model in Cancer Domain - MedUnA: Vision-Languag...
- @aaditya on Hugging Face: "Last Week in Medical AI: Top Research Papers/Models 🏅(September 1 -…": no description found
- AlphaProteo generates novel proteins for biology and health research: New AI system designs proteins that successfully bind to target molecules, with potential for advancing drug design, disease understanding and more.
HuggingFace ▷ #i-made-this (51 messages🔥):
PowershAI FeaturesGraphRAG UtilizationOm LLM ArchitectureFLUX.1 [dev] Model ReleaseOCR Correction Techniques
- PowershAI Simplifies AI Integration: PowershAI aims to facilitate AI usage for Windows users by allowing easy integration and invocation of AI models using PowerShell commands, enhancing script object-oriented capabilities.
- It supports features like function calling and Gradio integration, which helps users streamline workflows with multiple AI sources.
- Local GraphRAG Model Testing: A new repository was created to enable users to test Microsoft’s GraphRAG using various models from Hugging Face, beyond the limited options provided by Ollama.
- This allows greater flexibility for users looking to expand their graph retrieval capabilities without the associated costs of using the OpenAI API.
- Innovation in LLM Architecture with Om: Dingoactual introduced a novel LLM architecture named Om, emphasizing unique features like initial convolutional layers and multi-pass memory for handling long-context inputs.
- The design improvements focus on optimized processing while managing VRAM requirements effectively.
- Introduction of FLUX.1 [dev] Model: The FLUX.1 [dev] model, a 12 billion parameter flow transformer for image generation, has been released with open weights, allowing scientists and artists to leverage its capabilities.
- This model offers high-quality outputs comparable to leading closed-source alternatives, reinforcing the potential for innovative workflows in creative fields.
- OCR Correction and Creative Text Generation: Tonic highlighted a technique developed by Pleiasfr to correct OCR outputs, which can also be used creatively to generate historical-style texts in multiple languages.
- This method reflects the versatility and innovation in utilizing AI for both correcting data and creative endeavors.
Links mentioned:
- Chapter 34. Working with the Component Object Model (COM) · PowerShell in Depth: Discovering what COM is and isn’t · Working with COM objects
- Reflection 70B llama.cpp (Correct Weights) - a Hugging Face Space by gokaygokay: no description found
- Xtts - a Hugging Face Space by rrg92: no description found
- lazarzivanovicc/timestretchlora · Hugging Face: no description found
- black-forest-labs/FLUX.1-dev · Hugging Face: no description found
- Civitai | Share your models: no description found
- GitHub - NotTheStallion/graphrag-local-model_huggingface: Microsoft's graphrag using ollama and hugging face to support all LLMs (Llama3, mistral, gemma2, fine-tuned Llama3 ...).: Microsoft's graphrag using ollama and hugging face to support all LLMs (Llama3, mistral, gemma2, fine-tuned Llama3 ...). - NotTheStallion/graphrag-local-model_huggingface
- GitHub - BBC-Esq/VectorDB-Plugin-for-LM-Studio: Plugin that lets you use LM Studio to ask questions about your documents including audio and video files.: Plugin that lets you use LM Studio to ask questions about your documents including audio and video files. - BBC-Esq/VectorDB-Plugin-for-LM-Studio
- GitHub - dingo-actual/om: An LLM architecture utilizing a recurrent structure and multi-layer memory: An LLM architecture utilizing a recurrent structure and multi-layer memory - dingo-actual/om
- Tonics-OCRonos-TextGen - a Hugging Face Space by Tonic: no description found
- AssistantsLab/Tiny-Toxic-Detector · Hugging Face: no description found
- AssistantsLab/Tiny-Toxic-Detector · Hugging Face: no description found
- Tiny-Toxic-Detector: A compact transformer-based model for toxic content detection: This paper presents Tiny-toxic-detector, a compact transformer-based model designed for toxic content detection. Despite having only 2.1 million parameters, Tiny-toxic-detector achieves competitive pe...
- Hugging Face and Gradio Come to PowershAI: Learn How to Use Them: In this video, we’ll dive into the latest update of PowershAI: full support for Hugging Face and Gradio APIs! You’ll learn how to use PowershAI to connect di...
- GitHub - rrg92/powershai: Powershell + AI: Powershell + AI. Contribute to rrg92/powershai development by creating an account on GitHub.
- powershai/docs/en-US at main · rrg92/powershai: Powershell + AI. Contribute to rrg92/powershai development by creating an account on GitHub.
- SECourses 3D Render for FLUX - Full Dataset and Workflow Shared - v1.0 | Stable Diffusion LoRA | Civitai: Full Training Tutorial and Guide and Research For a FLUX Style Hugging Face repo with all full workflow, full research details, processes, conclusi...
HuggingFace ▷ #reading-group (6 messages):
Universal Approximation TheoremUncensored ModelsModel DefinitionsLeshno's TheoremHuggingFace Models
- Universal Approximation Theorem Depth Discussion: Members discussed the Universal Approximation Theorem, referencing Wikipedia’s article for depth-1 UAT details.
- It was noted that Haykin’s work is limited to monotone families, whereas Leshno et al. provide a more general definition that covers continuity.
- Uncensored Models Overview: A member recommended a detailed article explaining the process of creating uncensored models like WizardLM.
- Links to various WizardLM models were provided, including WizardLM-30B and Wizard-Vicuna.
- Clarification on Model Definitions: Clarifications were provided regarding what constitutes a model, specifically HuggingFace transformer models trained for instructed responses.
- The distinction was made that while many transformer models exist, only certain ones are designed for interactive chatting.
- Explaining Uncensored Models: A comprehensive explanation of uncensored models, like Alpaca and Vicuna, was shared, detailing their characteristics and uses.
- It was emphasized that these models are valuable for eliciting responses without typical content restrictions.
Links mentioned:
- Uncensored Models: I am publishing this because many people are asking me how I did it, so I will explain. https://huggingface.co/ehartford/WizardLM-30B-Uncensored https://huggingface.co/ehartford/WizardLM-13B-Uncensore...
- Universal approximation theorem - Wikipedia: no description found
HuggingFace ▷ #computer-vision (8 messages🔥):
Community Computer Vision CourseStanford CS231n CourseImgcap CLI ToolFace Recognition DatasetsData Training Methods with CSV Files
- Community Computer Vision Course Launched: A member shared a link to the Community Computer Vision Course, which covers various foundational topics in computer vision.
- The course is designed to be accessible and friendly for learners at all levels, emphasizing the revolutionizing impact of computer vision.
- Highly Recommended Stanford CS231n Course: A member suggested following the Stanford CS231n course as the best resource for learning computer vision.
- This recommendation highlights the course’s reputation and value in the field.
- Imgcap CLI Tool for Image Captioning Released: A new CLI tool called Imgcap was announced for generating captions for local images.
- The developer encouraged users to try it out and provide feedback on the results.
- Seeking Face Recognition Dataset: A member inquired about a medium-sized face recognition dataset organized by folder, similar to structures discussed on Data Science Stack Exchange.
- They found a dataset that meets their requirement, questioning the folder structure’s utility compared to naming conventions.
- Training Models with PNG and CSV Data: A member asked whether to use original PNG images or associated CSV files for training their model, given that the CSV contains image IDs and labels.
- They also wondered if using the CSV files would expedite model training, referencing client needs.
Links mentioned:
- Face dataset organized by folder: I'm looking for a quite little/medium dataset (from 50MB to 500MB) that contains photos of famous people organized by folder. The tree structure have to bee something like this: ...
- Welcome to the Community Computer Vision Course - Hugging Face Community Computer Vision Course: no description found
- GitHub - ash-01xor/Imgcap: A CLI to generate captions for images: A CLI to generate captions for images. Contribute to ash-01xor/Imgcap development by creating an account on GitHub.
HuggingFace ▷ #NLP (3 messages):
HF Trainer confusion matrixRAG-based retrieval evaluation
- Plotting Confusion Matrix in TensorBoard: A user inquired about how to plot the confusion matrix as an image in TensorBoard while training with HF Trainer.
- The query focuses on integrating visualization tools to enhance model evaluation during training.
- Evaluating RAG-based Retrieval Framework: Another user addressed the need for defining evaluation metrics for a project involving RAG-based retrieval for a specific domain.
- They also questioned whether to compare their RAG approach solely with other LLMs or against versions with and without RAG to assess effectiveness.
HuggingFace ▷ #diffusion-discussions (2 messages):
Transformer2DModelDiT
- Is Transformer2DModel the same as DiT?: A member inquired about the relationship between Transformer2DModel and DiT.
- They specifically questioned whether these models are equivalent or if there are key differences.
- Discussion on Model Comparisons: Another participant prompted for insights on various models and their functionalities, including DiT.
- This opened up a broader discussion about model architectures and their applications in the field.
aider (Paul Gauthier) ▷ #general (687 messages🔥🔥🔥):
DeepSeek and Aider PerformanceAI Development ConcernsAider Workflow StrategiesUsing a Config File for AiderConventions and Prompt Engineering
- DeepSeek’s Recent Benchmarking Issues: Users expressed concerns about the performance of the DeepSeek Coder model, suggesting that it may be using the wrong model ID for benchmarks and hitting bad stats on the dashboard.
- It was noted that both model IDs now point to the same DeepSeek 2.5 model, possibly affecting the performance.
- AI Development Worries and Feedback: Community members discussed the potential impact of AI on development jobs and the changing role of developers as AI tools become more advanced.
- There were thoughts on whether the reliance on AI might lead to oversaturation or obsolescence in the workforce.
- Aider Workflow and Use Cases: Users shared their workflows using Aider and integration with tools like CodeCompanion for efficient project setup, emphasizing the importance of clear planning.
- The idea of incorporating a reinvigorated system prompt that follows conventions and plans was mentioned, suggesting potential improvements in Aider’s output consistency.
- Configuring Aider Settings Properly: Discussions highlighted the need for efficient setup of environmental variables and configuration files to streamline Aider use, including the potential for using
.aider.conf.yml.- Community members also mentioned the use of
.envfiles for API keys, creating separation between Aider configuration and project-specific settings.
- Community members also mentioned the use of
- Issues with Google Cloud Quotas: Users reported encountering quota issues with Google Cloud’s Vertex AI, particularly new accounts facing a 429 error for prediction requests, leading to speculation about quota restrictions.
- There were observations of broader issues with Google’s services as users noted receiving unexpected rate limit errors with their various AI tools.
Links mentioned:
- no title found: no description found
- Tweet from Artificial Analysis (@ArtificialAnlys): Reflection Llama 3.1 70B independent eval results: We have been unable to replicate the eval results claimed in our independent testing and are seeing worse performance than Meta’s Llama 3.1 70B, not ...
- direnv – unclutter your .profile: unclutter your .profile
- Tweet from Chubby♨️ (@kimmonismus): GPT-5 photographed with presumed parameters: 3*5T (assumingly MoE). Correctly, GPT-4 is specified there with 1.7T parameters. In addition, 7000 B100 as compute. The official statements are getting lou...
- Specifying coding conventions: Tell aider to follow your coding conventions when it works on your code.
- Tweet from blueblue (@deep9483): @teortaxesTex We encountered some deployment issues with DeepSeek v2.5 and have temporarily fixed them. Could you please test it again?
- Chat modes: Using the chat, ask and help chat modes.
- Encountered 429 error "Quota exceeded for online_prediction_concurrent_requests_per_base_model" when using Claude 3 Haiku: I am using Claude 3 Haiku on Vertex AI and occasionally encounter the following error message: { "code": 429, "message": "Quota exceed...
- FAQ: Frequently asked questions about aider.
- git-lfs/docs/spec.md at main · git-lfs/git-lfs: Git extension for versioning large files. Contribute to git-lfs/git-lfs development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Model warnings: aider is AI pair programming in your terminal
- Tweet from Teortaxes▶️ (@teortaxesTex): Yeah it seems to work much better now, and better than previous models. I urge you to redo your tests. Quoting Teortaxes▶️ (@teortaxesTex) The new DeepSeek has a joy-killing, infuriating tendency o...
- Tweet from Matt Shumer (@mattshumer_): We’ve figured out the issue. The reflection weights on Hugging Face are actually a mix of a few different models — something got fucked up during the upload process. Will fix today. Quoting Matt Shu...
- Sure Moron GIF - Sure Moron - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- NEW: Replit AI Agents Destroy Cursor Composor?!? 🤖🤔 End-To-End Coding & Deployment AI Coding: NEW: Replit AI Agents Destroy Cursor Composor?!? 🤖🤔 End-To-End Coding & Deployment AI Codinghttps://replit.com/https://cursor.com/🤑 FREE VALUE:👉 Free 6-D...
- aider/benchmark/README.md at main · paul-gauthier/aider: aider is AI pair programming in your terminal. Contribute to paul-gauthier/aider development by creating an account on GitHub.
- "code": 429, "message": "Quota exceeded for aiplatform.googleapis.com/online_prediction_requests_per_base_model with base model: anthropic-claude-3-5-sonnet. Please submit a quota increase request. https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/docs/generative-ai/quotas-genai.", "status": "RESOURCE_EXHAUSTED" · Issue #18 · cg-dot/vertexai-cf-workers: "code": 429, "message": "Quota exceeded for aiplatform.googleapis.com/online_prediction_requests_per_base_model with base model: anthropic-claude-3-5-sonnet. Please submit a q...
aider (Paul Gauthier) ▷ #questions-and-tips (193 messages🔥🔥):
Aider Chat FunctionalityModel Performance ComparisonsGit Integration FeaturesLanguage Output BehaviorUsing Aider with Conventions
- Aider’s Command Execution and Initialization Delays: Users have noticed that running aider with specific models, such as
--model, can introduce initialization delays compared to running aider without it.- Instances of commands executing slower than expected may be due to the complexity of the chosen model or the initial loading process.
- Adjusting Aider’s Language Output: Aider can inadvertently switch languages during sessions, prompting users to specify desired output languages explicitly.
- Using the command
/chat-mode askor adding ‘answer in English’ to prompts helps maintain consistency in responses.
- Using the command
- Managing Git Integration with Aider: Aider is tightly integrated with git, automatically creating commits for changes, but it can be customized with the
--no-auto-commitsoption.- This allows users to manage how aider interacts with their git repositories, including whether it automatically creates new branches.
- Utilizing Aider for Automation in Workflows: Users can script interactions with aider through command line or Python for automated code modifications and pull request creation.
- While using aider as a library offers potential, it’s noted that aider does not currently have a stable API for this purpose.
- Setting Project Conventions with Aider: To instruct Aider on specific coding guidelines, users can create a
CONVENTIONS.mdfile and read it in, ensuring guidelines are followed.- Aider’s adherence to these conventions may require explicit reminders in prompts to maintain consistency.
Links mentioned:
- no title found: no description found
- Vertex AI: aider is AI pair programming in your terminal
- Tips: Tips for AI pair programming with aider.
- Chat modes: Using the chat, ask and help chat modes.
- Specifying coding conventions: Tell aider to follow your coding conventions when it works on your code.
- Scripting aider: You can script aider via the command line or python.
- GPT code editing benchmarks: Benchmarking GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 code editing skill using a new code editing benchmark suite based on the Exercism python exercises.
- Aider LLM Leaderboards: Quantitative benchmarks of LLM code editing skill.
- Git integration: Aider is tightly integrated with git.
- sahil2801/reflection_70b_v5 · Hugging Face: no description found
- Options reference: Details about all of aider’s settings.
- Thread By @shinboson - A story about fraud in the AI research c..: A story about fraud in the AI research community On September 5th Matt Shumer CEO of OthersideAI announces to the world that they've made a breakthrou
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- How To Develop 2 AI Apps in 10 Minutes!: You don't have to pay to try out building apps that use AI. With Ollama you can run AI models locally, for free. Vercel's AI library makes it easy to manage ...
- no title found: no description found
- Issues · ggerganov/llama.cpp: LLM inference in C/C++. Contribute to ggerganov/llama.cpp development by creating an account on GitHub.
- better prompting for LLM to suggest files · paul-gauthier/aider@6638efb: no description found
aider (Paul Gauthier) ▷ #links (14 messages🔥):
Reflection 70B vs Llama3 70BV0 updates and applicationsZed's GitHub discussionsYouTube AI coding videos
- Reflection 70B lags behind Llama3 70B: Reflection 70B scored 42% on the aider code editing benchmark, while Llama3 70B achieved 49%. It was noted that the current model won’t function properly with the released aider after modifying it to ignore certain tags.
- For further insights, see the leaderboards.
- Impressive results from recent V0 update: A member recommended checking out updates to v0, which is Vercel’s version of Claude tailored for NextJS UI’s, reporting impressive results. They also provided a YouTube video that demonstrates its capabilities.
- Demos and more information can be found at v0.dev/chat and other linked resources.
- Zed’s GitHub hints at upcoming subscription: Discussion revealed that there are multiple mentions on Zed’s GitHub regarding a forthcoming Zed Pro subscription. This collaboration with Anthropic is anticipated to introduce an ‘edit mode’ feature.
- Members speculated that this may enhance functionality greatly in upcoming updates.
- AI Coding Secret Sauce Explored: A newly shared YouTube video titled ‘SECRET SAUCE of AI Coding?’ investigates high-output AI coding techniques. It highlights various tools including Aider, Cursor, Bun, and Notion.
- The video is part of an ongoing exploration into practical AI coding solutions and methods.
Links mentioned:
- Hyperbolic AI Dashboard: no description found
- Tweet from Paul Gauthier (@paulgauthier): Reflection 70B scored 42% on the aider code editing benchmark, well below Llama3 70B at 49%. I modified aider to ignore the <thinking/reflection> tags. This model won't work properly with t...
- SECRET SAUCE of AI Coding? AI Devlog with Aider, Cursor, Bun and Notion: What's the secret sauce of HIGH OUTPUT AI Coding?🔗 More AI Coding with AIDERhttps://youtu.be/ag-KxYS8Vuw🚀 More AI Coding with Cursorhttps://youtu.be/V9_Rzj...
- Build anything with v0 (3D games, interactive apps): Try it out at https://v0.dev/chat.• Demos: https://x.com/v0/status/1826020673908535325• shadcn/ui: https://ui.shadcn.com• Deploy: https://vercel.com
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) ▷ #announcements (3 messages):
Reflection APIReflection-Tuning TechniqueSelf-Correcting AI Models
- Reflection API Now Open for Playtesting: The Reflection API is now available on OpenRouter for free playtesting, with a fixed version expected soon.
- Matt Shumer noted a distinct quality difference between hosted and internal APIs, indicating the current hosted version is not fully optimized.
- Introducing Reflection-Tuning Technique: The Reflection-70B model developed by Matt Shumer employs a new technique called Reflection-Tuning that enables the model to detect and correct mistakes in its reasoning.
- This model leverages synthetic data for training, enhancing its performance as noted in several sources, including a LinkedIn post.
- Community Resources on Reflection 70B: Users can access various resources about the Reflection 70B model, including a Medium article that discusses its self-correcting abilities.
- There are also insightful videos available, such as a YouTube discussion with Matt Shumer about this innovative model.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from OpenRouter (@OpenRouterAI): Reflection's own API is now available on OpenRouter for free playtesting: https://openrouter.ai/models/mattshumer/reflection-70b:free Stay tuned for a production endpoint for the fixed version so...
- no title found: no description found
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) ▷ #app-showcase (10 messages🔥):
ISO20022Bitcoin and CBDCscli_buddy GitHub projectOpen Source Multi-lingual ModelOpenRouter Usage
- Exploring ISO20022 for Crypto: A member highlighted the importance of ISO20022 in the context of ongoing developments in crypto, suggesting that others should investigate its implications.
- They encouraged a deeper look into this standard to understand its potential impact on financial transactions.
- Bitcoin’s Incompatibility with CBDCs: Bitcoin cannot be traded with CBDCs, sparking discussions about the implications of central bank digital currencies on decentralized cryptocurrencies.
- Members shared their surprise at this limitation and its potential effects on trading dynamics.
- Introducing cli_buddy for OpenRouter: A member shared a GitHub project called cli_buddy, designed to enhance interactions with OpenRouter by offering a variety of commands.
- The info command allows users to search for AI models and display credits available in OpenRouter, increasing accessibility.
- Development of Open Source Multi-lingual Model: Discussions emerged regarding a dataset currently under development, with 1.5GB in size, aimed at training an open source multi-lingual model.
- This dataset combines image position data, making it suitable for integration with vision models.
- Cost-effectiveness of Recent OpenAI Usage: Members compared the 1 week usage cost of OpenAI credits at roughly $2,500, considering it quite expensive in light of the other project expenses discussed.
- Participants pointed out the need for more affordable options amidst the rising costs of AI services.
Link mentioned: GitHub - rezmeplxrf/cli_buddy: Contribute to rezmeplxrf/cli_buddy development by creating an account on GitHub.
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) ▷ #general (611 messages🔥🔥🔥):
DeepSeek CoderReflection ModelOpenRouter API IssuesGemini ModelsMulti-Modal Models
- DeepSeek Coder experiencing issues: Users reported that the DeepSeek Coder is producing zero responses and that the API is malfunctioning, indicating potential upstream issues.
- Despite the DeepSeek status page showing no reported issues, users continue to experience problems with both the API and the OpenRouter chat.
- Concerns about Reflection Model: Discussion arose regarding the legitimacy of the Reflection model, with some users expressing skepticism over its claims and performance.
- There is a desire for the model to be removed from OpenRouter due to concerns over scams and misinformation.
- Errors in OpenRouter API Calls: Users encountered errors such as ‘httpx.RemoteProtocolError’ indicating that connections were prematurely closed, suggesting issues with the DeepSeek API.
- Some users are attempting to verify whether these errors stem from their own implementations or upstream problems.
- Interest in AI Model Hosting: Users discussed the hosting of models on OpenRouter, noting that Euryale 2.2 is a recommended choice for RP applications, while Magnum’s lack of updates is a concern.
- The conversation included comparisons to other models and requests for reliable options for roleplaying.
- Multi-Modal Model Usage: Users asked about integrating local images with multi-modal models, seeking guidance on how to format requests properly.
- Instructions on decoding images into base64 format for API requests were provided to assist users in utilizing multi-modal capabilities.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from cocktail peanut (@cocktailpeanut): OpenAI preparing to drop their new model
- no title found: no description found
- OpenRouter: LLM router and marketplace
- Transforms | OpenRouter: Transform data for model consumption
- Prompt Caching | OpenRouter: Optimize LLM cost by up to 90%
- Monopoly Guy Money GIF - Monopoly Guy Money - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Requests | OpenRouter: Handle incoming and outgoing requests
- DeepSeek Service Status: no description found
- Tweet from Matt Shumer (@mattshumer_): Quick update — we re-uploaded the weights but there’s still an issue. We just started training over again to eliminate any possible issue. Should be done soon. Really sorry about this. The amount of...
- Lumen Orbit: Join Lumen Orbit in pioneering sustainable space-based data centers. Learn how we use 90% less electricity and access 24/7 solar energy. Download our white paper today!
- Models: 'base>' | OpenRouter: Browse models on OpenRouter
- Tweet from OpenRouter (@OpenRouterAI): Reflection's own API is now available on OpenRouter for free playtesting: https://openrouter.ai/models/mattshumer/reflection-70b:free Stay tuned for a production endpoint for the fixed version so...
- Tweet from Matt Shumer (@mattshumer_): We’ve figured out the issue. The reflection weights on Hugging Face are actually a mix of a few different models — something got fucked up during the upload process. Will fix today. Quoting Matt Shu...
- python-aiplatform/google/cloud/aiplatform_v1/types/tool.py at 6d1f7fdaadade0f9f6a77c136490fac58d054ca8 · googleapis/python-aiplatform: A Python SDK for Vertex AI, a fully managed, end-to-end platform for data science and machine learning. - googleapis/python-aiplatform
- Llama 3.1 Euryale 70B v2.2 - API, Providers, Stats: Euryale L3.1 70B v2. Run Llama 3.1 Euryale 70B v2.2 with API
- no title found: no description found
- DeepSeek-Coder-V2 - API, Providers, Stats: DeepSeek-Coder-V2, an open-source Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) code language model. It is further pre-trained from an intermediate checkpoint of DeepSeek-V2 with additional 6 trillion tokens. Run DeepSeek...
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- What is Top K? - Explaining AI Model Parameters: Today, I delve into the concept of Top K in AI, a crucial parameter that influences text generation. By limiting the AI's word choices to the top K most like...
- Llama 3.1 405B (base) - API, Providers, Stats: Meta's latest class of model (Llama 3.1) launched with a variety of sizes & flavors. Run Llama 3.1 405B (base) with API
- Mixtral 8x7B (base) - API, Providers, Stats: A pretrained generative Sparse Mixture of Experts, by Mistral AI. Incorporates 8 experts (feed-forward networks) for a total of 47B parameters. Run Mixtral 8x7B (base) with API
- Brave Search: Search the Web. Privately. Truly useful results, AI-powered answers, & more. All from an independent index. No profiling, no bias, no Big Tech.
- Magnum 72B - API, Providers, Stats: From the maker of [Goliath](https://openrouter.ai/models/alpindale/goliath-120b), Magnum 72B is the first in a new family of models designed to achieve the prose quality of the Claude 3 models, notabl...
- This appears to be very similar to our Atlas-1 model, but with hard coded clicks. Is that correct? · Issue #21 · OthersideAI/self-operating-computer: Hey guys we've been training a very similar multi-modal model called Atlas-1, however we don't need to hard-code click positions like it appears here, because we trained our model to find UI-e...
- no title found: no description found
- Change Log | DeepSeek API Docs: Version: 2024-09-05
- feat: Add support for system instruction and tools in tokenization. · googleapis/python-aiplatform@72fcc06: PiperOrigin-RevId: 669058979
- Change Log | DeepSeek API Docs: Version: 2024-09-05
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) ▷ #beta-feedback (11 messages🔥):
Vertex AI Key CompatibilityJSON Formatting IssuesGoogle AI Studio UsageBase64 Encoding Workaround
- Vertex AI Key requires full JSON: A member noted that for the Vertex AI key, it indeed needs to be the whole JSON object, including the project_id and other details.
- This point was confirmed after some discussion about whether just the private_key would suffice.
- Google AI Studio is current requirement: Members discussed limitations in using Vertex AI, confirming that as of now, one can only use Google AI Studio.
- This indicates that further fixes are necessary to expand compatibility options.
- Base64 encoding suggested as solution: A clever workaround was suggested for upload issues with the JSON file: convert the whole JSON to Base64 and decode it before sending to Vertex AI.
- This method was mentioned as a stolen idea from a GitHub PR discussion.
Link mentioned: Add Vertex AI support by u-minor · Pull Request #45 · saoudrizwan/claude-dev: This PR adds support for Vertex AI in Google Cloud. At this time, the Application Default Credentials (ADC) must be set in the gcloud command to use Vertex AI. Authentication supports one of the fo…
Stability.ai (Stable Diffusion) ▷ #general-chat (592 messages🔥🔥🔥):
AI model training methodsGPU recommendations for image generationStable Diffusion models comparisonInfluencer culture and content creationUsing detail enhancing LoRAs
- Comparison of training methods: LoRA vs Dreambooth: LoRAs are smaller, easier to distribute, and can be combined during runtime, while Dreambooth outputs full checkpoints which occupy significantly more space.
- Both methods require minimal images for training, but the tools like Kohya and OneTrainer are preferable for LoRA, with Kohya being particularly popular.
- GPU recommendations under $600 for local image generation: For a budget of $600, a used 3090 or 2080 is suggested as a solid option for enhancing local image generation capabilities.
- Users emphasized the importance of VRAM for optimal performance, particularly when it comes to tasks such as local training.
- The evolution of SD models and their compatibility: There is a call for new models that are backwards compatible with SD1.5 LoRAs, as SD1.5 remains a classic tool for many users today.
- Current discussions highlight the strengths of SD1.5 in composition, with users noting how newer models haven’t diminished its effectiveness.
- Influencer culture in content creation: A critiqued influencer culture highlights the expectation for content creators to monetize their efforts through platforms like Patreon and YouTube.
- Some community members express a desire for a return to less commercialized forms of content creation, while acknowledging the prevalent use of influencer strategies.
- Detail enhancing LoRAs in image generation: Users report that details in AI-generated images rely significantly on workflow enhancements rather than prompting, with LoRAs being crucial for improving image quality.
- Several users utilize combinations of LoRAs, such as Detail Tweaker XL, for optimal results in their image generations.
Links mentioned:
- imgur.com: Discover the magic of the internet at Imgur, a community powered entertainment destination. Lift your spirits with funny jokes, trending memes, entertaining gifs, inspiring stories, viral videos, and ...
- imgur.com: Discover the magic of the internet at Imgur, a community powered entertainment destination. Lift your spirits with funny jokes, trending memes, entertaining gifs, inspiring stories, viral videos, and ...
- UVMapper - UV Mapping Software: no description found
- DC-Solver: Improving Predictor-Corrector Diffusion Sampler via Dynamic Compensation: Diffusion probabilistic models (DPMs) have shown remarkable performance in visual synthesis but are computationally expensive due to the need for multiple evaluations during the sampling. Recent predi...
- imgur.com: Discover the magic of the internet at Imgur, a community powered entertainment destination. Lift your spirits with funny jokes, trending memes, entertaining gifs, inspiring stories, viral videos, and ...
- Kijai/flux-fp8 · Hugging Face: no description found
- imgur.com: Discover the magic of the internet at Imgur, a community powered entertainment destination. Lift your spirits with funny jokes, trending memes, entertaining gifs, inspiring stories, viral videos, and ...
- Green Code: 01001000 01101001 00100001 00100000 01001001 00100000 01101101 01100001 01101011 01100101 00100000 01110110 01101001 01100100 01100101 01101111 01110011 00100000 01100001 01100010 01101111 01110101 01...
- Text Guided Flux Inpainting - a Hugging Face Space by Gradio-Community: no description found
- Wtf Movie Threat GIF - They Live Eat Trash Can Coub - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- stabilityai/stable-diffusion-3-medium · Hugging Face: no description found
- 🎲 DICE AI DEVELOPMENT 🎲: "Hi I'm DICE, a seasoned AI professional with over 10 years of experience working with AI coding and 20+ years of professional coding experience. As a ranked Master Generator on Civitai, I ha...
- Civitai | Share your models: no description found
- Amir Zand: Artist @ QuanticDream
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- Master AI image generation - ComfyUI full tutorial 2024: ComfyUI complete installation & tutorial. The ultimate image generator. Text to image, image to image, faceswap, controlnet, upscaling, external plugins, & m...
- Introducing Stable Fast 3D: Rapid 3D Asset Generation From Single Images — Stability AI: We are excited to introduce Stable Fast 3D, Stability AI’s latest breakthrough in 3D asset generation technology. This innovative model transforms a single input image into a detailed 3D asset, settin...
- ShaderMap - Normal Map Generator - Create Rendering and PBR Maps from Textures and 3D Models: no description found
- GitHub - wl-zhao/DC-Solver: [ECCV 2024] DC-Solver: Improving Predictor-Corrector Diffusion Sampler via Dynamic Compensation: [ECCV 2024] DC-Solver: Improving Predictor-Corrector Diffusion Sampler via Dynamic Compensation - wl-zhao/DC-Solver
- Best Usenet Service Providers 2024: Best Usenet Service Providers 2024 ranked by Newsgroup Access Newsservers, Usenet Search, Features & Free Trial. Add VPN for privacy.
- Understanding Normals in Blender: In this video, I will explain the basics of recalculating normals in Blender.● Help support the channel:• Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/ryankingart• Gumro...
- SECourses 3D Render for FLUX - Full Dataset and Workflow Shared - v1.0 | Stable Diffusion LoRA | Civitai: Full Training Tutorial and Guide and Research For a FLUX Style Hugging Face repo with all full workflow, full research details, processes, conclusi...
- GitHub - leejet/stable-diffusion.cpp: Stable Diffusion and Flux in pure C/C++: Stable Diffusion and Flux in pure C/C++. Contribute to leejet/stable-diffusion.cpp development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Audioreactively Generative Graffitis - [TouchDesigner + Stable Diffusion]: You can access this new patch, plus many more systems, experiments, and tutorials, through: https://linktr.ee/uisato#touchdesigner #stablediffusion #visuals
- --FINAL GUI RETARD GUIDE--: "HE WHO SHALL NOT BE NAMED" The definitive Stable Diffusion experience ™ ---NEW FEATURE SHOWCASE & HOWTO--- Notable: Inpainting/Outpainting, Live generation preview, Tiling, Upscaling, &...
- GitHub - tensorflow/tensorflow: An Open Source Machine Learning Framework for Everyone: An Open Source Machine Learning Framework for Everyone - tensorflow/tensorflow
- Using the PyTorch C++ Frontend — PyTorch Tutorials 2.4.0+cu121 documentation: no description found
- AI Art Prompts: no description found
- Underwater_movie_lora - underwater_movie_loraV1 | Stable Diffusion LoRA | Civitai: LoRa trained for the movie Underwater 2020.
- FLUX - Dev | Stable Diffusion Checkpoint | Civitai: FLUX.1 [dev] is a 12 billion parameter rectified flow transformer capable of generating images from text descriptions. For more information, please...
LM Studio ▷ #general (402 messages🔥🔥):
LM Studio UpdatesModel Performance and SettingsTraining Language ModelsUser Experience with LM StudioServer Interaction and API Requests
- Feedback on LM Studio v0.3: Users expressed concerns about the new interface in LM Studio v0.3, noting the removal of certain features and settings compared to v0.2. The developers assured that many updates and improvements are coming in future releases.
- Feedback included complaints about the loss of system prompts and the difficulty in adjusting settings, prompting users to consider downgrading.
- Model Configuration Issues: Users reported issues with model configurations, particularly related to GPU offloading and context length settings. Suggestions include adjusting GPU layers and ensuring dedicated VRAM to improve performance.
- One user faced errors when trying to continue assistant messages due to context overflow, leading to discussions about potential bug reporting.
- Training Language Models: Users discussed the feasibility of training small language models, expressing interest in datasets and parameter counts. There was an emphasis on understanding training loss and how it connects to model performance.
- The challenges of training smaller models for less common languages were highlighted, along with the importance of high-quality datasets.
- Interacting with LM Studio Server: Questions were raised about how to interact with the LM Studio server, with clarity provided on sending API requests rather than using a web interface. Users were guided to examples on the server tab for further assistance.
- One user quickly resolved their server interaction issues after understanding the required API request format.
- User Experiences and Suggestions: Users shared various experiences while using LM Studio, discussing both positive aspects and frustrations with recent updates. Suggestions for improvements included providing clear documentation and alternatives for accessing features.
- The need for better tutorials and guidance on the new interface was also highlighted, indicating a desire to increase user competency with LM Studio.
Links mentioned:
- Imgur: The magic of the Internet: no description found
- Audio Examples: Examples of ComfyUI workflows
- abetlen/Phi-3.5-vision-instruct-gguf · Hugging Face: no description found
- AGI-0/Artificium-llama3.1-8B-001 · Hugging Face: no description found
- Understanding AI/LLM Quantisation Through Interactive Visualisations: AI/LLM Quantisation Visualised
- LM Studio 0.3.0 | LM Studio: We're incredibly excited to finally share LM Studio 0.3.0 🥳.
- mattshumer/Reflection-Llama-3.1-70B · I created the Llama-3.1-8B Version: no description found
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- Free Download HWiNFO Sofware | Installer & Portable for Windows, DOS: Start to analyze your hardware right now! HWiNFO has available as an Installer and Portable version for Windows (32/64-bit) and Portable version for DOS.
- bartowski/Reflection-Llama-3.1-70B-GGUF at main: no description found
- GitHub - lmstudio-ai/lms: LM Studio CLI: LM Studio CLI. Contribute to lmstudio-ai/lms development by creating an account on GitHub.
- GitHub - Vasco0x4/Neo-AI: Neo AI integrates into the Linux terminal, capable of executing system commands and providing helpful information.: Neo AI integrates into the Linux terminal, capable of executing system commands and providing helpful information. - GitHub - Vasco0x4/Neo-AI: Neo AI integrates into the Linux terminal, capable of...
- microsoft/Phi-3.5-vision-instruct · Hugging Face: no description found
- What is the difference between System, User, and Assistant roles in ChatGPT?: According to Mastering the OpenAI API: Tips and Tricks - Arize AI : Commonly used roles include “system,” “user,” and “assistant.” The “system” provides high-level instructions, the “user” presents ...
- mostafaibrahim17: Weights & Biases, developer tools for machine learning
- A Deep Dive Into Learning Curves in Machine Learning: Understand machine learning better with our guide on accuracy and loss curves. We explain their differences, how to read them, and why they're important.
- Feature Request: Add support for Phi-3.5 MoE and Vision Instruct · Issue #9119 · ggerganov/llama.cpp: Prerequisites I am running the latest code. Mention the version if possible as well. I carefully followed the README.md. I searched using keywords relevant to my issue to make sure that I am creati...
- Add support for IQ1_S, IQ3_S, IQ2_S, IQ4_XS. IQ4_NL is not functional by mann1x · Pull Request #3657 · ollama/ollama: This patch adds support for IQ1_S, IQ3_S, IQ2_S, IQ4_XS. IQ4_NL is using a different format, have to investigate further what are the differences.
LM Studio ▷ #hardware-discussion (83 messages🔥🔥):
LM Studio and VOSKIntel A770 PerformanceNVIDIA Caution with VRAMReflection-Llama-3.1 IssuesApple's Upcoming Hardware
- LM Studio integrates VOSK for Language Prompts: After configuring LM Studio to receive prompts from Vector and respond through VOSK on an Intel A770, performance improvements were noted, with response times described as ‘almost instantaneous’.
- Fine-tuning is still needed, with suggestions to limit the response length to around 100-200 words for conciseness.
- Intel A770 and SYCL Performance Discussions: Discussions around the Intel A770 highlighted its ability to infer using Vulkan and fp16 math, with members inquiring about token throughput, averaging around 7000 TPS.
- The conversation also covered leveraging Q8 quantization, which reportedly enhances performance without sacrificing model intelligence.
- Concerns Over NVIDIA VRAM Limitations: Users expressed disappointment over NVIDIA’s lack of significant VRAM increases, voicing that the anticipated VRAM sizes have not materialized in recent generations despite expectations.
- Discussions indicated that manufacturers are shifting focus away from consumer cards to more profitable enterprise solutions.
- Issues Loading Reflection-Llama-3.1 Model: A user reported failures to load the Reflection-Llama-3.1-70B-Q4_0_4_4.gguf model, facing CUDA memory allocation errors despite having substantial VRAM configured.
- They were advised to consider using a corrected version of the model available on Hugging Face to resolve loading issues.
- Excitement Around Apple’s Hardware Launch: Interest was expressed in upcoming announcements from Apple, with speculation on the capabilities of the 5090 GPU and its memory configuration relative to prior models.
- There is expectation that Apple will continue to dominate the unified memory market with its new hardware offerings.
Links mentioned:
- mattshumer/ref_70_e3 · Hugging Face: no description found
- Vector: Vector using Phi 3 LLM generated locally using Arc A770.
Perplexity AI ▷ #general (334 messages🔥🔥):
Perplexity Subscription IssuesPromo Code Leak ControversyModel Usage LimitsWeb Scraping by LLMsTechnical Issues with Perplexity
- Cancellation of Subscriptions with Promo Codes: Many users expressed frustration over the cancellation of their subscriptions after using leaked promo codes, with some receiving emails claiming they cancelled their subscriptions themselves.
- Users are seeking clarification from Perplexity’s support team but report receiving little to no response.
- Concerns Over Model Limitations and Access: Users are confused about the limits imposed on model usage, with discussions indicating limits of 450 queries for pro models and 50 for Claude Opus.
- Some users are questioning how to specify which model they are using when writing, as current functionality seems to obscure this.
- Alternatives to Perplexity’s LLM Functionality: A discussion emerged about other search engines and LLMs, such as You.com and Kagi, that utilize web scraping to provide data in responses.
- These alternatives are highlighted as solving some of the issues related to knowledge cutoffs and hallucinated responses.
- Technical Difficulties with Perplexity: Users reported various technical problems, including issues with accessing their ‘Pages’ and receiving inadequate responses to queries.
- Many are experiencing these problems across different browsers and devices, indicating potential widespread issues with the platform.
- Upcoming Features and Updates: Questions arose regarding the addition of new features such as the Reflection LLM and details about model hosting specifications like FP16 or FP8.
- Users are actively seeking updates on product enhancements and clarifications on current offerings from Perplexity.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from lmsys.org (@lmsysorg): ⚠️WARNING: offensive content ahead. Introducing RedTeam Arena with Bad Words—our first game. You've got 60 seconds to break the model to say the bad word. The faster, the better. (Collaboration ...
- ProLLM Benchmarks | Toqan: no description found
Perplexity AI ▷ #sharing (49 messages🔥):
One Piece DocumentationAI ServicesCarbon Capture TechnologiesKung Pao Chicken RecipeAI Tutors Engagement
- Diving into One Piece Documentation: Started working on a comprehensive documentation for One Piece, focusing on adding all the arcs.
- This project reflects a commitment to organizing and enhancing accessibility for One Piece fans.
- Top AI Services Discussed: Members shared interest in the top AI services available and their impact on engagement.
- The discussion highlighted how AI contributes to various fields, driving innovation and efficiency.
- Exploring Carbon Capture Technologies: Members discussed novel approaches to carbon capture and storage, emphasizing its importance in climate action.
- This conversation underscored the technological strides being made to mitigate environmental impact.
- Mastering Kung Pao Chicken: A delightful recipe for Kung Pao Chicken was shared, promising a flavorful cooking experience.
- Members exchanged tips and variations to enhance the dish, fostering a culinary community.
- AI Tutors Boost Student Engagement: A presentation illustrated how AI tutors are effectively doubling student engagement in learning environments.
- The implications of this technology suggest a shift in educational methodologies and student interaction.
Link mentioned: YouTube: no description found
Perplexity AI ▷ #pplx-api (13 messages🔥):
API response lengthAPI access issuesPayment method errorsModel deprecationSearch domain filter
- API Responses Need More Depth: A user noted that API responses are short and dry compared to web responses, despite identical queries, and sought recommendations on parameters to adjust.
- Suggestions for improvement could enhance the richness of API replies.
- 404 Error on API URL: A user encountered an HTTP ERROR 404 when trying to access the API at the specified URL.
- Another user pointed out the correct endpoint as https://api.perplexity.ai/chat/completions.
- Payment Method Authentication Problems: A user reported issues with the authentication of their payment method while setting up API access, receiving errors on multiple cards.
- Another participant confirmed similar experiences, particularly with security code errors.
- Concerns Over Deprecation of Models: A user expressed frustration that many models were deprecated, affecting access to updated information and links.
- They inquired about methods to prompt models for more direct link access.
- Using the Search Domain Filter: A user suggested utilizing the
search_domain_filterparameter in the API to regulate the domains the model searches.- This approach might help users retrieve more accurate information from current models.
Link mentioned: no title found: no description found
Cohere ▷ #discussions (334 messages🔥🔥):
Cohere techHaircuts and stylesRole of bots in moderationAI scams and cryptoMultimodal models and projects
- Cohere tech shines in moderation: Members discussed how the Cohere classification technology effectively eliminates crypto spam, enhancing server conversations.
- One user emphasized that the bot is a necessary tool to keep discussions focused and enjoyable after encountering rampant spam.
- Haircuts trending in the chat: Participants engaged in a lighthearted conversation about haircuts, specifically referencing Aidan Gomez’s hairstyle and sharing their own experiences.
- Several members contemplated getting similar cuts, highlighting the fun community vibe while sharing hair-related anecdotes.
- Crypto influences on AI: There were concerns raised about crypto scammers infiltrating the AI space, with members expressing frustration about associated scams.
- One long-time AI enthusiast shared experiences dealing with such spam and mentioned the negative impact on the perception of legitimate AI advancements.
- Exploration of Cohere products: New members expressed their excitement about exploring Cohere products and learning more about the platform’s capabilities.
- Discussions highlighted the latest updates to R and R+ which have improved coding experiences for users.
- Multimodal models and projects: There were discussions about the potential of vision models in planning tasks, with community members sharing insights from their own experiences in robotics and AI.
- The conversation reflected on how different AI models could contribute to more realistic problem-solving approaches.
Links mentioned:
- ChatGPT 5 and Beyond: OpenAI’s Five-Level Roadmap to AGI Unveiled: In a recent development, OpenAI has unveiled a new five-level system to track its progress towards achieving Artificial General…
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- Aidan Gomez: What No One Understands About Foundation Models | E1191: Aidan Gomez is the Co-founder & CEO at Cohere, the leading AI platform for enterprise, having raised over $1BN from some of the best with their last round pr...
- no title found: no description found
Cohere ▷ #questions (25 messages🔥):
Recruiting Team ContactUse of Cohere ProductsMrDragonFox's PresenceEmbed vs Embed Jobs
- Recruiting Team Contact Inquiry: A member sought the contact information for the recruiting team after finding a part-time remote role on LinkedIn and being redirected to the Discord server.
- Another member suggested they will get a contact once the team gets back to them, noting the server is meant for tech discussions, not recruitment.
- Exploring Cohere Products: In response to a question about what people are using Cohere products for, it was noted that customer use cases are regularly published on the Cohere blog.
- Discord members also share their use cases in a dedicated channel, and cookbooks offer inspirational starter code for various applications.
- MrDragonFox’s Ubiquitous Presence: Members joked about MrDragonFox being everywhere in the server, with one member humorously questioning if he is even human.
- MrDragonFox replied affirmatively about being human, humorously adding that he is ‘just connected’.
- Difference Between Embed and Embed Jobs: A member asked for clarification on the difference between the terms ‘embed’ and ‘embed jobs’, indicating they understood the embed process.
- The discussion was aimed at simplifying the technical distinctions between these two concepts.
Link mentioned: Cookbooks — Cohere: no description found
Cohere ▷ #api-discussions (20 messages🔥):
Configuring Output LengthsSearch Query CostsUsing Calendar AgentInvalid Raw Prompt ErrorChat Turns in API
- Configuring Output Lengths discussion: Members discussed how to configure output lengths and early stop sequences, indicating a need for clearer instructions.
- A participant mentioned they would ask Alicja for further assistance since she is currently on a gap year.
- Understanding Search Query Costs: A member inquired if a query with 10 documents counts as 0.1 of a search, to which it was clarified that any number up to 100 counts as a single search.
- There is no fractional execution; whether you search for 1 or 99 documents, it is still considered one search query.
- Using the Calendar Agent: Questions arose regarding the usage of the Calendar agent and how to book appointments through proper API calls.
- The user was directed to specific documentation but still struggled to get the expected output as demonstrated in the examples.
- Handling Invalid Raw Prompt Error: One member reported a 400 Bad Request error when using the
raw_promptingparameter and asked for clarification on ‘valid chat turns’.- It was clarified that a chat turn is defined as a user, system, or agent interaction.
Link mentioned: Calendar Agent with Native Multi Step Tool — Cohere: This page describes how to use cohere Chat API with list_calendar_events and create_calendar_event tools to book appointments.
Cohere ▷ #projects (13 messages🔥):
LLM Web App LaunchStreamlit Hosting PlansLangchain IntegrationAdmin Access Concern
- Wittgenstein launches a simple LLM web app: A member announced the coding of a simple LLM web app and shared the GitHub link for others to explore.
- They expressed enthusiasm and invited questions, asserting that Cohere is a great tool.
- Plans to host the app on Streamlit: Members discussed the possibility of hosting the LLM app on Streamlit for easier access, prompting the developer to agree.
- Integration of Langchain: The developer confirmed the app was built as a learning project involving Langchain, enhancing its functionality.
- App Deployed in the Cloud: Wittgenstein shared that the app is now deployed in the cloud, providing the link to access it: Streamlit App.
- They conveyed gratitude for the motivation received during development.
- Admin Access Issue Identified: Concerns arose when it was discovered that the app allows easy admin login via JSON output, revealing administrative passwords.
- Members reacted with humor regarding the password being ‘admin’, pointing out a potential security risk.
Links mentioned:
- GitHub - xettrisomeman/llm_simple_app: Simple LLM APP: Simple LLM APP. Contribute to xettrisomeman/llm_simple_app development by creating an account on GitHub.
- no title found: no description found
Nous Research AI ▷ #general (199 messages🔥🔥):
Reflection 70B PerformanceUpcoming AI ModelsNous Forge PresentationBenchmark EvaluationsAI Model Mislabeling
- Reflection 70B’s Underwhelming Benchmarks: Recent evaluations show that Reflection 70B consistently underperforms compared to Llama 3.1 across various benchmarks, indicating possible overpromising on its capabilities.
- Independent tests reveal lower scores, leading to skepticism about its initial claims and raising questions about why certain weights have not been released.
- Community Skepticism on AI Claims: Members of the community express doubts regarding the performance claims of new AI models, labeling the situation as potentially misleading or a marketing gimmick.
- Some discussions suggest that continued releases might not reflect the model’s actual abilities, akin to earlier hype cycles within AI advancements.
- Nous Forge’s Potential Appearance at 38C3: There’s consideration for a Nous Forge presentation at the upcoming Chaos Communication Congress 2024, with members discussing the relevance of the event.
- While the event may cater primarily to German speakers, its bilingual format could still allow for comprehensive presentations on digital freedom and AI.
- Importance of Diverse Benchmarking: Participants agree on the necessity of utilizing diverse benchmarks to gauge AI models, pointing out risks of overfitting to certain datasets.
- Examples like Alice benchmark indicate that specific weaknesses may not accurately represent overall model performance and can lead to skewed evaluations.
- Need for Cleaner Pretraining Data: There’s a consensus that the issues observed in certain AI models are symptomatic of pretraining data cleanliness, rather than systemic flaws in transformer architecture.
- Suggestions include the use of synthetic data to improve model training and mitigate biases or misleading patterns found in datasets.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from undefined: no description found
- Tweet from cocktail peanut (@cocktailpeanut): OpenAI preparing to drop their new model
- Tweet from Paul Gauthier (@paulgauthier): Reflection 70B scored 42% on the aider code editing benchmark, well below Llama3 70B at 49%. I modified aider to ignore the <thinking/reflection> tags. This model won't work properly with t...
- Tweet from undefined: no description found
- Tweet from OpenRouter (@OpenRouterAI): Reflection's own API is now available on OpenRouter for free playtesting: https://openrouter.ai/models/mattshumer/reflection-70b:free Stay tuned for a production endpoint for the fixed version so...
- Tweet from Paul Gauthier (@paulgauthier): For clarity, the 42% score was without the specific recommended system prompt. With that prompt, it scored 43%.
- Tweet from N8 Programs (@N8Programs): CPU single-threaded impementation of mnist training of neural network. Runs at nearly 20000 images/sec. Pure Javascript with a WASM extension for SIMD. Designed to run in NodeJS. https://github.com/...
- Tweet from Artificial Analysis (@ArtificialAnlys): Reflection 70B update: Quick note on timeline and outstanding questions from our perspective Timeline: - We tested the initial Reflection 70B release and saw worse performance than Llama 3.1 70B. - ...
- Tweet from Terry Yue Zhuo (@terryyuezhuo): As requested, here are the new results of the updated Reflection model. (1) No thinking + No system prompt: Complete 33.1 (> Llama-3.1-405B, 30.4, == a few close LLMs) Instruct 23.0 (still ~< ...
- mattshumer/ref_70_e3 · Hugging Face: no description found
- комару комару кот GIF - Комару Комару кот Komaru - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Tweet from Weiyang Liu (@Besteuler): 🧐 Interesting finding: we test Reflection-70B on our SGP-Bench (https://sgp-bench.github.io/, a benchmark evaluating symbolic program understanding). Despite Reflection-70B claims to outperform many ...
- Tweet from anton (@abacaj): @ArtificialAnlys @mattshumer_ still waiting for the correct weights to try the model locally, not sure why it has to remain behind an api (hard to tell what is being served then)
- Tweet from Wenhu Chen (@WenhuChen): We updated MMLU-Pro leaderboard with some recent models like Reflection, GPT-4o (0806) and Arx-0.3 (A startup by Thomas Baker).
- Tweet from Jenia Jitsev 🏳️🌈 🇺🇦 (@JJitsev): (Yet) another tale of Rise and Fall: Reflection-70B release claims strong frontiers LLM performance - relying on common benchmarks like MMLU. Can it handle AIW problems, which reveal generalizati...
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- ARX: ARX from Applied General Intelligence (AGI)
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- optillm/plansearch.py at main · codelion/optillm: Optimizing inference proxy for LLMs. Contribute to codelion/optillm development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- GitHub - cpldcpu/MisguidedAttention: A collection of prompts to challenge the reasoning abilities of large language models in presence of misguiding information: A collection of prompts to challenge the reasoning abilities of large language models in presence of misguiding information - cpldcpu/MisguidedAttention
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- Sci-Hub | The dynamical hypothesis in cognitive science | 10.1017/S0140525X98001733: no description found
- The European Pirate Party: no description found
- CONFIRMED: REFLECTION 70B'S OFFICIAL API IS SONNET 3.5: Posted in r/LocalLLaMA by u/TGSCrust • 1,043 points and 303 comments
Nous Research AI ▷ #ask-about-llms (7 messages):
DeepSeek v2.5 PerformanceLLM for Book and Movie QueriesFaceNet for One-Shot RecognitionHermes Nemo Release DateAnything LLM Interest
- Testing DeepSeek v2.5 Performance: A member asked others using DeepSeek v2.5 to report on any noticeable improvements compared to the previous version.
- Feedback on performance would help gauge the enhancements introduced in the new version.
- Seeking LLM for Movie and Book Questions: A user inquired about an LLM service capable of answering questions about movies or books, like the age of Harry Potter in his first chapter.
- The expectation was that the LLM would either provide a correct answer or acknowledge its limitations.
- FaceNet’s Feasibility in One-Shot Recognition: Wondering about the capabilities of FaceNet, a member questioned if anyone has tested it for one-shot face recognition.
- The inquiry suggests interest in exploring the effectiveness of facial recognition technology in specific scenarios.
- Anticipation for Hermes Nemo: One member raised curiosity about the release date for Hermes Nemo.
- The upcoming model generation seems to have piqued the interest of the group.
- General Interest in Anything LLM: A few members expressed interest in the broader scope of anything LLM related topics.
- This indicates an ongoing curiosity about developments and discussions in the LLM community.
Nous Research AI ▷ #research-papers (2 messages):
Medical LLMsContinual In-Context LearningFrameworks for Medical AILLM Digital Twins
- New Developments in Medical LLMs: The week highlighted various Medical LLMs including CancerLLM, which serves the cancer domain, and MedUnA, a vision-language model for medical imagery.
- Key advancements like the Foundation Model for Robotic Endoscopic Surgery and DHIN, a Decentralized Health Intelligence Network, point towards innovative uses in healthcare.
- Evaluations of Medical AI Benchmarks: Several evaluations emerged such as TrialBench, which provides clinical trial datasets and benchmarks, alongside MedFuzz, that explores the robustness of medical LLMs.
- The focus on assessing LLM bias in diagnosis through initiatives like DiversityMedQA illustrates a proactive approach to fairness in medical AI.
- Digital Twins in Medical Applications: Digital Twins were a crucial topic, with efforts in creating models for rare gynecological tumors and forecasting patient health using DT-GPT.
- This technology underscores potential improvements in patient-specific medical interventions through predictive analytics.
- Frameworks for Robust Medical AI: Innovations such as Rx Strategist enable LLM-based prescription verification, enhancing the reliability of medical AI tools.
- Additionally, developments in guardrails for medical LLMs suggest a growing concern for safety and reliability in AI applications within healthcare.
- Advancements in Continual In-Context Learning: The architecture of Continual In-Context Learning with Adaptive Transformers extends transformer models for dynamic learning scenarios, focusing on effective gradient flow.
- This system supports rapid adaptation to new tasks, thereby reducing risks of catastrophic failure while preserving learning integrity.
Link mentioned: Tweet from Open Life Science AI (@OpenlifesciAI): Last Week in Medical AI: Top Research Papers/Models 🏅(September 1 - September 7, 2024) Medical LLM & Other Models : - CancerLLM: Large Language Model in Cancer Domain - MedUnA: Vision-Languag…
Nous Research AI ▷ #interesting-links (19 messages🔥):
PlanSearch introduces diverse LLM outputsRedTeam Arena launches with gamificationReflection 70b model capabilitiesInsights on AI research fraudItext2kg as a knowledge graph tool
- PlanSearch introduces diverse LLM outputs: Scale SEAL released a new method called PlanSearch, which significantly improves LLM reasoning by encouraging diversity during code generation through a natural language search method.
- Hugh Zhang expressed that this method enables LLMs to reason more deeply at inference time, marking a promising direction within AI.
- RedTeam Arena launches with gamification: A new game called RedTeam Arena invites participants to challenge models to say offensive words within 60 seconds, designed for engaging AI hackers in testing capabilities.
- The game aims to create a community-driven platform focused on competitive prompting and red teaming, with all datasets and prompts to be made public post-disclosure.
- Reflection 70b model capabilities: The newly discussed Reflection 70b model reportedly has a built-in scratchpad that utilizes XLM tags, sparking curiosity about its potential for advanced reasoning.
- Community members speculated whether reflection-focused models might signal a new paradigm in multi-step problem-solving, although some felt prompts still play a more critical role.
- Insights on AI research fraud: A thread highlighted alleged fraud involving OthersideAI’s announcement of a breakthrough in training models, with skepticism about its legitimacy.
- The discussion referenced a timeline of deception, emphasizing the importance of accountability in AI research and development.
- Itext2kg as a knowledge graph tool: A GitHub project called Itext2kg offers a user-friendly tool to construct incremental knowledge graphs from unstructured documents using LLMs, with a direct connection to Neo4j.
- Users can now leverage their ontologies effortlessly in production, presenting an accessible alternative to more traditional academic tools like GraphRAG.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from lmsys.org (@lmsysorg): ⚠️WARNING: offensive content ahead. Introducing RedTeam Arena with Bad Words—our first game. You've got 60 seconds to break the model to say the bad word. The faster, the better. (Collaboration ...
- Planning In Natural Language Improves LLM Search For Code Generation: While scaling training compute has led to remarkable improvements in large language models (LLMs), scaling inference compute has not yet yielded analogous gains. We hypothesize that a core missing com...
- Tweet from Alexandr Wang (@alexandr_wang): New SOTA test-time compute result from Scale SEAL⚡️ We are releasing a new SOTA test-time compute method called PlanSearch. It meaningfully outperforms existing approaches on LiveCodeBench via a new...
- Tweet from 𝞍 Shin Megami Boson 𝞍 (@shinboson): A story about fraud in the AI research community: On September 5th, Matt Shumer, CEO of OthersideAI, announces to the world that they've made a breakthrough, allowing them to train a mid-size mod...
- GitHub - AuvaLab/itext2kg: Incremental Knowledge Graphs Constructor Using Large Language Models: Incremental Knowledge Graphs Constructor Using Large Language Models - AuvaLab/itext2kg
Nous Research AI ▷ #research-papers (2 messages):
Medical LLM advancementsContinual In-Context LearningTransformer architectureRobotic Endoscopic SurgeryDecentralized Health Intelligence
- Innovative models lead Medical AI advancements: Highlighted models like CancerLLM and MedUnA are paving the way in the field of medical language models and vision-language tasks, enhancing applications in oncology and medical imagery.
- The models play a crucial role in clinical environments and are further backed by initiatives like OpenlifesciAI’s thread detailing their impact.
- Continual In-Context Learning with Adaptive Transformers: The architecture of ‘Continual In-Context Learning with Adaptive Transformers’ extends transformer applicability in varied tasks, utilizing a pre-trained transformer with additional layers for adaptive learning.
- It employs a two-fold approach where it initially uses in-context learning and modifies the system only if performance falls short, aiming for a balance between adaptability and risk management.
- Expansion of Medical Benchmarks: New benchmarks like TrialBench and DiversityMedQA are introduced to assess medical LLM performance in clinical settings and tackle bias in diagnostic processes.
- These evaluations are fundamental in improving model reliability and demonstrating the evolving standards of medical AI applications.
- Digital Twins and Patient Forecasting: Emerging technologies like Digital Twins for Rare Gynecological Tumors and DT-GPT are set to revolutionize patient health forecasting, enabling more personalized healthcare solutions.
- These innovations signify advancements in utilizing AI to simulate patient conditions and predict outcomes effectively.
- Frameworks for Medical AI applications: Frameworks such as Rx Strategist and Guardrails for Medical LLMs are being developed to enhance prescription verification and establish safety protocols in AI usage.
- These efforts are critical in ensuring that the deployment of AI in healthcare meets high standards of safety and efficacy.
Link mentioned: Tweet from Open Life Science AI (@OpenlifesciAI): Last Week in Medical AI: Top Research Papers/Models 🏅(September 1 - September 7, 2024) Medical LLM & Other Models : - CancerLLM: Large Language Model in Cancer Domain - MedUnA: Vision-Languag…
Nous Research AI ▷ #reasoning-tasks (2 messages):
AGI through RLTransformers and SSIImportance of ScalingBreakthroughs Needed in AI
- AGI can come from intense training and RL: A discussion highlighted that AGI can potentially be achieved through intense training and reinforcement learning (RL).
- However, there are doubts about transformers leading to Supervised Semantic Intelligence (SSI).
- Scaling may enhance reasoning abilities: It was noted that scaling up models may help solve reasoning challenges by training on large, diverse, and clean datasets.
- This approach could make a significant difference, although not sufficient to fully emulate human cognitive systems.
- Resource demands hinder cognitive simulations: Concerns were raised about the resource demands of simulating human cognitive systems, which makes it super hard to scale.
- This suggests that a new breakthrough in AI is much needed to overcome these challenges.
CUDA MODE ▷ #general (16 messages🔥):
Together AI's MLP KernelsROCm/AMD vs. NVIDIARTX 5XXX Architecture GenerationReflection DramaPyTorch on ROCm
- Curiosity about Together AI’s MLP Kernels: Members discussed the 20% speed enhancement of MLP kernels from Together AI, with specific mention of SwiGLU as a potential factor.
- Tri Dao might address this topic further at the upcoming CUDA MODE IRL event.
- ROCm/AMD’s Struggles Compared to NVIDIA: There were inquiries on why ROCm/AMD isn’t capitalizing on the AI boom as effectively as NVIDIA/CUDA, questioning whether it relates to corporate trust.
- Another member pointed out that PyTorch does run on ROCm, yet real-world performance still leans heavily towards NVIDIA hardware.
- Speculation on RTX 5XXX Architecture: Discussions included speculation about whether the upcoming RTX 5XXX series will feature Blackwell or Hopper architecture generation.
- There were also questions regarding the potential inclusion of int/fp4 tensor cores.
- Reflection Drama Causes Embarrassment: Conversations centered on the Reflection drama, which one member described as embarrassing, urging others to disregard it.
- A link was shared to a Reddit discussion outlining lessons learned from Reflection 70B, stressing the importance of replicating benchmarks.
- PyTorch Compatibility on ROCm: A member confirmed that PyTorch does indeed run on ROCm, adding to the ongoing conversations about hardware performance.
- Despite its compatibility, there’s still a perceived performance gap when compared to NVIDIA’s offerings.
Links mentioned:
- Supercharging NVIDIA H200 and H100 GPU Cluster Performance With Together Kernel Collection: no description found
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
CUDA MODE ▷ #triton (49 messages🔥):
Triton Internals ArticleFP16 vs BFP16 PerformanceKernel Optimization StrategiesQuantization Techniques
- Final Insights on Triton Internals: The final article in the series on Triton Internals discusses MLIR generation and progressive IR lowering, providing a valuable learning experience.
- Members showed appreciation for the series, with comments reflecting on its usefulness.
- Testing FP16 Accumulation Speedup: A member expressed curiosity about the speedup of FP16 with FP16 accumulation compared to other types.
- It was noted that while FP16 accumulation is generally faster, its support is limited to specific conditions, especially on consumer devices.
- Optimizing Kernel Loads: There was a discussion on creating a kernel that packs metadata with weights to reduce the number of loads, which could increase efficiency.
- Concerns were raised about the overhead and the implications of packing scales and zeros with weights, leading to potential optimizations for batch sizes.
- Benchmarking and Performance Comparisons: Members discussed the challenges of finding consistent speeds across different batch sizes and the importance of benchmarking with TFlops.
- They noted that reporting speedups compared to unquantized FP16 is common, and considerations on performance enhancements were actively explored.
- Future Kernel Development Suggestions: A suggestion was made to develop a kernel focusing on batch-size 1 optimization to eliminate wasted resources from padding.
- Ultimately, the community showed interest in experimenting with different configurations for performance enhancements, particularly with low-bit precision.
Link mentioned: BitBLAS/benchmark at main · microsoft/BitBLAS: BitBLAS is a library to support mixed-precision matrix multiplications, especially for quantized LLM deployment. - microsoft/BitBLAS
CUDA MODE ▷ #torch (6 messages):
Dynamo Call Analysisgetitem PerformancePyTorch Container ModuleTorchDynamo Cache Lookup
- Analyzing Dynamo Calls: Members discussed tracing the calls in Dynamo, particularly focusing on performance gaps associated with getitem methods.
- One member expressed interest in understanding the origin of these calls and their respective timing.
- Identifying Source in PyTorch’s container.py: A relevant line in the PyTorch container module was identified as potentially responsible for the iterative getitem calls.
- The specific line being investigated is line 320, which ignited discussions regarding its implications.
- Challenges in TorchDynamo Cache Lookup: A member remarked that searching for torchdynamo cache lookup resulted in a wrapper but lacked specific details on direct calls.
- This prompted an exploration for more insight on the cache management within Dynamo.
Link mentioned: pytorch/torch/nn/modules/container.py at 31c4e0d37d8efc37a0697159e5b9121ec34d5141 · pytorch/pytorch: Tensors and Dynamic neural networks in Python with strong GPU acceleration - pytorch/pytorch
CUDA MODE ▷ #algorithms (2 messages):
Self Promotion in Messages
- Server Limits Self Promotion: A member highlighted the importance of limiting messages that focus on self-promotion, stating that only performance-related content is considered engaging.
- Another member acknowledged the feedback with an oopsie, indicating they understood the point made.
- Feedback on Message Content: The conversation emphasized the need for value in server messages, discouraging posts with just links unless they are performance-related.
- This feedback was well-received, showing a community commitment to constructive interactions.
CUDA MODE ▷ #cool-links (18 messages🔥):
Course Lab NotebooksZen, CUDA, and Tensor CoresVLLM Office HoursAdEMAMix OptimizerHerbie Tool for Numerical Analysis
- Course Lab Notebooks are highly valued: Members discussed the 2023 lab notebooks for a course, emphasizing their quality and usefulness for studies.
- A member noted they’re waiting for future releases, but expressed confidence in the existing materials.
- Exciting YouTube Content on CUDA: A YouTube video titled Zen, CUDA, and Tensor Cores - Part 1 was shared, providing an overview of key concepts and insights.
- This video is part of a series, with more information available at Computer Enhance.
- Recording of Latest VLLM Office Hours: A link to the latest VLLM office hours recording discussing quantized CUTLASS GEMM optimizations was shared with interested members.
- This is targeted at those keen on optimizing performance in NVIDIA CUDA-related work, providing valuable insights for AI collaboratives.
- Introduction to AdEMAMix Optimizer: An arXiv paper and GitHub repository were shared discussing the AdEMAMix Optimizer, highlighting advancements in optimizer efficiency.
- Herbie Tool Enhances Numerical Analysis: A member introduced Herbie, a tool designed to improve the speed and accuracy of input equations via various implementations.
- It’s suggested to install Herbie for personal use to avoid limitations from the web demo.
Links mentioned:
- Herbie web demo: no description found
- Zen, CUDA, and Tensor Cores - Part 1: See https://www.computerenhance.com/p/zen-cuda-and-tensor-cores-part-i for more information, links, addenda, and more videos in this series.
- Advanced AI Accelerators and Processors with Andrew Feldman of Cerebras Systems: On this episode, we’re joined by Andrew Feldman, Founder and CEO of Cerebras Systems. Andrew and the Cerebras team are responsible for building the largest-e...
- GitHub - nanowell/AdEMAMix-Optimizer-Pytorch: The AdEMAMix Optimizer: Better, Faster, Older.: The AdEMAMix Optimizer: Better, Faster, Older. Contribute to nanowell/AdEMAMix-Optimizer-Pytorch development by creating an account on GitHub.
CUDA MODE ▷ #beginner (27 messages🔥):
Tensor Core EfficiencyWMMA UsageCUDA Kernel OptimizationOccupancy in Tensor CoresCUDA Development Templates
- Understanding Tensor Core Efficiency in Matmul: A member explained that using 4 WMMA operations per warp allows for better pipelining in matrix multiplication compared to using just 1 WMMA per warp, enhancing overall performance.
- The discussion highlighted that with NVIDIA’s Ampere architecture, higher arithmetic density leads to improved performance, specifically suggesting a 4x4 layout for operations.
- Critique of WMMA for Performance Gains: One participant discouraged using WMMA, suggesting that frameworks like CUTLASS are necessary for extracting optimal performance from tensor cores, especially in FP32 operations.
- They noted that integrating NVIDIA’s WMMA sample into their code resulted in better performance than standard FP32 FMAs but remained behind cuBLAS.
- Challenges of Occupancy and Register Allocation: A discussion around occupancy revealed that while higher occupancy allows for better resource usage, it necessitates fewer registers per thread, limiting data reuse.
- A member noted that with the arrival of the Hopper architecture, dynamic register reallocation between warps could potentially improve both occupancy and performance.
- New CUDA Development Template Shared: One member introduced a GitHub template designed to simplify CUDA C++ kernel development, facilitating testing within Python/PyTorch.
- This initiative aimed to help provide a streamlined setup for future CUDA developers and received positive feedback from the community.
- Clarification on Matrix Multiplication Code: Members clarified code snippets involving wmma::mma_sync, confirming that the example actually performed 16 matmuls instead of the originally stated 2x2 configuration.
- The conversation highlighted the importance of correct terminology and understanding of kernel operations in optimizing matrix multiplication.
Links mentioned:
- nvidi - Overview: nvidi has one repository available. Follow their code on GitHub.
- GitHub - tobiasvanderwerff/cuda-pytorch-template: A clean and simple template for developing CUDA C++ kernels and testing them in Python/PyTorch 🚀🚀: A clean and simple template for developing CUDA C++ kernels and testing them in Python/PyTorch 🚀🚀 - tobiasvanderwerff/cuda-pytorch-template
- Leikoe - Overview: I ❤️ accelerators . Leikoe has 42 repositories available. Follow their code on GitHub.
- Major FP32 llm.c improvements/refactoring/etc. by ademeure · Pull Request #696 · karpathy/llm.c: I got slightly carried away and this ended up significantly changing nearly every single kernel in train_gpt2_fp32.cu! I have also added a lot of comments to the kernels - possibly too many, but if...
- cuda-explore/matmul_tc_4x4.cu at main · Leikoe/cuda-explore: my cuda tinkering repo. Contribute to Leikoe/cuda-explore development by creating an account on GitHub.
- cuda-explore/matmul_tc.cu at main · Leikoe/cuda-explore: my cuda tinkering repo. Contribute to Leikoe/cuda-explore development by creating an account on GitHub.
CUDA MODE ▷ #pmpp-book (2 messages):
PMPP Book for Parallel ComputingCUDA Resource Stream on GitHub
- PMPP Book Recommended for Beginners: A member inquired if the PMPP book is the best starting point for learning parallel computing.
- In response, another member confirmed that it is a good choice for newcomers.
- Explore CUDA Resources on GitHub: A participant suggested checking out the CUDA Resource Stream GitHub Repository for additional helpful materials and links.
- This repository compiles various CUDA related news and material links, assisting developers in staying updated.
Link mentioned: GitHub - cuda-mode/resource-stream: CUDA related news and material links: CUDA related news and material links. Contribute to cuda-mode/resource-stream development by creating an account on GitHub.
CUDA MODE ▷ #torchao (2 messages):
Build FixesGitHub Pull Requests
- Fixing Build Issues with Pull Request #826: A member suggested that this pull request should fix the ongoing build issues after PR #621.
- Another member confirmed, stating that it seems to have fixed it for them, expressing gratitude for the help.
- Collaboration in Debugging: The conversation highlighted collaboration, with one member tagging another for assistance regarding the build issue.
- This approach reflects a proactive community effort in resolving technical challenges that arise during development.
Link mentioned: Unbreak build after #621 by andrewor14 · Pull Request #826 · pytorch/ao: no description found
CUDA MODE ▷ #off-topic (14 messages🔥):
Marathon ExperienceInjury RecoveryCUDA Related ContentSpoiler Over ImagesHiking Accident
- Marathon Challenge and Setback: A member shared excitement about running a marathon but ultimately tapped out around mile 20 due to a severe leg cramp, prioritizing health over completion.
- They humorously acknowledged the struggle, expressing their intent not to get injured while attempting the event.
- Bad Ankle Injury During Hiking: Another member reported a serious ankle injury sustained while hiking, leading to a recent surgery that went well.
- They expressed frustration about being stuck in their room during recovery and the challenge of maintaining motivation.
- Injury Leads to More Programming: One member reflected on how injuries forced them to get into more programming since they couldn’t play sports, finding a silver lining in a tough situation.
- They noted the shift in focus as a coping mechanism, highlighting the impact of physical limitations on hobbies.
- Seeking Video Recommendations for Recovery: The injured member requested recommendations for CUDA related videos and algorithms to help pass the time during recovery.
- They indicated a motivational slump, seeking content to keep their mind engaged despite physical limitations.
- Technical Inquiry on Spoiler Images: The discussion included a question about how to put a spoiler over an image, leading to a solution being found quickly.
- The member shared a link to their badly bruised ankle, now resolved, showing a proactive use of the platform.
CUDA MODE ▷ #irl-meetup (6 messages):
Toronto GPU Programming MeetupsTriton LearningCutlass Interest
- Toronto GPU Programming Meetups in the Works: A member expressed interest in organizing GPU programming meetups in Toronto, welcoming others to collaborate if there’s sufficient interest.
- Curious to see who here is based in Toronto!
- Formation of a GPU Programming Reading Group: The idea of a GPU programming reading group or work group was mentioned, with enthusiasm for deeper engagement in the topic.
- A member noted that would be really cool!
- Excitement for Learning Triton and Cutlass: Members shared a keen interest in Triton and Cutlass, highlighting a growing desire to learn more about these GPU programming tools.
- Both noted their personal interest in exploring Triton and Cutlass further.
CUDA MODE ▷ #triton-puzzles (10 messages🔥):
Triton-Puzzles Error HandlingInstalling Triton-Viz403 Error on Localhost
- Users Grapple with Triton-Puzzles Error: A member reported encountering a TypeError with the message ‘_init_args_hst() missing 1 required positional argument: ‘kwargs’’ when running Triton-Viz, and noted it relates to an existing GitHub issue.
- Another member clarified that AlphaGo had provided a solution, although it was not applicable to the current error encountered.
- Attempting to Fix the Error by Rebuilding Environment: After deleting their virtual environment, a member mentioned they followed AlphaGo’s installation instructions but continued to face the same error.
- They shared an updated output that indicated the app was running on
http://127.0.0.1:5000, but encountered a 403 error upon navigating to that address.
- They shared an updated output that indicated the app was running on
Links mentioned:
- no title found: no description found
- Triton Puzzle was broken (by a recent change?) · Issue #33 · Deep-Learning-Profiling-Tools/triton-viz: When trying a colab notebook here: https://colab.research.google.com/github/srush/Triton-Puzzles/blob/main/Triton-Puzzles.ipynb#scrollTo=_981RFRp4Avz I got a early error with regards to kwargs not ...
- Build software better, together: GitHub is where people build software. More than 100 million people use GitHub to discover, fork, and contribute to over 420 million projects.
CUDA MODE ▷ #hqq-mobius (2 messages):
HFGeneratorBatch Size Support
- HFGenerator limited to batch size of 1: It was confirmed that the HFGenerator only supports batch_size=1, and using the default Hugging Face generator is an alternative.
- Mobicham expressed uncertainty about whether the static cache supports batch_size > 1 in Hugging Face.
- Default Hugging Face Generator as Alternative: The default Hugging Face generator can be utilized as an alternative since the HFGenerator is restricted to a batch size of one.
- This alternative could help users who need to process larger batches despite the limitation.
CUDA MODE ▷ #llmdotc (2 messages):
H100 ScalingNCCL Multi-GPU Training
- Chinthysl showcases linear scaling on 472x H100s: Chinthysl demonstrated running on 472x H100s back in June, achieving linear scaling up to at least 128 GPUs during the training process.
- Members noted the ease of scheduling jobs using Slurm compared to MPI, especially for multi-node setups.
- Discussion on token scaling performance: The discussion highlighted that there may not have been updates on the earlier token scaling numbers over 128 GPUs, raising curiosity about the adjustments made after some fixes.
- Members found it impressive that the system was able to scale well, leading to excitement about future performance benchmarks.
Link mentioned: NCCL only multi-gpu multi-node training without MPI by chinthysl · Pull Request #426 · karpathy/llm.c: Scheduling jobs using Slurm seems much easier in a multi-node training setup compared to setting up MPI for the cluster. This draft contains the changes to use mpirun for single-node training and S…
CUDA MODE ▷ #rocm (1 messages):
AMD's UDNA ArchitectureDeprioritization of High-End Gaming GPUsTransition from GCN to RDNA and CDNA
- AMD unifies RDNA and CDNA into UDNA: At IFA 2024 in Berlin, AMD’s Jack Huynh announced the unification of consumer-focused RDNA and data center-focused CDNA architectures into a single microarchitecture called UDNA, designed to compete better with Nvidia’s CUDA ecosystem.
- This development marks a strategic shift for AMD, aiming to improve its competitive stance in the market as it addresses both gaming and compute-centric demands.
- AMD deprioritizes flagship gaming GPUs: AMD has decided to deprioritize high-end gaming graphics cards to enhance its market share, as reflected in Huynh’s announcements.
- This shift indicates AMD’s focus on broader strategic goals over competing exclusively in the high-end gaming segment.
- From GCN to new architectures: When moving on from GCN microarchitecture in 2019, AMD opted to create distinct designs for its graphics microarchitecture: RDNA for gaming GPUs and CDNA for compute and HPC workloads.
- The unification into UDNA signifies a pivotal evolution in AMD’s approach to the GPU landscape, merging gaming and compute capabilities.
Link mentioned: AMD announces unified UDNA GPU architecture — bringing RDNA and CDNA together to take on Nvidia’s CUDA ecosystem: Two become one.
CUDA MODE ▷ #arm (1 messages):
ExecuTorchPyTorch
- ARM Work Progress in ExecuTorch: A member mentioned they have been working on ARM tasks specifically in ExecuTorch and PyTorch.
- Just dropping in to say hi indicates ongoing engagement with the community.
- Discussion on PyTorch Applications: The member’s involvement in PyTorch indicates a focus on applying the framework in practical scenarios related to ARM.
- They seem eager to share their insights, suggesting a collaborative spirit within the community.
CUDA MODE ▷ #liger-kernel (19 messages🔥):
Liger's Swiglu Kernels vs Together AI BenchmarksOptimizations in cuBLAS and PyTorch ImplementationsHandling of ignore_index in Cross EntropyConv2D Performance IssuesBenchmarking with Phi3 on A100
- Liger’s Swiglu Kernels outperform cuBLAS: A member claimed that their specialized kernel is 22-24% faster than common implementations using cuBLAS and PyTorch eager mode.
- They inquired how Together AI achieves significant speedups, sparking discussion on performance benchmarks.
- Addressing ignore_index concerns in Code: Concerns were raised about potential invalid memory access when
y_i == ignore_index, but it was clarified that the kernel handles this case without issues due to early returns.- An additional test case confirming the handling of
ignore_indexwas shared, demonstrating robust testing.
- An additional test case confirming the handling of
- Conv2D Performance Degradation: Issues were noted with Conv2D performance, which appears to degrade with an increase in input and output channels, despite performing similarly on smaller benchmarks.
- The discussion emphasized the need for improvements as the performance seems to diminish relative to Torch under certain conditions.
- Benchmarking Challenges with Phi3: A user reported difficulties in achieving expected token throughput on a single A100 40GB while using Flyte to orchestrate benchmarking.
- They referenced adapting an example provided in the repository and plan to explore multi-GPU distributed training.
- Next Steps for Performance Tuning: Members acknowledged certain inaccuracies in index handling during performance tuning discussions and mentioned ongoing investigations into pyproject.toml issues.
- A proposed fix was highlighted that could address packaging detection issues in nightly and main releases.
Links mentioned:
- Supercharging NVIDIA H200 and H100 GPU Cluster Performance With Together Kernel Collection: no description found
- Liger-Kernel/test/transformers/test_cross_entropy.py at 638b31057d283a0d841a1795f742068a63b7dcdd · linkedin/Liger-Kernel: Efficient Triton Kernels for LLM Training. Contribute to linkedin/Liger-Kernel development by creating an account on GitHub.
- (fix) fix pyproject.toml by wizyoung · Pull Request #226 · linkedin/Liger-Kernel: Summary In #218, I fixed the tool.setuptools.packages.find field and tested it only in editable mode with pip install -e .. However, in production mode with pip install ., only the env_report.py fi...
- Liger-Kernel/src/liger_kernel/ops/cross_entropy.py at 638b31057d283a0d841a1795f742068a63b7dcdd · linkedin/Liger-Kernel: Efficient Triton Kernels for LLM Training. Contribute to linkedin/Liger-Kernel development by creating an account on GitHub.
- GitHub - linkedin/Liger-Kernel at 638b31057d283a0d841a1795f742068a63b7dcdd: Efficient Triton Kernels for LLM Training. Contribute to linkedin/Liger-Kernel development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Benchmarking phi3 on single A100 40gb GPU: unable to reproduce benchmark results · Issue #236 · linkedin/Liger-Kernel: 🐛 Describe the bug I'm using flyte to reproduce the token throughput and memory savings results reported in this repo's README under slightly different conditions: using the microsoft/Phi-3-m...
- Liger-Kernel/examples/huggingface at main · linkedin/Liger-Kernel: Efficient Triton Kernels for LLM Training. Contribute to linkedin/Liger-Kernel development by creating an account on GitHub.
CUDA MODE ▷ #thunder (4 messages):
Thunder channel introductionTriton Matmul exampleFusing operationsLiger kernel application
- Introducing the Thunder Channel for Source-to-Source Compilation: The Thunder channel aims to compile vanilla PyTorch models into optimized Python functions, featuring contributions from members like <@790925083828682752>, <@222363567192670219>, and <@761222713611386900>.
- They invite others to try Thunder and provide feedback to improve its functionality.
- Exploring Triton Matmul Integration: A week ago, a session covering the Triton Matmul example showed how to integrate custom kernels into models using Thunder, featured in the YouTube video.
- The session emphasized practical applications over theory for understanding the integration process.
- Adding Fusing Operations to Thunder: This week, the Thunder team announced the addition of fusing operations to their compiler, shared in the latest session on YouTube.
- This advancement continues the discussion on enhancing efficiency in deep learning compilers.
- Next Steps: Applying Fusions to Liger Kernel: The team’s next goal is to apply the fusing technique to the liger kernel, demonstrating ongoing development in Thunder’s capabilities.
- This reflects a commitment to expanding Thunder’s functionality and performance.
Links mentioned:
- The Thunder Sessions | Session 6 | More Transforms, Less Theory: In today's session, Luca and Tom will focus on more Transforms, and less Theory!The Thunder Sessions is a chat about deep learning compilers and how the saus...
- The Thunder Sessions | Session 7 | Fusing Kernels with Thunder & Triton: The Thunder Sessions is a chat about deep learning compilers and how the sausage is made, with hosts Luca Antiga, CTO, and Thomas Viehmann, Principal Researc...
OpenAI ▷ #ai-discussions (112 messages🔥🔥):
Reflection Llama-3.1 updatesOpenAI model announcementsAI hardware requirementsLearning OpenAI APIPerformance of local models
- Reflection Llama-3.1’s performance update: The recently released Reflection Llama-3.1 70B is touted as the world’s top open-source LLM, utilizing a technique called Reflection-Tuning designed to enhance the model’s reasoning capabilities.
- Users noted that there were initial issues with the model that have since been addressed, urging testers to retry for better results.
- Clarifications on OpenAI’s model announcements: Discussions revealed skepticism about the terminology ‘GPT Next’, clarified by OpenAI as merely a figurative placeholder without concrete implications.
- Despite mixed opinions, some members expressed frustration about the lack of tangible updates from OpenAI amid the hype surrounding upcoming models.
- Hardware specifications for running models: To effectively run local models like Llama 3.1 70B, users require either a PC with a sufficient GPU or a Mac with Apple Silicon; 8GB of VRAM is mentioned as a minimum requirement for optimal performance.
- One user shared their experience running intensive models on a high-spec MacBook Pro, comparing it with setups lacking adequate resources, underscoring the importance of hardware.
- Learning OpenAI API and usage limits: A member faced error code 429 while trying to use the OpenAI API, inquiring about account limitations despite it being a new account.
- Others suggested purchasing credits or utilizing the model’s free usage options to mitigate issues and recommended starting with simpler models for ease of learning.
- Exploration of performance in local models: Users debated the feasibility of running large models on low-spec hardware, sharing anecdotes about poor performance on a low-end laptop with only 4GB RAM.
- It was concluded that while experimenting can be fun, high-performance models necessitate robust computing resources for practical usage.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Steven Heidel (@stevenheidel): something ever happens
- OpenAI clarifies: No, "GPT Next" isn't a new model.: Confusion from a presentation got OpenAI fans in a tizzy.
- Prompt Engineering Guide: A Comprehensive Overview of Prompt Engineering
- bartowski/Meta-Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct-GGUF · Hugging Face: no description found
- mattshumer/Reflection-Llama-3.1-70B · Hugging Face: no description found
- Tweet from Adam.GPT (@TheRealAdamG): Angel - if the fact that I was enjoying an inside joke with a coworker is that problematic that your basically telling me to shut up - that’s kind of unfair and I would suggest you should mute me for...
OpenAI ▷ #gpt-4-discussions (7 messages):
GPT handling booksVoice access rollout
- GPT’s Handling of Books as Knowledge Files: A member inquired about how well GPT manages entire books when uploaded as knowledge files, to which another member explained that GPT uses the files as references for searching specific information, rather than fully ‘knowing’ the content.
- This insight seemed to reassure the inquirer, who noted the usefulness of this feature and appreciated the explanation.
- Concerns Over Advanced Voice Access Rollout: A member questioned whether the rollout of advanced voice features was genuine or merely a tactic to delay access for users, sparking curiosity among others.
- This led to a few confirmations of similar frustrations from other users, with at least one member trying unsuccessfully to gain access.
OpenAI ▷ #prompt-engineering (30 messages🔥):
AI Reasoning BreakdownPrompt Engineering InsightsStock Market Prompt Use CasesDifferent Response StylesPrompt Library Channel Location
- AI Reasoning Breakdown is Interesting: Members discussed the appeal of asking AI to break down its reasoning for provided responses, inviting others to refresh queries for varied perspectives.
- One member compared this fluidity to a toddler trying to provide desirable answers, making it a playful observation.
- Using Prompts in Specific Styles for Better Outputs: One member suggested that preface prompts with styles like ‘In the writing style of Terry Pratchett’ could yield fantastic results.
- This approach indicates that adapting prompts can enhance creativity and engagement in AI responses.
- Concerns Over LLMs for Stock Analysis: A discussion arose regarding using LLMs to gauge interest in stock data, with opinions expressing limitations and inefficiencies in this approach.
- Members advised against relying solely on prompts for stock analysis, advocating traditional models for data assessment.
- ChatGPT’s Response to Prompt Engineering: Members shared that output templates are recommended for effective prompt engineering, hinting at structured approaches to improve interactions.
- A member also pointed out that continuous updates from live data enhance performance in tasks related to stock evaluations.
- Searching for the Prompt Library Channel: A query was raised regarding the location of the prompt library channel, highlighting the importance of easy access to resources.
- Another member responded promptly by directing the inquirer to the specific channel for assistance.
OpenAI ▷ #api-discussions (30 messages🔥):
AI reasoning breakdownResponse variation in AIAPI discussion and promptsStock history analysis with AIJudging interestingness with AI
- AI reasoning breakdown sparks interest: Members find it interesting when asking the AI to explain its reasoning behind responses, creating diverse insights based on repeated prompts.
- Madame_architect noted, *‘refresh the response a few times and see how many different ways it responds and different
- API discussion for better outcomes: Multiple users discussed the importance of using output templates and chunking tasks when interacting with the API to achieve better results.
- Darthgustav shared insights on prompt engineering, emphasizing that while they’re not an API expert, effective prompts facilitate stronger interactions.
- Stock analysis limitations in AI: Members cautioned against using OpenAI models to analyze stocks without comprehensive data, stressing the importance of live updates.
- Niko3757 explained the necessity of historical data and real-time updates for accurate assessments, suggesting downloadable stock histories from reliable sources.
- Exploring prompts for judging interest: A user sought use cases for creating prompts that evaluate the ‘interestingness’ of various input factors, aiming to leverage LLMs as judges.
- Sps0707 clarified their intent was not solely stock-related but focused on broader prompt applications for gauging interest.
- Conversational collaboration in AI discussions: Members engaged in a collaborative discussion, sharing tips and experimenting with prompts to achieve desired AI behavior.
- The tone remained light-hearted, with jokes and casual encouragement exchanged among participants.
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #general (80 messages🔥🔥):
Integrating C and MojoLLVM Developer Meeting InsightsSubprocess Implementation in MojoMojo Community Meeting TransitionHash Functions Presentation
- Integrating C with Mojo via DLHandle: Members discussed how to integrate C code with Mojo using
DLHandleto dynamically link to shared libraries, allowing for function calls between the two.- An example was provided where a function to check if a number is even was executed successfully after being loaded from a C library.
- Insights from the LLVM Developer Meeting: The upcoming Fall LLVM Developer Meeting in October will feature 5 talks by Modular on topics including Mojo and GPU programming.
- Attendees expressed excitement over expected discussions and shared that recorded sessions will be available on YouTube after the event.
- Desire for Subprocess Implementation in Mojo: A member shared interest in implementing Subprocess capabilities for the Mojo stdlib in the future, reflecting a desire to enhance the library.
- Members also discussed resource concerns when trying to set up development environments for Mojo, particularly on older hardware.
- Transition in Community Meeting Leadership: Tatiana announced the transition of the Mojo Community Meetings leadership to Caroline, thanking everyone for their participation and contributions thus far.
- The community meeting agenda included discussions on SIMD in complex algorithms and hash functions.
- Hash Functions Presentation by mzaks: A member shared a PDF of their presentation titled ‘Hash Functions and Where to Find Them’, linking to their GitHub repository with implemented functions in Mojo.
- This presentation was part of the community meeting, showcasing practical implementations and sharing resources for participants.
Links mentioned:
- no title found: no description found
- DLHandle | Modular Docs: Represents a dynamically linked library that can be loaded and unloaded.
- Join our Cloud HD Video Meeting: Zoom is the leader in modern enterprise video communications, with an easy, reliable cloud platform for video and audio conferencing, chat, and webinars across mobile, desktop, and room systems. Zoom ...
- LLVM: The official llvm.org YouTube channel. See LLVM Developers' Meetings videos and more!
- mojo-hash/HashFunctionsAndWhereToFindThem.pdf at main · mzaks/mojo-hash: A collection of hash functions implemented in Mojo - mzaks/mojo-hash
- [Public] Mojo Community Meeting: Mojo Community Meeting This doc link: https://modul.ar/community-meeting-doc This is a public document; everybody is welcome to view and comment / suggest. All meeting participants must adhere to th...
- Join our Cloud HD Video Meeting: Zoom is the leader in modern enterprise video communications, with an easy, reliable cloud platform for video and audio conferencing, chat, and webinars across mobile, desktop, and room systems. Zoom ...
- Announcing the 2024 LLVM Developers' Meeting Program: I’m pleased to announce the 2024 LLVM Developers’ Meeting program! As a quick reminder, Early Bird Registration is ending September 20th. This is also the registration deadline to guarantee a t-shirt...
- LLVM Developers' Meeting 2024: no description found
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #mojo (96 messages🔥🔥):
DType as Dict keyMultiple-precision integer arithmeticMojo hardware access driversVariant type usageCreating bindings for GStreamer
- DType cannot be used as Dict key: Discussion focused on why
DTypecannot serve as a key in a Dict, with DType.uint8 noted as a value rather than a type.- It was mentioned that changing the implementation might not be straightforward due to its relationship with SIMD types, which currently have specific constraints.
- Exploring Multiple-precision integer support in Mojo: Members discussed the potential for multiple-precision integer arithmetic packages in Mojo, referencing implementations similar to ones found in Rust.
- One participant shared a GitHub link showcasing their progress on a
uintpackage for multiple-precision arithmetic.
- One participant shared a GitHub link showcasing their progress on a
- Mojo’s capability for hardware access drivers: It was confirmed that Mojo can write userspace drivers, though it currently lacks support for low-level kernel development.
- The main goal is to replace components like CUDA, with a focus on userspace interactions rather than bare-metal programming.
- Using Variant type for multiple element types: The conversation highlighted using
Variantto create polymorphic lists containing different struct types in Mojo.- Examples demonstrated how members can utilize
Variantto store different elemental types, though storing instances of aTraitremains unsupported for now.
- Examples demonstrated how members can utilize
- Creating bindings in Mojo for GStreamer: A user inquired about creating bindings for GStreamer within Mojo, prompting discussion on available methodologies.
- It was suggested to use the FFI module
DLHandleor alternatively import through Python, although no specific GStreamer details were provided.
- It was suggested to use the FFI module
Links mentioned:
- variant | Modular Docs: Defines a Variant type.
- Freestanding and hosted implementations - cppreference.com: no description found
- IntLiteral | Modular Docs: This type represents a static integer literal value with infinite precision. They can't be materialized at runtime and must be lowered to other integer types (like Int), but allow for compile-ti...
- Mojo Lang - Tomorrow's High Performance Python? (with Chris Lattner): Mojo is the latest language from the creator of Swift and LLVM. It’s an attempt to take some of the best techniques from CPU/GPU-level programming and packag...
- Types | Modular Docs: Standard Mojo data types.
- [BUG] Can't use SIMD data types as keys for Dicts · Issue #3455 · modularml/mojo: Bug description Can't use SIMD data types (UInt8, Int16, etc.) as Dict keys despite that SIMD seems to fit KeyElement requirements. Steps to reproduce from collections import Dict var map1 = Dict[...
- r - Overview: r has 4 repositories available. Follow their code on GitHub.
- GitHub - zmalatrax/uint: Mojo `uint` package - Multiple-precision integer arithmetic: Mojo `uint` package - Multiple-precision integer arithmetic - GitHub - zmalatrax/uint: Mojo `uint` package - Multiple-precision integer arithmetic
- GitHub - recmo/uint: Rust Uint crate using const-generics: Rust Uint crate using const-generics. Contribute to recmo/uint development by creating an account on GitHub.
- mojo/stdlib/src/utils/variant.mojo at main · modularml/mojo: The Mojo Programming Language. Contribute to modularml/mojo development by creating an account on GitHub.
Eleuther ▷ #general (124 messages🔥🔥):
DeepMind's TransitionQuora Data ScrapingContinual In-Context LearningAdaptive TransformersAI Hackathons
- DeepMind Employees Share Insights: A former DeepMind employee indicated that the compute required for projects heavily depends on their product-focus, shedding light on current shifts in resource allocation post-genai pivot.
- This sparked discussions on how being in foundational research may lead to fewer resources as highlighted by community skepticism.
- Scraping Quora Data Challenges: Members discussed the potential inclusion of Quora’s data in AI training datasets, noting its valuable but often restricted content.
- Concerns were raised regarding Quora’s TOS, suggesting that scraping may not be viable due to stringent regulations.
- Discussing Adaptive Transformers Architecture: A detailed description of ‘Continual In-Context Learning with Adaptive Transformers’ was shared, focusing on how it enables transformers to adapt to new tasks using prior knowledge without modifying their parameters.
- This approach aims for high adaptability while minimizing the risk of catastrophic failure, attracting interest in its implications for various domains.
- AI Hackathon Curiosities: Several members reminisced about an AI hackathon organized by Eleuther AI, recalling its interesting participants and experiments.
- A specific mention was made of an RLHF hackathon, though the exact location was uncertain.
- Suggestions for AI Model Training: Users discussed model recommendations for moderation tasks in chatbots, with Mistral 7b and LLaMA-3.1-8b mentioned as potential starting points for further exploration.
- The community suggested utilizing a rejection dataset to enhance the moderation capabilities of chosen models.
Links mentioned:
- Simple and Effective Masked Diffusion Language Models: While diffusion models excel at generating high-quality images, prior work reports a significant performance gap between diffusion and autoregressive (AR) methods in language modeling. In this work, w...
- Language Modeling by Estimating the Ratios of the Data Distribution | Aaron Lou: no description found
Eleuther ▷ #research (20 messages🔥):
Cosine Similarity of GradientsLaplace Approximation in Bayesian Deep LearningWeight Decay and Orthogonal RegularizationPrior in Bayesian ApproachesTraining Dynamics and Phase Changes
- Cosine Similarity Indicates Gradient Patterns: Comparing the cosine similarities of gradients at steps N and N+1 reveals that gradients increasingly align over certain sequences in the training dataset, indicating a notable pattern.
- This suggests that the issue extends beyond just large magnitudes of gradients, as patterns may emerge leading to consistent directional shifts.
- Laplace Approximations Simplify Bayesian Analysis: Members discussed the use of the Laplace approximation in simplifying the analysis of ReLU networks by focusing on the Hessian of output layers.
- The conversation pointed to the challenges of tuning prior precision and balancing covariance scaling during implementations.
- Debating Weight Decay with Orthogonal Regularization: A member posed concerns regarding the use of weight decay alongside orthogonal regularization in projections, pondering potential issues like collapse due to conflicting forces.
- While weight decay could lead to desirable sparsification, its interaction with loss-based orthogonal regularization raises questions about stability.
- Importance of the Prior in Bayesian Models: The omission of the prior in Bayesian approaches was recognized to be significant, with discussions indicating that considering it can greatly impact model performance.
- A humorous comment highlighted the role of exponential distributions as a memoryless prior in these contexts.
- Radius Nearest Neighbor for Efficient Attention: A suggestion was made to implement radius nearest neighbor queries in attention mechanisms to potentially achieve asymptotically faster computations.
- This approach relies on the structural properties of latents, opening avenues for optimization in handling attention tasks.
Links mentioned:
- distily/distily_attn_mlp_sweep · Training metrics: no description found
- Theory, Analysis, and Best Practices for Sigmoid Self-Attention: Attention is a key part of the transformer architecture. It is a sequence-to-sequence mapping that transforms each sequence element into a weighted sum of values. The weights are typically obtained as...
- Being Bayesian, Even Just a Bit, Fixes Overconfidence in ReLU Networks: The point estimates of ReLU classification networks---arguably the most widely used neural network architecture---have been shown to yield arbitrarily high confidence far away from the training data. ...
- Laplace Redux -- Effortless Bayesian Deep Learning: Bayesian formulations of deep learning have been shown to have compelling theoretical properties and offer practical functional benefits, such as improved predictive uncertainty quantification and mod...
- Bayesian Low-rank Adaptation for Large Language Models: Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) has emerged as a new paradigm for cost-efficient fine-tuning of large language models (LLMs), with low-rank adaptation (LoRA) being a widely adopted choice....
Eleuther ▷ #scaling-laws (13 messages🔥):
Power Law Curves in MLSelf-Organized CriticalityScaling Laws in Statistical EstimationSandpile Avalanche ModelCritical Systems and Fluctuations
- Discussion on Power Law Curves: Members discussed why power law curves seem effective for modeling performance scaling in ML, including theories and frameworks. They referenced specific statistical models that relate to the scaling laws observed in statistical estimation tasks.
- A member suggested that scaling laws for LLM loss are similar to those in statistical estimation, noting that mean squared error in estimating means scales as N^(-1/2).
- Self-Organized Criticality Explained: The concept of self-organized criticality was introduced, asserting that many systems converge on a critical point exhibiting power-law fluctuations. This phenomenon is important for understanding the behavior of critical systems in various fields.
- One member highlighted that this concept originated with Per Bak, providing a link to Bak’s evolution model demonstrating the theory.
- Sandpile Model Demonstrates Criticality: A historical reference was made to an experiment by Bak, Tang, and Wiesenfeld studying avalanches in a sandpile model. They observed that the size distribution of avalanches followed a power law when the slope reached a critical angle, leading to convergence at that angle.
- It’s important to clarify that the experiment was a mathematical model rather than a physical setup, aiming to capture the dynamics of critical points.
- Skepticism Surrounding Power Law Evidence: Concerns were raised regarding the validity of claims about power law scaling, noting many simpler explanations might exist. Additionally, instances of only demonstrating a few orders of magnitude in log-log plots were pointed out as weak evidence for universal power laws.
- Members agreed that more orders of magnitude in scaling are necessary to convincingly demonstrate that a universal power law is in effect.
Link mentioned: Per Bak: How Nature Works: The Science of Self-Organised Criticality: no description found
Eleuther ▷ #interpretability-general (12 messages🔥):
Layer Responsibilities in ModelsGraph Cluster Detection ProbabilityResidual Stream DifferencesSAE Latent Activation VariationsCommunication Network Protection
- Consensus on Final Layer’s Functionality: There seems to be a consensus that final layers primarily focus on constructing the surface form of the output, akin to motor neurons according to one member.
- However, it was noted that this assumption has not been thoroughly validated, leaving room for uncertainty.
- Exploration of SAE Reconstructions: One member shared notable findings on their project where middle layer residual streams showed significantly lower SAE reconstruction loss compared to final layers.
- This suggests varying effectiveness in complexity acquisition across layers, particularly in the context of latent activation vectors.
- Detecting Clusters in High Dimensional Space: A member inquired about deriving detection probability for clusters in a graph, emphasizing the challenge given high dimensionality and sparsity.
- Responses highlighted the importance of model specifics relating to signal, noise, and the detection algorithm to accurately establish detection probabilities.
- Understanding Network Protection Strategies: In discussing communication network protection, one member described goals related to enhancing channel security through diversity of characteristics.
- They pointed out the relevance of their strategy’s modeling for obfuscation, with synthetic datasets being utilized to assess detection limits in a recent paper.
- Empirical Testing with Graph Neural Networks: Members noted that empirical testing on real or simulated data with known ground truth is a common approach for evaluating detection probability in cluster scenarios.
- The discussion reflects the interpretability aspects and the complexity involved in utilizing graph neural networks for network data modeling.
Links mentioned:
- Exploring Concept Depth: How Large Language Models Acquire Knowledge at Different Layers?: no description found
- google-research/graph_embedding/simulations/sbm_simulator.py at master · google-research/google-research: Google Research. Contribute to google-research/google-research development by creating an account on GitHub.
Eleuther ▷ #lm-thunderdome (5 messages):
Generate Until Tasks BugTurkishMMLU ReleaseCommunity Feedback on Changes
- Generate Until Tasks May Have Bug: A user inquired if omitting the ‘until’ parameter in generate until tasks would default to the model’s tokenizer EOS, but observed that it gets overridden by the fewshot delimiter.
- Another user confirmed that this seems to be unintended behavior and offered to fix it or allow others to do so.
- TurkishMMLU Released and Added to Repository: A member announced the release of TurkishMMLU and provided links to the dataset and the corresponding GitHub issue.
- This contribution aims to enhance language model evaluation in Turkish, detailed in a provided paper.
- Community Conversation on Feedback: A user prompted for further thoughts from Hailey regarding previous discussions on the forum.
- Hailey confirmed she had responded, indicating ongoing engagement with the community.
Links mentioned:
- lm-evaluation-harness/lm_eval/api/task.py at 543617fef9ba885e87f8db8930fbbff1d4e2ca49 · EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness: A framework for few-shot evaluation of language models. - EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness
- Added TurkishMMLU to LM Evaluation Harness by ArdaYueksel · Pull Request #2283 · EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness: In this pull request, I would like to add our work TurkishMMLU: Measuring Massive Multitask Language Understanding in Turkish to LM Evaluation Harness. You can find the details of our work in our r...
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #news (144 messages🔥🔥):
Reflection API issuesIncompetence in AI model releasesAutomated AI researchEvaluation of LLMsHugging Face community response
- Reflection API under scrutiny for low performance: The Reflection 70B model’s performance continues to be questioned, with indications that it might have been a LoRA trained on benchmark test sets, built on top of Llama 3.0. Multiple discussions indicated that earlier claims of top-tier performance were misleading and tied to flawed evaluation processes.
- Reports suggest that initial private API tests showed better results than the public version, which raised questions about the apparent discrepancies between various releases.
- Concerns voiced about AI model release practices: Commentators remarked on the incompetence of announcing significant model breakthroughs without robust validation, questioning how someone could attempt to mislead the community about AI capabilities. There were various mentions of internal failures and oversights attributed to inflated expectations and incomplete evaluation.
- Members expressed disbelief at methods employed in the release and stressed the need for rigorous standards in evaluating AI models before public claims are made.
- Hugging Face community responds with humor: In light of the Reflection API debacle, members of the Hugging Face community shared humorous takes on the situation, highlighting their platform’s reliability compared to the released models. Some HF employees joked about the ease of uploading large models, suggesting that frustrating experiences are not typical for their platform.
- The light-hearted criticism reflects a broader sentiment about community standards in AI model evaluation and releases.
- Novelty of LLM-generated research ideas: A new study claims that LLM-generated ideas are statistically more novel than those produced by expert human researchers, raising questions about the effectiveness of AI in creative fields. However, confounding factors like existing literature awareness among reviewers were considered when evaluating these claims.
- Concerns about limiting the research area to ‘prompting based’ fields suggest that findings may not reflect general applicability across other domains.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Matt Shumer (@mattshumer_): Quick update — we re-uploaded the weights but there’s still an issue. We just started training over again to eliminate any possible issue. Should be done soon. Really sorry about this. The amount of...
- Tweet from 𝞍 Shin Megami Boson 𝞍 (@shinboson): A story about fraud in the AI research community: On September 5th, Matt Shumer, CEO of OthersideAI, announces to the world that they've made a breakthrough, allowing them to train a mid-size mod...
- Tweet from Matt Shumer (@mattshumer_): Quick update — we re-uploaded the weights but there’s still an issue. We just started training over again to eliminate any possible issue. Should be done soon. Really sorry about this. The amount of...
- Tweet from Matt Shumer (@mattshumer_): @JacquesThibs We shouldn’t need to but we’ve tried literally everything and no matter what we do there are issues in the model on HF. Nowhere close to the perf we should be seeing/are seeing locally
- Tweet from CLS (@ChengleiSi): Automating AI research is exciting! But can LLMs actually produce novel, expert-level research ideas? After a year-long study, we obtained the first statistically significant conclusion: LLM-generate...
- Tweet from Matt Shumer (@mattshumer_): We’ve figured out the issue. The reflection weights on Hugging Face are actually a mix of a few different models — something got fucked up during the upload process. Will fix today. Quoting Matt Shu...
- Tweet from Riley Goodside (@goodside): @TheXeophon Agree — a more fair baseline for big multi-step prompt pipelines would be universal self-consistency scaled up to the same inference budget
- mattshumer/ref_70_e3 · Hugging Face: no description found
- Tweet from Teknium (e/λ) (@Teknium1): @terryyuezhuo Its pretty confusing lmao there's like single model parts uploaded disparately on the repo between random readme updates.. Not even in mergeland have I seen that
- Tweet from kalomaze (@kalomaze): 🤔
- Tweet from Xeophon (@TheXeophon): Papers which compare their sophisticated prompting setup against one run of a CoT prompt are fundamentally unserious. At least re-run the CoT prompt multiple times, you'd be surprised how effec...
- Tweet from Omar Sanseviero (@osanseviero): Here is a step-by-step guide on how to upload 70B+ models to Hugging Face Step 1. pip install huggingface_hub Step 2. huggingface-cli upload-large-folder <repo-id> <local-path> --repo-ty...
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- Tweet from Joseph (@RealJosephus): "Reflection API" is a sonnet 3.5 wrapper with prompt. And they are currently disguising it by filtering out the string 'claude'. https://www.reddit.com/r/LocalLLaMA/comments/1fc98fu/c...
- Tweet from Artificial Analysis (@ArtificialAnlys): Reflection 70B update: Quick note on timeline and outstanding questions from our perspective Timeline: - We tested the initial Reflection 70B release and saw worse performance than Llama 3.1 70B. - ...
- Tweet from Yuchen Jin (@Yuchenj_UW): Update on Reflection Llama 3.1 70B: @mattshumer_ and his team dropped the "new, working version of the Reflection Llama 3.1 70B model" on Huggingface, so we're now serving the new weights ...
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- The AI industry is obsessed with Chatbot Arena, but it might not be the best benchmark | TechCrunch: LMSYS' Chatbot Arena is perhaps the most popular AI benchmark today -- and an industry obsession. But it's far from a perfect measure.
- CONFIRMED: REFLECTION 70B'S OFFICIAL API IS SONNET 3.5: Posted in r/LocalLLaMA by u/TGSCrust • 1,043 points and 303 comments
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #ml-drama (3 messages):
GPT NextKDDI Summit Presentation
- OpenAI Clarifies GPT Next Confusion: Following a presentation by Tadao Nagasaki at the KDDI Summit, speculation arose around a new model termed GPT Next; however, an OpenAI spokesperson confirmed it was merely a figurative placeholder representing future evolution of models.
- The spokesperson emphasized that the graphical representation in the slide was illustrative, not a timeline of upcoming releases.
- Nagasaki Highlights AI Growth Potential: Nagasaki stated that the future AI model labeled ‘GPT Next’ is expected to evolve nearly 100 times based on past performance, highlighting the exponential growth of AI technology.
- He contrasted this with traditional software development, pointing out that AI technology grows exponentially, as reported by ITmedia.
Link mentioned: OpenAI clarifies: No, “GPT Next” isn’t a new model.: Confusion from a presentation got OpenAI fans in a tizzy.
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #random (12 messages🔥):
OpenAI team dynamicsGoogle's recent activitySystem prompts focus
- OpenAI’s Transition to Anthropic: Members discussed the surreal nature of OpenAI’s transition, especially mentioning co-founder John Schulman now at Anthropic.
- “How often can you write ‘XY from OpenAI (now at Anthropic)’?” was a light-hearted remark highlighting the change.
- Anthropic and OpenAI’s Community Vibes: There was a split in sentiments as one member described Anthropic as having good vibes, while OpenAI was seen as having mixed vibes.
- Concerns were raised about the time taken for adjustments within OpenAI’s framework, reflecting ongoing community sentiments.
- Debate on Model Specs and Prompts: A conversation emerged around the focus on system and dev prompts in the open, questioning if hierarchy is necessary for specifications.
- One member pondered the effectiveness of a spec without hierarchy, showcasing a discussion on prompt structures.
- Google’s Awakening Rumor Mill: A member noted that Google is waking up, hinting at potential emerging competition and exciting developments in the AI landscape.
- This statement garnered laughter, indicating an ongoing playful skepticism towards Google’s strategic moves.
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #posts (2 messages):
Internal bureaucracy at GoogleChallenges of scaling within large organizations
- Google’s Bureaucratic Burden: An ex-Googler expressed feeling overwhelmed by the massive bureaucracy at Google, citing too many internal stakeholders and processes.
- It’s a miracle anything ever gets shipped there as employees often find themselves too busy navigating internal forces to focus on the big picture.
- Navigating Internal Forces: The ex-Googler noted that being busy with internal processes leaves little room for long-term vision and innovation.
- The sentiment highlights the challenges faced by employees in large organizations, where internal politics can stifle productivity.
Latent Space ▷ #ai-general-chat (47 messages🔥):
AI Codex for CursorReflection APIApple Intelligence UpdatesGemini Enum ModePhotorealistic LoRA Model
- AI Codex Enhances Cursor’s Capabilities: The new AI Codex for @cursor_ai offers a self-improving system with features such as auto-saving insights and smart categorization.
- One user suggested that utilizing AI Codex for a month could reveal valuable learning outcomes.
- Reflection API Sparks Controversy: The newly identified Reflection API is reported to be a Sonnet 3.5 wrapper, purportedly filtering out references to Claude to disguise its nature according to multiple sources.
- Various evaluations found that this API may not perform as well as previously claimed, leading to discussions about the methodology behind such performance benchmarks.
- Apple Announces Significant AI Developments: During the latest Apple event, updates on Apple Intelligence hinted at noteworthy advancements, including a potentially improved Siri and an AI phone ahead of competitors.
- These developments have triggered excitement about the implications for AI deployments and prompted calls for insights from Apple engineers.
- Introducing Enum Mode in Gemini API: Logan K announced the release of a new Enum Mode in the Gemini API, which allows for selecting from pre-defined output options, enhancing structured output capabilities.
- This addition aims to streamline the decision-making process for developers using the Gemini framework.
- Innovative Photorealistic LoRA Model Emerges: A user highlighted an insane photorealistic LoRA that has generated interest within the Stable Diffusion community, showcasing its capabilities through various images.
- Discussion around the model’s performance and its unexpected inclusion of anime images has caught the community’s attention.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Artificial Analysis (@ArtificialAnlys): Reflection Llama 3.1 70B independent eval results: We have been unable to replicate the eval results claimed in our independent testing and are seeing worse performance than Meta’s Llama 3.1 70B, not ...
- Tweet from Ziad Beyens (@zbeyens): Introducing AI Codex: the self-improving system for @cursor_ai. ◆ http://codex.md: Error and learning repository. ◆ http://learn.md: Auto-save new insights. ◆ http://split-codex.md: Smart categorizat...
- Tweet from Joseph (@RealJosephus): "Reflection API" is a sonnet 3.5 wrapper with prompt. And they are currently disguising it by filtering out the string 'claude'. https://www.reddit.com/r/LocalLLaMA/comments/1fc98fu/c...
- Large Language Model Agents: no description found
- Tweet from clem 🤗 (@ClementDelangue): As we're seeing more and more everyday, evaluation is one of the most important steps - if not the most important one - in AI. Not only do we need to improve general benchmarking but we should als...
- Tweet from swyx 🇸🇬 (@swyx): wow. Apple might just have fixed Siri. and beat OpenAI to the first AI phone. and commoditized OpenAI with Google. and casually dropped a video understanding model. incredibly well executed. (se...
- no title found: no description found
- Tweet from swyx 🇸🇬 (@swyx): Diffusion transformers are awesome, but while we all wait for Sora, I like @toinfinityai's approach - severely constrain the usecase to just video sync (not just lip sync) - and go from there. B...
- Tweet from Logan Kilpatrick (@OfficialLoganK): We just shipped a new variant of Structured Outputs in the Gemini API called Enum Mode, which allows you to easily constrain the model to pick between pre-defined options 🚢
- dotai/codex/learn.md at main · udecode/dotai: Contribute to udecode/dotai development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Apple Event - September 9: Watch the special Apple Event to learn about the next generation of iPhone, Apple Watch, and AirPods, and so much more.To watch the event interpreted in Amer...
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- GitHub - huggingface/lighteval: LightEval is a lightweight LLM evaluation suite that Hugging Face has been using internally with the recently released LLM data processing library datatrove and LLM training library nanotron.: LightEval is a lightweight LLM evaluation suite that Hugging Face has been using internally with the recently released LLM data processing library datatrove and LLM training library nanotron. - hug...
Latent Space ▷ #ai-in-action-club (76 messages🔥🔥):
Open Source AI Code EditorsCollaboration ToolsError Handling in CodeFine Tuning with LorasZed VS Cursor
- Exploring Open Source AI Code Editors: Members discussed various open source AI code editors such as Melty and PearAI as alternatives to Cursor.
- One member suggested spending time on each tool to evaluate their features and usability.
- Handling Code Errors Efficiently: A member pointed out that handling non-happy-path scenarios in coding is what distinguishes engineering from simple prototyping.
- Another user noted that their happy path code only constitutes about 10% of their total code, highlighting the importance of error management.
- Zed Code Editor Trends: Discussion on the functionality of the Zed editor took place, with members appreciating its new Linux version but noting a lack of bitmap font support.
- Users shared enthusiasm about its potential for high-performance collaboration with AI and human coders.
- Aider’s Edge in Code Editing: Members highlighted the Aider tool for its effective code editing capabilities and presented leaderboards to evaluate various LLMs’ editing skills.
- It was mentioned that Claude 3.5 Sonnet is recognized as one of the best-performing models in code editing capabilities.
- Fine Tuning Using Loras: A user expressed interest in covering fine-tuning using Loras for quantization in upcoming discussions, indicating potential community learning.
- Another member queried whether the focus would be on image models or language models, indicating a divergence in application.
Links mentioned:
- Aider LLM Leaderboards: Quantitative benchmarks of LLM code editing skill.
- Zed - The editor for what's next: Zed is a high-performance, multiplayer code editor from the creators of Atom and Tree-sitter.
- GitHub - meltylabs/melty: Open source AI code editor. To download the packaged app:: Open source AI code editor. To download the packaged app: - meltylabs/melty
- GitHub - trypear/pearai-app: The Open Source AI-Powered Code Editor. A fork of VSCode and Continue.: The Open Source AI-Powered Code Editor. A fork of VSCode and Continue. - trypear/pearai-app
- go-go-labs/cmd/apps/catter at main · go-go-golems/go-go-labs: GO GO EXPERIMENTAL LAB. Contribute to go-go-golems/go-go-labs development by creating an account on GitHub.
- AI In Action: Weekly Jam Sessions: no description found
- GitHub - MikeBirdTech/ai-toolkit: A collection of community created AI tools to improve your life: A collection of community created AI tools to improve your life - MikeBirdTech/ai-toolkit
OpenInterpreter ▷ #general (38 messages🔥):
OpenInterpreter PerformanceAI Skills on OpenInterpreter01 iOS App FeaturesUsing OpenInterpreter with LLMsConnecting with Venture Capitalists
- OpenInterpreter struggles with resource management: Users reported that while the 01 app can quickly access and play audio files, its performance on Mac may falter, causing inconsistent results.
- A user mentioned they prefer using plain OI due to stability issues with 01 on their device.
- AI Skills development discussion: Questions arose about when skills will be available for standard OpenInterpreter instead of just the 01 app, highlighting a user preference for improved functionality.
- One user expressed frustration about the performance of the 01 app compared to plain OI.
- Exploring the 01 iOS App capabilities: The 01 iOS app is designed for seamless control of computers and smart homes via voice commands, boasting capabilities like file management and smart device integration.
- Users noted that the app is compatible with iPadOS, confirming accessibility across devices.
- Creating Custom LLMs with OpenInterpreter: Discussions focused on the potential of OpenInterpreter to communicate with LLMs and possibly create custom models, with encouragement for users to experiment with fine-tuning.
- A user was excited about the possibilities of using OpenInterpreter for their upcoming LLM workshop.
- Seeking Funding Guidance: A user inquired about reaching out to Venture Capitalists for their AI application, expressing willingness to sell for the right price.
- The community was engaged in guidance and connections related to funding opportunities.
Links mentioned:
- 01 Light: Control your computer and smart home with voice commands from anywhere. The 01 connects to a server on your home machine, enabling remote access to your files, apps, and IoT devices. Capabilities: ...
- 01 by @techfren | Suno: deep house atmospheric electronic song. Listen and make your own with Suno.
- Tweet from killian (@hellokillian): Open Interpreter’s Local III is out today. We are building computer-controlling agents that work offline. This is our biggest step forward. - interpreter --local sets up fast, local LLMs. - We are h...
- Ooh Despicable Me 4 GIF - Ooh Despicable me 4 Surprised - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- open-interpreter/interpreter/core/computer/skills/skills.py at dbc52593e608d3ce3d25a0eece4e84cf57bb7892 · OpenInterpreter/open-interpreter: A natural language interface for computers. Contribute to OpenInterpreter/open-interpreter development by creating an account on GitHub.
- from interpreter import AsyncInterpreterinterpreter = AsyncInterpreter()# - Pastebin.com: Pastebin.com is the number one paste tool since 2002. Pastebin is a website where you can store text online for a set period of time.
- import os - Pastebin.com: Pastebin.com is the number one paste tool since 2002. Pastebin is a website where you can store text online for a set period of time.
OpenInterpreter ▷ #O1 (54 messages🔥):
Torch installation issues01 Light discontinuationRefund process for 0101 app launch detailsUsing OpenInterpreter
- Struggles with Torch Installation: Many users encountered issues installing Torch 2.3.1 using Poetry, leading to RuntimeError stating there are no installation candidates. A user shared that switching Python versions and even updating their VS Code seemed to resolve it for them.
- Ohhhhh boy have I had that same problem described their journey of repeatedly attempting to fix the issue.
- Discontinuation of 01 Light: The 01 Light has been officially discontinued, and the team announced they will be refunding all hardware orders while launching a free 01 app. This decision aimed to enable the software team to focus on advancing their platform without compromising software capabilities.
- Users expressed disappointment about the discontinuation, especially those who had been eagerly waiting for their devices.
- Refund Process for 01 Hardware: Users inquired about the refund policy for the 01 Light with assurances that refunds are being processed by emailing [email protected]. Some users worried about receiving refunds if their purchases were made via gift cards.
- Mikebirdtech confirmed that refunds are available, stating, Now worries, you’ll get your money back.
- Launch of 01 App: The team announced the launch of a free 01 app, stating it retains all functionalities of the 01 Light. They encouraged users to try the app despite the discontinuation of the hardware device.
- Creative responses acknowledged that smartphones can perform similar functions, making the discontinuation less critical.
- Running OpenInterpreter on Different Platforms: Some users asked about running the app on iOS and Windows, indicating interest in cross-platform compatibility. Concerns were raised about issues related to Poetry configurations, especially when missing a
pyproject.tomlfile.- Users offered tips while grappling with the intricacies of managing virtual environments and running commands.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from killian (@hellokillian): Today we're discontinuing the 01 light, refunding everyone, and launching a free 01 app. We're also open-sourcing all our manufacturing materials + a major 01.1 update. Why? Focus. This soft...
- Open Interpreter - It should have been an app: Official changelog for the open-source Open Interpreter project.
OpenInterpreter ▷ #ai-content (5 messages):
Scriptomatic with open source modelsInstructor Python library
- Scriptomatic integrates with Open Source Models: A member reported successfully getting Scriptomatic to work with structured output from open source models, indicating that they will submit a PR soon.
- They expressed gratitude for the framework provided for Dspy and noted their process involved a lot of grepping and printing.
- Instructor Library Enhances LLM Outputs: A message shared a link to the Instructor library, which simplifies working with structured outputs from LLMs using a user-friendly API built on Pydantic.
- Instructor promises to streamline validation, retries, and streaming responses for users looking to improve their LLM workflows.
- YouTube Resource for Scriptomatic: A member posted a link to a YouTube video that worked for them in relation to the ongoing discussions about Scriptomatic.
- This resource seems to be aimed at helping others navigate the tools discussed in the channel.
Link mentioned: instructor: structured outputs for llm
LlamaIndex ▷ #blog (9 messages🔥):
Agentic System DeploymentRunning Reflection 70BAdvanced RAG PipelinesAutomating Financial AnalysisDynamic ETL for RAG
- Deploy Agentic System with llama-deploy: If you’re looking for an end-to-end example of deploying an agentic system as microservices, check out this full-stack example using @getreflex and LlamaIndex.
- It simplifies the process significantly and is perfect for developers who want to streamline their chatbot systems.
- Run Reflection 70B Effortlessly: You can now run Reflection 70B using Ollama directly from LlamaIndex if your laptop supports it, as mentioned here.
- This allows developers to experiment with this advanced model without needing extensive infrastructure.
- Build Advanced RAG Pipelines: A guide is available for building advanced agentic RAG pipelines using Amazon Bedrock that includes dynamic query routing and top-k vector search.
- This comprehensive tutorial covers everything needed to optimize RAG implementations.
- Automate Financial Analysis with Agentic Workflows: This blog post discusses how to build an agentic summarization system to automate quarterly and annual financial analysis, which can aggregate results effectively (read more).
- Such automation can greatly enhance efficiency in financial reporting and decision-making.
- Dynamic ETL with LLMs: Instead of fixed chunking, LLMs can automate the ETL processes in RAG environments with data-specific decisions, as demonstrated in this tutorial (link).
- This approach streamlines data extraction and filtering, adapting to the characteristics of different datasets.
LlamaIndex ▷ #general (51 messages🔥):
Cohere RerankerLlamaIndex Node PostprocessorsLlama Parse Service StatusLlamaIndex Structured OutputsUsing Llama 3 with LlamaIndex
- Using Cohere Reranker with Azure: A user inquired about utilizing the Cohere reranker as a node postprocessor in Azure AI studio, referencing potential issues with existing imports.
- Another member confirmed that Azure doesn’t currently have a dedicated rerank module, but mentioned that creating one is feasible as the base class is simple.
- Understanding LlamaIndex Workflows: A member asked about the differences between passing data through Context and setting instance properties in LlamaIndex workflows, seeking clarification on persistence across runs.
- It was explained that Context is not shared between nested workflows to promote modularity, whereas setting attributes on ‘self’ retains data across multiple runs.
- Llama Parse Service Status Update: Concerns were raised about the operational status of the Llama Parse service, prompting updates and current status indications from participants.
- As of the latest updates, the service appeared to be back online but still showed some degradation due to a backlog in processing.
- Structured Outputs Support in LlamaIndex: A user inquired if LlamaIndex supports structured outputs with OpenAI, which was confirmed to be supported with specific usage instructions provided.
- In addition, links to documentation were shared to illustrate how to implement structured prediction using LlamaIndex with OpenAI.
- Examples of Llama 3 Usage with LlamaIndex: A user sought examples of working with Llama 3 using LlamaIndex instead of OpenAI, reflecting a need for resources focused on this integration.
- One member directed them to relevant documentation that details how to set up and utilize Llama 3 with LlamaIndex effectively.
Links mentioned:
- Node Postprocessor - LlamaIndex: no description found
- Starter Tutorial (Local Models) - LlamaIndex: no description found
- Ollama - Llama 3.1 - LlamaIndex: no description found
- LlamaIndex Status: no description found
- Self-querying | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: Head to Integrations for documentation on vector stores with built-in support for self-querying.
- OpenAI - LlamaIndex: no description found
Torchtune ▷ #general (25 messages🔥):
Gemma model configurationSupport for gemma 2PR for torchtune adjustmentsTokenizer eos problem
- Gemma Model Configuration Updates: To configure a Gemma 9B model using Torchtune, a member suggested replacing the
modelentry in the config with specific parameters includingvocab_size,num_layers, and more.- This utilizes the underlying component builder for Gemma, aiming for versatility in model sizes based on values from the config.json.
- Support Challenges for Gemma 2: A discussion highlighted obstacles in supporting Gemma 2 in Torchtune primarily due to the logit-softcapping and bandwidth issues.
- It was noted that the enhancements in Gemma 2 architecture have not yet been requested, increasing the backlog of features to implement.
- PR Proposal for Torchtune Improvements: A member identified a potential bug in Torchtune regarding padding sequence behavior and proposed a PR to rectify it.
- They suggested modifying the flip method for clarity and aimed to ensure feature parity with torch pad_sequence.
- Clarification Needed on Dataset Return Types: Concerns were raised about the misleading return types in the ConcatDataset implementation in Torchtune, which might require defining a consistent type for all datasets.
- The discussion also mentioned that while Torchtune excludes support for negative indexing, the reasoning behind this decision was questioned.
- Tokenizer Eos Problem in Mistral & Gemma: A member offered to submit a PR to address the eos token issue but noted that the current Mistral and Gemma tokenizers lack the
add_eosoption.- This highlights a limitation in the tokenizer’s capabilities that could affect implementations relying on end-of-sequence tokens.
Links mentioned:
- pytorch/test/nn/test_packed_sequence.py at main · pytorch/pytorch: Tensors and Dynamic neural networks in Python with strong GPU acceleration - pytorch/pytorch
- GitHub - pytorch/torchtune: A Native-PyTorch Library for LLM Fine-tuning: A Native-PyTorch Library for LLM Fine-tuning. Contribute to pytorch/torchtune development by creating an account on GitHub.
- torchtune/torchtune/data/_collate.py at main · pytorch/torchtune: A Native-PyTorch Library for LLM Fine-tuning. Contribute to pytorch/torchtune development by creating an account on GitHub.
- torchtune/torchtune/datasets/_concat.py at main · pytorch/torchtune: A Native-PyTorch Library for LLM Fine-tuning. Contribute to pytorch/torchtune development by creating an account on GitHub.
Torchtune ▷ #dev (32 messages🔥):
Compiling Generation MethodsCache Handling During GenerationHandling Non-Contiguous InputsTensor.is_inference() Method ProposalProposed Implementation of Chunked Linear + CE
- Compiling Generation Methods for Speed: The user aims to utilize
torch.compileforgenerate_next_tokento enhance generation speeds, akin to their previous successes with the PPO loss step.- However, they report no expected speedups, possibly due to issues like activation checkpointing and non-contiguous inputs.
- Cache Handling During Generation Discussion: Discussion revolves around the need for consecutive forward calls in attention modules to behave differently based on cache status during generation.
- They propose using
torch.inference_modebut acknowledge that passing an explicit flag to.forward()might be the better approach.
- They propose using
- Proposing Tensor.is_inference() Method: The user proposes implementing a
Tensor.is_inference()method to better manage caching behavior across multiple forward calls.- Despite interest, they are concerned about the challenges of integrating this change into existing maintainers’ workflows.
- Implementation Concerns Regarding Attributes: There’s a suggestion to add a toggle attribute to the model for checking caching behavior without modifying the
.forward()signature.- Concerns were raised about potential issues with
torch.compilewhen mutating non-Tensor module attributes.
- Concerns were raised about potential issues with
- Clean Implementation of Chunked Linear + CE: A member referenced a clean implementation of chunked linear combined with cross-entropy from a GitHub gist as a point of interest.
- They noted that integrating a similar approach into torchtune may prove difficult due to its separation of the LM-head and the loss calculation.
Links mentioned:
- chunked_lce.py: chunked_lce.py. GitHub Gist: instantly share code, notes, and snippets.
- [dynamo] Add support for tensor's is_complex method by YangQun1 · Pull Request #124927 · pytorch/pytorch: This PR is to add support for tensor's is_complex method in dynamo. Take the following code as an example: def test_tensor_is_complex(x): if x.is_complex(): return x + 1...
LangChain AI ▷ #general (41 messages🔥):
Decoding .astream_events()Gradio Upload LimitationsLangChain Azure IntegrationData Set Creation StrategiesAudio Transcription with Claude
- Frustrations with Decoding .astream_events(): Users are encountering challenges decoding streams from .astream_events(), with one mentioning that manual serialization through all branches and event types is tedious.
- A participant inquired about finding a reference implementation, highlighting the lack of good resources on the topic.
- Gradio Concurrency Issues: A user noted that after launching Gradio with 10 tabs open, only 6 requests began generating, indicating limits despite setting a higher concurrency limit.
- Despite high token rates, it seems the hardware is not handling more than 6 concurrent requests, signaling a potential configuration or limitation issue.
- Troubleshooting Azure OpenAI Integration: A user reported facing a 500 error when trying to interact with Azure OpenAI, seeking advice on parameters and possible endpoint issues.
- Another member pointed out that validating environment variables and naming conventions, especially around endpoints, could resolve the issues.
- Creating Datasets from Diverse Documents: A user asked whether to build individual datasets for different sets of documents or save input text alongside the corresponding documents in one dataset.
- This highlights a common dilemma in dataset creation regarding efficiency and organization.
- Exploring Audio Processing Capabilities of Claude: Discussion around whether it’s possible to pass audio data to Claude’s 3.5 LLM using Langchain for transcription purposes sparked some interest.
- Participants noted that while Claude supports image input, there was uncertainty about audio functionality.
LangChain AI ▷ #share-your-work (9 messages🔥):
VAKX platformSelenium and GPT-4 vision integrationAI Reddit Manager toolMocking LLM embedderRAG chatbot using OpenAI and LangChain
- VAKX: Your No-Code Assistant Builder: A member introduced VAKX, a no-code LLM orchestration platform that enables users to build AI assistants quickly. They invited feedback and provided links to explore the platform further: VAKX and Start Building for Free.
- They highlighted features like VAKChat integration for adding AI-powered chat to sites and outlined simple setup steps to engage users.
- Selenium Meets GPT-4 Vision: A member shared their experimental project integrating Selenium and the GPT-4 vision model, detailing the integration process in this YouTube video. They also provided a link to their GitHub repository containing the code: GitHub Repository.
- Discussion ensued about the purpose of this integration, focusing on benefits for integration testing with vector databases instead of using live embedding models.
- Create Posts with AI Reddit Manager: A member showcased their AI Reddit Manager that autonomously curates and posts content to subreddits using the Lyzr Agent API and Streamlit. They aimed to save time by generating posts based on specific topics, although their linked Medium article is currently a broken link.
- They provided a YouTube link to demonstrate their tool’s functionality: YouTube Video.
- Guide on Mocking LLM Embedder: A member wrote a guide on how to mock an LLM embedder for integration testing with MongoDB Atlas, available here. They spoke about the challenges faced when using live embedding models during integration.
- Discussion included clarifying that the goal of this work is integration testing rather than focusing on the embedding model itself, facilitating integration with LangChainGo.
- RAG Chatbot Embracing OpenAI and LangChain: A member introduced their RAG chatbot utilizing OpenAI and LangChain, available for users at AdaletGPT. They encouraged members to reach out for assistance as needed.
- This chatbot represents an application of recent AI advancements for engaging conversation and interaction.
Links mentioned:
- no title found: no description found
- no title found: no description found
- Integrating Selenium and gpt-4 vision: In this recording I show a use case where I integrated GPT4 vision model with selenium.code:https://github.com/rajib76/browser_agent
- no title found: no description found
- VAKX | Empower Your Documentation with AI-Powered Assistance: no description found
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) ▷ #general (33 messages🔥):
Overfitting in ModelsBenchmark LimitationsScam in AI ToolRAG APIs
- Overfitting Throughout Training: Concerns were raised about overfitting by a member, highlighting that benchmarks can be misleading and that models will get overfitted regardless of their size.
- “I don’t believe benchmarks anymore” reflects skepticism about the reliability of models evaluated on insufficient data.
- Benchmark Limitations Acknowledged: One member shared insights on benchmark limitations, noting that while benchmarks are often flawed, they remain one of the few comparison tools available.
- They expressed hope for their article on benchmark issues to be accepted at NeurIPS, exposing the challenges in current evaluation methods.
- New AI Tool Turns Out to Be a Scam: A member revealed that a hyped AI tool was a scam, misrepresenting itself with a private model claiming comparison to Claude 3.5 or GPT-4.
- Concerns were echoed about the distraction caused by such scams, with a member noting the time loss and discussions around it proliferating across platforms.
- Exploration of RAG APIs: A member inquired about experience with RAG APIs, expressing urgency for a project needing support as their own model is not yet ready.
- They sought alternatives to avoid the costs associated with 24/7 hosting, highlighting the practical challenges of managing AI projects.
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) ▷ #general-help (2 messages):
H100 loading support8-bit model loading
- Question on H100’s 8-bit support: A member inquired about why H100 does not support loading models in 8-bit format.
- They asked if anyone had information regarding this limitation.
- Seeking Answers on H100 Limitations: The same member expressed urgency in wanting to know if there are known reasons for the H100’s lack of 8-bit model loading support.
- They reiterated the request for insights or explanations from the community.
LAION ▷ #general (21 messages🔥):
Factory Network x Tech: Berlin AI HackathonFinegrain Object CutterConcrete ML and Homomorphic EncryptionOpen Source AI Event by GitHub
- Join the Factory Network x Tech: Berlin AI Hackathon: The Factory Network x Tech: Berlin AI Hackathon is set for September 28-29 at Factory Berlin Mitte, catering to 50-100 ambitious builders eager to innovate with AI.
- Participants can enhance products or launch new ideas in a collaborative environment focused on AI-driven innovations.
- Finegrain Releases Open-Source Image Segmentation Model: A new image segmentation model by Finegrain outperforms closed-source APIs and is available as open-source under the MIT License on Hugging Face.
- They are working on adding a subtler prompting method to enhance disambiguation beyond basic bounding boxes.
- Exploring Concrete ML for Encrypted Models: Discussion around Concrete ML revealed it requires Quantization Aware Training (QAT) for proper functioning with homomorphic encryption, raising concerns about performance overhead.
- Members shared skepticism over the documentation mainly focusing on smaller models, implying challenges in scaling to larger networks.
- GitHub to Host Open Source AI Panel: An Open Source AI panel hosted by GitHub is scheduled for September 19 in SF, featuring panelists from various AI organizations like Ollama and Nous Research.
- The event is free but requires registration, as capacity is limited and approval is needed.
Links mentioned:
- Finegrain Object Cutter - a Hugging Face Space by finegrain: no description found
- Factory Network x {Tech: Berlin} AI Hackathon · Luma: Are you ready to transform your AI ideas into reality? Join us at the Factory Network x {Tech: Berlin} AI Hackathon, an exclusive event designed for ambitious…
- GitHub Presents: Open Source AI - Access, Democratization, and Responsibility · Luma: AI is rapidly transforming industries from software development, content creation, agentic workflows and beyond. Central to this transformation is open source…
- GitHub - zama-ai/concrete-ml: Concrete ML: Privacy Preserving ML framework using Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE), built on top of Concrete, with bindings to traditional ML frameworks.: Concrete ML: Privacy Preserving ML framework using Fully Homomorphic Encryption (FHE), built on top of Concrete, with bindings to traditional ML frameworks. - zama-ai/concrete-ml
LAION ▷ #research (9 messages🔥):
Multimodality in LLMsReflection-70B Performance ClaimsAI Scams and FraudTool Augmented Generation
- Multimodality Gains Attention: A member highlighted the growing interest in multimodality with examples like Meta AI transfusion and DeepMind RT-2 for their significant contributions.
- They suggested an exploration of tool augmented generation involving RAG, API calls, web search, and Python interpreters as well.
- Reflection-70B Overhyped: Claims regarding Reflection-70B and its tuning were described as overstated, with performance aligning more closely to Llama 3 70B and Qwen 2 72B according to preliminary tests.
- Concerns were raised over its reliance on standardized benchmarks, asserting it reflects generalization and reasoning deficits in state-of-the-art (SOTA) models, as discussed in this paper.
- Discussion on AI Scams: Members expressed disappointment over the emergence of scammers in the AI/LLM space, with historical references to figures like Siraj Raval as early examples.
- The issue of deceptive practices was reinforced by one member’s comment about cryptobros invading the space.
- Suspicion Over OthersideAI Claims: A story circulated about Matt Shumer, CEO of OthersideAI, claiming to have achieved a breakthrough with mid-size models but was reported to be false.
- The community was urged to critically evaluate bold claims in AI, noting that if it sounds too good to be true, it probably is.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Jenia Jitsev 🏳️🌈 🇺🇦 (@JJitsev): (Yet) another tale of Rise and Fall: Reflection-70B release claims strong frontiers LLM performance - relying on common benchmarks like MMLU. Can it handle AIW problems, which reveal generalizati...
- Tweet from 𝞍 Shin Megami Boson 𝞍 (@shinboson): A story about fraud in the AI research community: On September 5th, Matt Shumer, CEO of OthersideAI, announces to the world that they've made a breakthrough, allowing them to train a mid-size mod...
LAION ▷ #paper-discussion (1 messages):
erkinalp: https://arxiv.org/abs/2408.06292
DSPy ▷ #show-and-tell (2 messages):
LanceDB IntegrationPull Request for dspyGitHub Review Process
- LanceDB Integration PR Submitted: A member raised a PR for LanceDB Integration to add it as a retriever for handling large datasets in the project.
- They requested feedback and changes from a specific user for the review process on this integration.
- Call for PR Review: The same member tagged another user to prompt a review of the submitted PR, emphasizing the need for any required changes.
- This highlights the collaborative nature of the project and the importance of peer review in enhancements.
Link mentioned: Lancedb Integration by PrashantDixit0 · Pull Request #1444 · stanfordnlp/dspy: This PR adds LanceDB as a retriever to handle large datasets.
DSPy ▷ #general (26 messages🔥):
Deprecation of GPT-3.5MIPROv2 ErrorFinetuning LLMsCookLangFormatter IssuesRetrieval Models in DSPy
- Mixed feelings on GPT-3.5 deprecation: Members are discussing varying user experiences with models following the deprecation of GPT-3.5, noting inconsistent performance especially with open models like 4o-mini.
- One user suggested using top closed models as teachers for lower ones to improve consistency.
- Encountering ‘NoneType’ Error in MIPROv2: A user reported encountering an
AttributeErrorwhile using MIPROv2, indicating that a potential issue arises within theGenerateModuleInstructionfunction.- Another member suggested that the problem might lie within the CookLangFormatter code, leading to a discussion on possible fixes.
- Finetuning small LLMs with unique datasets: A member shared their success in finetuning a small LLM using a special reflection dataset, available for interaction on Hugging Face.
- They were asked about the dataset used and provided a link while encouraging others to explore their findings.
- Exploring issues with CookLangFormatter: Members discussed potential issues in the CookLangFormatter class, narrowing down the source of errors stemming from its method signatures.
- After some modifications were made, one user reported a positive outcome, suggesting the necessity of logging the issue on GitHub for future reference.
- Inquiring about colpali as a retrieval model: A user raised the question of whether anyone had experimented with colpali as a retrieval model within a DSPy module.
- This inquiry reflects ongoing explorations into optimizing retrieval methods within the DSPy framework.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from fullstack (@DavidFSWD): It works! HF spaces to show proof of concept <Reflection></> tags LLM base finetune of Gemma 2 2.8B finetuned on -> _Maheswar's_ <- reflection dataset trained in two minutes...
- forcemultiplier/fmx-reflective-2b · Hugging Face: no description found
- mahiatlinux (Maheswar KK): no description found
- GitHub - SylphAI-Inc/AdalFlow: AdalFlow: The “PyTorch” library to auto-optimize any LLM tasks.: AdalFlow: The “PyTorch” library to auto-optimize any LLM tasks. - SylphAI-Inc/AdalFlow
tinygrad (George Hotz) ▷ #general (6 messages):
WebGPU PR #6304WGPU buffer limit increaseDependency issues with Rubicon ObjCTime zone change announcement
- WebGPU PR #6304 is a promising start: A member highlighted the importance of bring back webgpu by geohot as a good initiative that works on Asahi Linux.
- Notably, there’s a $300 bounty for this pull request, indicating its significance in the community.
- WGPU gains a buffer limit boost: A new flag in wgpu allows for an increase in the buffer limit per kernel, enabling it to match Metal’s 32.
- This change could enhance performance and compatibility for developers working within this ecosystem.
- Challenges with ObjC in WGPU: One member expressed frustration that using wgpu as a dependency leads to reliance on rubicon_objc, particularly on macOS.
- This sentiment resonated with others who share similar grievances toward ObjC’s complexities.
- Change in meeting schedule: A member announced there will be no meeting today due to a scheduling shift to Hong Kong time.
- This adjustment indicates the group’s ongoing effort to maintain effective communication across time zones.
Link mentioned: bring back webgpu [run_process_replay] by geohot · Pull Request #6304 · tinygrad/tinygrad: This works on Asahi Linux!
tinygrad (George Hotz) ▷ #learn-tinygrad (17 messages🔥):
Multi-GPU Tensor IssuesPTX Compilation Time for TinygradGGUF PRs StatusConst with dtype ucharModel Performance with Sharding
- Multi-GPU Tensor Issues haunt developers: Members expressed frustrations with errors related to multi-GPU tensor operations, including an
AssertionErrorindicating all buffers must have the same device.- A user stated, ‘I’ve spent enough time… convinced this goal is orthogonal to how tinygrad currently handles multi-gpu tensors.’
- Long PTX Compilation Times for MLPerf BERT: A user with H100 and H200 SXM GPUs inquired about expected PTX compile times for running tinygrad MLPerf BERT, which seems lengthy.
- Another member estimated, ‘probably something like 30min on tinybox?’, indicating that compile times can be substantial.
- GGUF PRs Lack Merges and Roadmap Clarity: There is concern among members regarding the status of various GGUF PRs, which appear stuck and the associated bounty has disappeared.
- One user asked if there is a roadmap for GGUF, highlighting the need for clarity on the project’s direction.
- Question on Const with Dtype uchar: A user questioned whether a constant with dtype uchar could accept
-1as an argument, indicating potential type limitations.- Another member speculated, ‘self.arg is never interpreted as a uchar -1…’, suggesting subtleties regarding variable interpretation.
- Model Sharding Challenges: Discussions arose around issues related to sharding models across multiple devices, where a specific model setup worked on a single GPU but failed when distributed.
- A user noted that ‘George gave pushback on my workaround…’, indicating ongoing collaborative troubleshooting.
Link mentioned: tinygrad/examples/mlperf/training_submission_v4.1/tinycorp/benchmarks/bert/implementations/tinybox_green/run_and_time.sh at 22e33795785f6c72449480e380ffdc213b5c7bbc · tinygrad/tinygrad: You like pytorch? You like micrograd? You love tinygrad! ❤️ - tinygrad/tinygrad
Gorilla LLM (Berkeley Function Calling) ▷ #leaderboard (10 messages🔥):
xLAM System Prompt DifferencesFunction Calling Documentation for LLaMAMerge Conflicts in GitHub Pull RequestsModel Evaluation with VLLMHammer-7b Handler Pull Request
- xLAM System Prompt Divergence Explained: Members discussed the distinct system prompt used for xLAM compared to other OSS models, noting it is documented in their Hugging Face model card.
- The conversation emphasized that models use personalized prompts when well-documented, deviating from the BFCL default if such information is available.
- LLaMA Lacks Function Calling Documentation: There was recognition that the LLaMA model does not provide documentation on function calling, which was questioned by members amid discussions on prompt formats.
- It was clarified that LLaMA is categorized as a prompt model, while the disparity in handling function calling may stem from its documentation approach.
- Resolving GitHub Pull Request Conflicts: A member noted that their pull request, #625, faced merge conflicts preventing successful merging.
- After addressing the conflicts, they resubmitted a new pull request, #627, to facilitate integration of their contributions.
- Evaluating Models Using VLLM: One user inquired about evaluating their own model after setting up the service with VLLM.
- The conversation reflects a wider interest in model assessment techniques and best practices within the community.
- Introduction of Hammer-7b Handler: The community discussed the introduction of the Hammer-7b handler in the context of the pull request, highlighting new features and performance metrics.
- Documentation includes a detailed CSV table overview of the model’s accuracy and execution summaries.
Links mentioned:
- Trelis/Meta-Llama-3-70B-Instruct-function-calling · Hugging Face: no description found
- Salesforce/xLAM-7b-fc-r · Hugging Face: no description found
- [BFCL] add MadeAgents/Hammer-7b handler by linqq9 · Pull Request #625 · ShishirPatil/gorilla: This PR add MadeAgents/Hammer-7b. Here's the CSV table converted to markdown format: Overall Acc Model AST Summary Exec Summary Simple AST Multiple AST Parallel AST Parallel Multiple AST...
- [BFCL] add MadeAgents/Hammer-7b handler by linqq9 · Pull Request #627 · ShishirPatil/gorilla: This PR add MadeAgents/Hammer-7b. Here's the CSV table converted to markdown format: Overall Acc Model AST Summary Exec Summary Simple AST Multiple AST Parallel AST Parallel Multiple AST...
LLM Finetuning (Hamel + Dan) ▷ #general (2 messages):
4090 GPU capabilitiesHybrid search with MilvusEmbedding modelsReranking metadata
- 4090 GPU can handle larger models: With a 4090 GPU, you should be able to run a larger embedding model concurrently with Llama-8b, and it’s suggested to consider the 3.1 version as well.
- This opens up possibilities for enhanced model performance and efficiency in processing tasks.
- Utilize Hybrid Search with Milvus: The discussion pointed to using hybrid search with BGE and BM25 on Milvus, supported by an example from the GitHub repository.
- The example illustrates how to incorporate sparse and dense hybrid search efficiently.
- Reranking with Metadata: If you have metadata for each chunk, implementing a reranker will effectively help sort and filter results further.
- This strategy aims to refine data handling, increasing the relevance of retrieved information.
Link mentioned: pymilvus/examples/hello_hybrid_sparse_dense.py at master · milvus-io/pymilvus: Python SDK for Milvus. Contribute to milvus-io/pymilvus development by creating an account on GitHub.
Alignment Lab AI ▷ #general (1 messages):
RAG based retrievalEvaluation metrics for RAGComparative analysis of RAG vs other LLMs
- Understanding RAG based retrieval evaluation: A member inquired about the necessary evaluation metrics for assessing a RAG based retrieval system in a domain-specific context.
- They expressed their uncertainty on whether to compare their RAG approach to other LLMs or evaluate it against results without using RAG.
- Comparison Strategies for RAG: The same member pondered whether to conduct comparisons exclusively with and without RAG or also against other large language models.
- This question sparked interest, as members considered various approaches to evaluating the effectiveness of RAG in their projects.
MLOps @Chipro ▷ #events (1 messages):
Open Source AIGitHub Panel EventPanelists
- GitHub Hosts Open Source AI Panel: GitHub is hosting a free Open Source AI panel next Thursday (9/19) at their office in San Francisco, inviting all to register and join.
- Panelists include representatives from Ollama, Nous Research, Black Forest Labs, and Unsloth AI, exploring access, democratization, and the impact of open source on AI.
- Registration Approval Required: Attendees must register for the event, with their registration subject to approval by the host.
- This requirement aims to manage attendance effectively as the event gains interest in the AI community.
Link mentioned: GitHub Presents: Open Source AI - Access, Democratization, and Responsibility · Luma: AI is rapidly transforming industries from software development, content creation, agentic workflows and beyond. Central to this transformation is open source…
{% else %}
The full channel by channel breakdowns have been truncated for email.
If you want the full breakdown, please visit the web version of this email: [{{ email.subject }}]({{ email_url }})!
If you enjoyed AInews, please share with a friend! Thanks in advance!
{% endif %}
