AI News for 7/24/2024-7/25/2024. We checked 7 subreddits, 384 Twitters and 30 Discords (474 channels, and 4280 messages) for you. Estimated reading time saved (at 200wpm): 467 minutes. You can now tag @smol_ai for AINews discussions!
It’s been a good month for neurosymbolic AI. As humans gather for the 2024 Summer Olympics, AI has been making great advances in Math Olympics. Early this month, Numina won the first AIMO Progress Prize, solving 29/50 private set problems of olympiad math level.
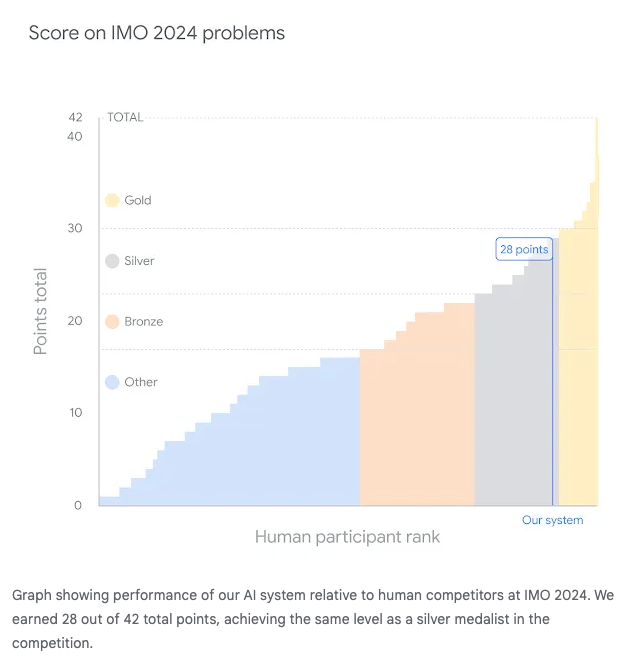
While 6 teenagers on team USA won the 65th International Math Olympiad, taking back China’s crown, Google DeepMind announced that their new combination of AlphaProof and a new V2 of AlphaGeometry solved four out of six problems from the IMO (including solving Problem 4 in 19 seconds), with human judges (including the IMO Problem Selection Committee Chair) awarding it 28 points out of a maximum 42, 1 point short of the cutoff for a Gold.
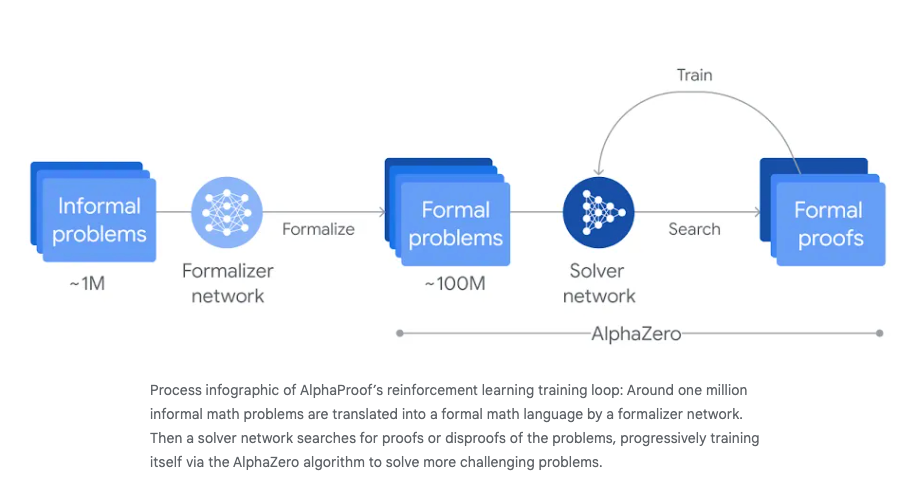
AlphaProof is a finetuned Gemini model combined with AlphaZero (paper) that proves mathematical statements in Lean, and uses an AlphaZero style aporoach to find solutions:
AlphaGeometry 2 is a neuro-symbolic hybrid system in which the language model was based on Gemini and trained from scratch on an order of magnitude more synthetic data than its predecessor. [It] employs a symbolic engine that is two orders of magnitude faster than its predecessor. When presented with a new problem, a novel knowledge-sharing mechanism is used to enable advanced combinations of different search trees to tackle more complex problems. Before this year’s competition, AlphaGeometry 2 could solve 83% of all historical IMO geometry problems from the past 25 years, compared to the 53% rate achieved by its predecessor.
However it’s not all roses: Tim Gowers, one of the human IMO judges, noted:
The main qualification is that the program needed a lot longer than the human competitors — for some of the problems over 60 hours — and of course much faster processing speed than the poor old human brain. If the human competitors had been allowed that sort of time per problem they would undoubtedly have scored higher.
This is also similar to 2022 OpenAI work on Lean provers.
How can AI solve both AIMO problems and fail to solve 9.11 > 9.9? There are a couple thoughts on “Jagged Intelligence” that fall to the everpresent problem of generalization.
Nevertheless it’s been a big day for prediction markets and private bets on AI in the IMO.
{% if medium == ‘web’ %}
Table of Contents
[TOC]
{% else %}
The Table of Contents and Channel Summaries have been moved to the web version of this email: [{{ email.subject }}]({{ email_url }})!
{% endif %}
AI Twitter Recap
all recaps done by Claude 3.5 Sonnet, best of 4 runs.
Llama 3.1 and Mistral Large 2 Release
-
Model Specifications: @GuillaumeLample announced Meta’s Llama 3.1 with a 405B parameter model and Mistral AI’s Large 2 with 123B parameters, both featuring 128k context windows. Llama 3.1 also includes smaller 8B and 70B versions.
-
Performance Comparisons: @GuillaumeLample shared that Mistral Large 2 outperforms Llama 3.1 405B on coding tasks like HumanEval and MultiPL-E, while Llama 3.1 405B shows superior performance in math.
-
Multilingual Capabilities: @GuillaumeLample highlighted Mistral Large 2’s strong performance on Multilingual MMLU, significantly surpassing Llama 3.1 70B base.
-
Licensing and Availability: @osanseviero noted Llama 3.1’s more permissive license allowing training on outputs. Mistral Large 2 is available under a research license for non-commercial use, as mentioned by @GuillaumeLample.
-
Deployment Options: @abacaj shared that Llama 3.1 is accessible through Together API and Fireworks. Mistral Large 2 can be tested for free on Le Chat, according to @GuillaumeLample.
Open Source AI and Industry Impact
-
Ecosystem Growth: @ClementDelangue emphasized the rapid progress of open-source AI, with models now rivaling closed-source alternatives in performance.
-
Computational Requirements: @HamelHusain mentioned that running Llama 3.1 405B locally requires significant hardware, such as 8xH100 GPUs.
AI Development and Research
-
Training Innovations: @GuillaumeLample revealed that Llama 3.1 utilized a large amount of synthetic data in its training process.
-
Evaluation Challenges: @maximelabonne discussed the need for standardized benchmarks and highlighted limitations in current evaluation methods.
-
Emerging Research Areas: @LangChainAI and @llama_index shared ongoing work in few-shot prompting and structured extraction respectively.
Industry Trends and Observations
-
Model Lifecycle: @far__el coined the term “Intelligence Destruction Cycle” to describe the rapid obsolescence of AI models.
-
Implementation Challenges: @nptacek highlighted the complexities of deploying AI systems in production environments beyond model capabilities.
-
Ethical Considerations: @ylecun contributed to ongoing discussions about AI safety and societal impact of large language models.
AI Reddit Recap
/r/LocalLlama Recap
Theme 1. Open Source AI Models Challenging Closed Platforms
-
Anthropic Claude could block you whenever they want. (Score: 84, Comments: 44): Anthropic’s Claude AI has reportedly blocked a user without apparent cause, highlighting the potential for arbitrary account restrictions under their terms of service. In response, the user is switching to Meta’s open-source Llama 3.1 70B model for all tasks, emphasizing the need for accessible, unrestricted AI models.
- Users expressed gratitude for open-source models catching up to proprietary ones, with many citing reliability issues and arbitrary account restrictions as reasons for switching away from closed AI platforms like Claude and ChatGPT.
- Several users reported being banned from Claude without explanation, often for using a VPN or within minutes of account creation. The lack of transparency and communication regarding account suspensions was a common complaint.
- Discussion highlighted the advantages of open-source AI, including data privacy, customization, and independence from corporate control. Some users noted switching to models like Mixtral 8x22B and Llama 3.1 70B for their workflows.
-
With the latest round of releases, it seems clear the industry is pivoting towards open models now (Score: 196, Comments: 96): The AI industry is shifting towards open models, with Meta releasing Llama 3 and Llama 3.1, including the 405B version, while Mistral has made their latest flagship model Mistral Large 2 available for download. Google has entered the open model arena with Gemma 2, Microsoft continues to release high-quality small models under Free Software licenses, and Yi-34B has transitioned to the Apache license, marking a significant change from late 2023 when a move away from open releases seemed likely. This trend suggests that closed-only vendors like OpenAI, despite upcoming releases like Claude 3.5 Opus from Anthropic, may face increasing competition from rapidly improving open models.
- Apple, Nvidia, AMD, Intel, X.ai, Amazon, and other tech giants are potential “sleeping giants” in AI development. Amazon has invested $4 billion in Anthropic, while X.ai is reportedly working on Grok 3, a multimodal model incorporating images, video, and audio.
- The shift towards open models is driven by the need for extensive testing and R&D. The open-source community provides valuable insights, use-cases, and problem-solving, creating a symbiotic relationship between companies and developers. This approach may be more effective than closed methods in advancing AI technology.
- Despite rapid improvements in open models, some users express concerns about potential diminishing returns in transformer architecture optimization. However, others argue that progress remains exponential, citing examples like Llama 3.1 8B outperforming earlier, much larger models like GPT-3.5 (175 billion parameters).
Theme 2. Breakthroughs in Specialized AI Capabilities
-
DeepSeek-Coder-V2-0724 released today, 2nd place in aider leaderboard (Score: 87, Comments: 15): DeepSeek has released DeepSeek-Coder-V2-0724, which has achieved 2nd place in the aider leaderboard for coding assistants. This new version demonstrates improved performance in coding tasks, positioning it as a strong competitor in the field of AI-powered programming tools.
- Users appreciate DeepSeek’s frequent updates and performance gains, with some expressing a desire for similar rapid iterations from other models like “Llama-3.2 next month, and 3.3 the month after”.
- The API for DeepSeek-Coder-V2-0724 is described as “dirt cheap” and offers tools+json capability. However, some users report issues with the model generating full code blocks despite prompts asking otherwise.
- There’s interest in the model’s availability on Hugging Face, with the developer noting that release of weights might take some time, similar to the previous version (Deepseek-V2-0628).
-
Introducing InternLM-Step-Prover. A SOTA math prover on MiniF2F, Proofnet, and Putnam benchmarks. (Score: 68, Comments: 8): InternLM-Step-Prover achieves state-of-the-art performance on math proving benchmarks including MiniF2F, Proofnet, and Putnam, solving 3 IMO problems in MiniF2F, including one (IMO1983P6) never before solved by ATP. The model and its training dataset, which includes Lean-Github data, have been open-sourced and are available on Hugging Face and GitHub, with the full research paper accessible on arXiv.
- The discussion highlights the shifting goalposts for defining AI intelligence, with users noting how proving mathematical theorems, once considered a benchmark for true intelligence, is now achievable by LLMs. This shift mirrors the abandonment of the Turing test as a standard.
- A user points out that according to pre-2010 definitions, current LLMs would be considered intelligent, while more recent definitions have made the term “intelligence” nearly meaningless. The rapid progress in ARC (Abstract Reasoning Corpus) scores is cited as an example.
- Some comments suggest that the constant redefinition of AI intelligence may be driven by fear among intellectuals of being surpassed by machines, leading to denial and attempts to delay acknowledging AI’s capabilities.
Theme 3. Uncensored AI Models and Ethical Considerations
-
Mistral Nemo is uncensored (Score: 131, Comments: 40): Mistral Nemo, a highly performant and uncensored model, outperforms other ~13b models on the UGI leaderboard, with its instruct version being more uncensored than the base model. Despite limited benchmarks, Mistral’s track record suggests it will compete with larger models, and a Dolphin finetune has been released by Cognitive Computations, potentially making it even more uncensored.
- Mistral Nemo 12b is praised as the best model in its size category, with users reporting no refusals even with “gnarly” prompts. However, it still exhibits limitations due to its 12b size, including common GPT-isms and difficulty with complex instructions.
- Users compare Mistral Nemo 12b favorably to larger models, describing it as a “Gemma 2 27b lite” version. It performs well in roleplaying scenarios, maintaining coherence and character tracking even when quantized (Q8_0).
- The model is noted for being highly “open-minded,” with a temperature of 0.3 producing wild results. It’s now available in GGUF format, compatible with llama.cpp, making it accessible for users with limited hardware.
-
Multimodal Llama 3 will not be available in the EU, we need to thank this guy. (Score: 164, Comments: 78): The post criticizes Thierry Breton, the EU Commissioner for Internal Market, for potentially restricting the release of multimodal Llama 3 in the European Union. The author suggests that Breton’s actions, including a tweet about AI regulation, may lead to Meta not making the multimodal version of Llama 3 available in the EU, similar to how GPT-4V is currently unavailable in the region.
- Users discussed the practical implications of EU restrictions, noting that individuals can still access models via VPNs or self-hosting. However, EU businesses may face legal challenges in using these models commercially, potentially leading to an “AI colony” situation.
- The irony of Mark Zuckerberg becoming a “savior” for open AI access was noted, contrasting with Sam Altman’s previous efforts to restrict open-source models. Users in Germany reported successfully downloading Llama 3.1 models using LM Studio.
- Criticism was directed at Thierry Breton and the EU’s approach to AI regulation, with some calling it “dysfunctional” and potentially causing the EU to fall behind in AI development. Users questioned the effectiveness of blocking access to models trained on European data.
All AI Reddit Recap
r/machinelearning, r/openai, r/stablediffusion, r/ArtificialInteligence, /r/LLMDevs, /r/Singularity
AI Model Releases and Benchmarks
-
Llama 405B achieves SOTA performance: In /r/singularity, a post discusses how Llama 405B’s success challenges the notion that OpenAI has proprietary techniques, achieving comparable performance without novel methods.
-
“AI Explained” channel’s Simple Bench results: A comparison of Llama 405B against other models on a private 100-question benchmark called “Simple Bench” is shared on /r/singularity.
-
Open-source model surpasses GPT-4: /r/singularity reports on a second open-source model outperforming GPT-4, highlighting rapid progress in publicly available AI.
-
Mistral Large 2 announced: Mistral AI introduces Mistral Large 2, a new model in their lineup, as reported on /r/singularity.
AI Applications and Improvements
- Udio 1.5 audio quality enhancement: Udio releases version 1.5 with significantly improved audio quality, as shared on /r/singularity.
AI Generation Challenges
-
Stable Diffusion prompt struggles: A humorous post on /r/StableDiffusion illustrates the challenges of generating specific content without unwanted elements, particularly in character generation.
- Comments suggest using
rating_safein positive prompts andrating_questionable, rating_explicitin negative prompts for better control. - Discussion touches on model biases, tagging systems, and the importance of careful prompt engineering.
- Comments suggest using
AI Discord Recap
A summary of Summaries of Summaries
1. AI Model Releases and Benchmarks
- Mistral Large 2 Takes on Llama 3.1: Mistral AI unveiled Mistral Large 2, a 123 billion parameter model with a 128k context window, outperforming competitors like Llama 3.1 70B by an average of 6.3% on multilingual benchmarks.
- The model excels in code generation, mathematics, and supports multiple languages, designed for efficient single-node inference. This release highlights the rapid advancements in open-source AI models competing with proprietary offerings.
- DeepMind’s AlphaProof Scores Silver at IMO: Google DeepMind announced that their AlphaProof system, combined with AlphaGeometry 2, achieved silver medal level performance at the International Mathematical Olympiad, solving 4 out of 6 problems.
- This breakthrough demonstrates AI’s growing capabilities in formal reasoning and mathematics, though it required significantly more time than human competitors. The achievement sparked discussions about AI’s potential impact on mathematical research and education.
2. AI Search and Information Retrieval
- OpenAI Unveils SearchGPT Prototype: OpenAI announced testing for SearchGPT, a new AI search feature aimed at providing fast, relevant answers with clear source attribution, initially involving 10,000 users.
- This move signals OpenAI’s entry into the search market, potentially challenging traditional search engines. The community expressed both excitement and skepticism, with discussions on its impact on existing AI-powered search tools like Perplexity.
- Reddit’s Exclusive Deal with Google Raises Concerns: Reddit implemented a policy to block most search engines except Google from indexing its content, tied to a $60 million annual agreement between the two companies.
- This decision has sparked controversy regarding open internet practices and data accessibility, particularly concerning its impact on AI training datasets and the broader implications for information retrieval and model development.
3. Open Source AI and Community Efforts
- Llama 3.1 Sparks Optimization Efforts: The release of Llama 3.1 by Meta, especially the 405B parameter version, has prompted discussions and efforts in the open-source community to optimize its deployment and fine-tuning across various hardware setups.
- Developers are exploring techniques like quantization, distributed inference, and memory optimizations to run these large models efficiently. Platforms like Hugging Face are facilitating access and implementation of these models.
- Collaborative Tools for AI Development: New tools and libraries are emerging to support collaborative AI development, such as stack-pr for managing stacked pull requests, and discussions around sharing optimized kernels for GPU efficiency.
- These initiatives highlight the community’s focus on improving development workflows and resource utilization in AI projects. There’s growing interest in peer-to-peer sharing of optimizations and caches to leverage collective efforts in model training and inference.
4. AI Ethics and Data Usage
- Runway AI’s Training Data Controversy: A leak revealed that Runway’s AI video generation tool was trained on scraped content from YouTube and pirated films, raising ethical questions about data usage in AI training.
- This revelation sparked intense debate within the AI community about the ethics of using publicly available but potentially copyrighted content for training AI models, highlighting the ongoing challenges in balancing innovation with intellectual property rights.
- Condé Nast’s Legal Action Against Perplexity: Condé Nast issued a cease-and-desist letter to AI search engine Perplexity, demanding they stop using content from Condé Nast publications in their AI responses.
- This legal action underscores the growing tensions between traditional media companies and AI-powered platforms over content usage rights, potentially setting precedents for how AI companies can use and cite published material.
PART 1: High level Discord summaries
Unsloth AI (Daniel Han) Discord
- Data Privacy Fears in Discord AI Training: Concerns emerged regarding using Discord logs for AI training under GDPR regulations, indicating that public data reuse may still require permission.
- Participants agreed that disregarding privacy rights could lead to significant violations, despite the perceived accessibility of public messages.
- Llama 3’s Fine-Tuning Challenges: Users reported Out-Of-Memory (OOM) errors and inference quality issues while fine-tuning Llama 3, emphasizing the need for dataset sanitization.
- Advice included switching to instruct models to enhance response quality and addressing formatting inconsistencies in datasets.
- The Importance of Batching for Inference Speed: Participants stressed that batching data effectively can dramatically accelerate inference speed, noting that not using HF transformers can hinder performance.
- Discussion highlighted that many users experience negligible speeds, averaging 30-100 tokens/sec, due to mismanagement of batching.
- Inference Process Sluggishness Unpacked: A participant explained how the autoregressive inference process leads to slower response generation, as it computes each token sequentially.
- This sequential generation was critiqued for its inefficiency, prompting calls for improved methodologies for real-time applications.
- AI’s Job Security Debate Heats Up: Discussion arose on the potential job displacement caused by AI, particularly in software engineering, revealing varied opinions on the urgency of these impacts.
- Participants reflected on both anxiety and acceptance regarding AI’s integration into the workforce, questioning legislative responses to the fast-evolving landscape.
LM Studio Discord
- LM Studio 0.2.28 Supports Llama 3.1: The latest version of LM Studio, 0.2.28, is essential for utilizing Llama 3.1 effectively, as noted by users who have encountered limitations with previous versions.
- It seems upgrading is crucial for accessing new features, especially since auto-updater lacks this version.
- Understanding LLaMA’s Pretraining Dataset: The LLaMA model’s pretraining dataset comprises 50% general knowledge, 25% math reasoning, 17% code, and 8% multilingual, critical for its overall performance.
- This data mix’s significance was shared through a data mix summary.
- Beta 1 Faces Performance Issues: Users are reporting significant CPU spikes in Beta 1, leading to sluggish performance during chat interactions, with one individual experiencing crashes.
- The general sentiment echoed among users is a keen interest in resolving these performance bottlenecks before the anticipated Beta 2 release.
- Mistral Large Model Is Here: Mistral Large, characterized by its imatrix design for size management, is now available with capabilities scaling up to 70GB.
- Users are urged to experiment with this model via its Hugging Face page, as it promises robust performance.
- Optimizing GPU Configurations for LLMs: Discussions highlighted various GPU setups, notably the P40 compared to newer models like the RTX 3090, revealing stark contrasts in speed and heat management.
- Notably, users have recorded speeds of 3.75 tokens/s with Llama 3.1 on the P40, but thermal issues demand cooling solutions for sustained performance.
HuggingFace Discord
- Llama 3.1 Hits the Scene: The much-anticipated Llama 3.1 is now available, enhancing the community’s favorite AI chat models. Explore its capabilities on the official blogpost and utilize it via this link.
- Interested users can follow the Hugging Face recipes on GitHub for implementation details.
- Hugging Face Access Stumbles in China: Discussion highlighted the challenges of accessing Hugging Face in China, where the site is blocked, leading some developers to rely on VPNs for model access.
- Suggestions include negotiating with Chinese regulators to restore access, as well as promoting localized content.
- Dolphin 2.9.3 Model Revolutionizes AI: The newly released Dolphin 2.9.3 Mistral Nemo 12b model, curated by Eric Hartford, features a 128K context and an 8192 sequence length.
- This enhancement stems from the Mistral-Nemo-Base-2407 model, promising improved performance.
- Open Source Bounty Programs Flourish: Members shared that several open-source bounty programs are available encouraging contributions to implement various models.
- Such programs not only provide compensation for completed work but also facilitate skill development and collaboration.
- Optimizing with Quantized Diffusers: A new feature supporting quantized Diffusers models via Quanto offers a 50% reduction in memory usage, as detailed in this GitHub PR.
- Moreover, the Orig PixArt Sigma checkpoint size dropped significantly, from 2.44GB to 587MB, enhancing model access and processing speed.
Nous Research AI Discord
- Hermes 2 Theta 70B Surpasses Llama-3: Nous Research released Hermes 2 Theta 70B, which surpasses benchmarks set by Llama-3 Instruct and matches performance with GPT-4. This model features capabilities such as function calling and feature extraction.
- The launch reflects significant advances in model architecture, indicating a competitive edge in versatile AI applications.
- Mistral Large 2 Revolutionizes AI: On July 24, 2024, Mistral AI unveiled Mistral Large 2, boasting 123 billion parameters and a 128,000-token context window. This model excels in code generation and mathematics, edging out Llama 3.1.
- The introduction of this model is a step forward in scaling AI applications, possibly nearing parity with leading benchmarks like GPT-4.
- Reddit’s New Indexing Policy: Reddit’s update to block most search engines except Google sparked controversy linked to a $60 million agreement with Google. This change prevents unauthorized indexing, raising questions about open internet practices.
- Members debated the implications of restricted access to data, illuminating concerns over content availability in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
- Condé Nast’s Legal Action Against Perplexity: Condé Nast issued a cease-and-desist letter to Perplexity, demanding an end to content use from its publications. This escalates tensions between conventional media and AI-powered search engines amid Perplexity’s rise in valuation.
- The move reflects broader issues of content ownership and usage rights in an era of AI-driven information retrieval.
- LLaMA 3.1 under Scrutiny: Users reported disappointing results from the LLaMA 3.1 instruct model, which performed worse than LLaMA 3.0 in knowledge benchmarks. Discussions centered on the impact of RoPE on performances, suggesting it may be detrimental.
- Members noted that turning off RoPE could lead to better outcomes, especially for smaller models, indicating potential areas for optimization.
Modular (Mojo 🔥) Discord
- Modular releases new Git tool - stack-pr: Modular introduced a new open-source tool called stack-pr designed for managing stacked pull requests on GitHub, aimed at streamlining integration for developers.
- This tool supports smaller contributions, benefitting code reviews by enabling smoother updates during the PR evaluation process.
- Interest in Posits for AI applications: Discussion around the role of posits in AI revealed interest in implementations like Gosit and the llvm-xposit, with potential integration into MLIR on the horizon.
- However, members noted that transitioning from traditional floating-point systems to posits could pose significant challenges.
- Open sourcing Mojo matrix multiplication: A member announced the open-sourcing of their matrix multiplication implementation in Mojo, inviting others to share their performance benchmarks on their setups.
- This initiative aims to foster collaboration and technical discussions surrounding the performance metrics utilized.
- Discussions on SIMD Comparisons: The community engaged in discussions on SIMD comparisons, debating between preserving both element-wise and total comparison results to accommodate various functionalities.
- There is a push to ensure SIMD performance remains robust without compromising its integration with list behaviors, especially for databases.
- Introducing Llama 3.1 with enhanced capabilities: Meta unveiled its Llama 3.1 model, now featuring a 128K context length and support for eight languages, pushing the boundaries of open intelligence advancements.
- This model provides unique capabilities that match those of leading closed-source models, expanding potential AI applications.
Perplexity AI Discord
- Perplexity AI Scheduled Downtime Alert: Perplexity announced a 10-minute scheduled downtime on <t:1722060000:R> for essential database maintenance to enhance system reliability.
- The team expressed gratitude to users for their patience during this crucial maintenance period.
- Mistral Large 2 Gains Ground in AI: On July 24, 2024, Mistral AI introduced Mistral Large 2, enhancing capabilities with 123 billion parameters and a 128,000-token context window, significantly outperforming the Llama 3.1 70B in multilingual MMLU benchmarks.
- Mistral Large 2 demonstrated an average improvement of 6.3% over its competitors, especially in code generation and mathematics.
- Reddit Places Search Engine Restrictions: Reddit’s recent move blocks most search engines from indexing its content, granting access only to Google due to a $60 million annual agreement.
- This decision has sparked debates about data access implications for the scraping and training of AI models.
- Condé Nast Challenges AI Search Practices: Condé Nast has issued a cease-and-desist against Perplexity for allegedly using its publications without approval, indicating escalating tensions in media-AI content usage.
- This legal action puts a spotlight on the complexities of content rights as AI tools proliferate and seek to monetize information.
- Microsoft Teams Connector Error Reported: A user encountered an unspecified error message while attempting to upload a Perplexity Connector ZIP file into Microsoft Teams.
- This prompted inquiries about successful integration experiences and potential workarounds within the community.
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) Discord
- Llama 405B gets a 10% price cut: The price of Llama 405B has been reduced by 10% as announced by OpenRouterAI, part of ongoing competitive strategies in the market.
- This trend suggests a filtering mechanism for user choice amid aggressive pricing tactics in AI model offerings.
- Middle-out transform to be turned off by default: Starting August 1, the middle-out transform will be turned off by default, shifting from its historical setting to enhance user control.
- Users reliant on this feature should refer to the documentation to adjust their requests accordingly.
- Traffic surge causes database strain: OpenRouter experienced a 5x traffic surge, leading to a scheduled downtime at 10:05 PM ET for database upgrades.
- Post-upgrade services were reported to be back online promptly, but with unresolved performance concerns due to recurrent database issues.
- Llama 3.1 exhibits variable performance: Reports indicate inconsistent outputs from Llama 3.1, particularly during high context loads, with some responses being off-topic.
- Users noted that switching providers sometimes improved output quality, indicating a potential issue with inference engine effectiveness.
- Mistral Large 2 showcases multilingual prowess: Mistral Large 2 excels in multiple languages, demonstrating substantial capability in languages including English, Spanish, and Mandarin.
- The performance positions it as a significant contender in multilingual language processing domains.
OpenAI Discord
- OpenAI tests SearchGPT Prototype: OpenAI introduces SearchGPT, a prototype aimed at enhancing search capabilities with fast, relevant answers and clear sourcing, rolling out initially to select users for feedback. More info can be found at OpenAI’s SearchGPT page.
- User feedback during testing will be crucial for refining SearchGPT before its fully integrated into ChatGPT.
- Long Downloads for Mistral Model: Users reported lengthy download times for the Mistral Large model, with one noting a download duration of 2.5 hours and achieving 18 tk/s on their MacBook Pro performance. Despite slow downloads, the MacBook Pro M2 Max’s capabilities with 96GB RAM generated excitement for future improvements.
- Anticipation for internet upgrades was palpable, as one user plans to boost their speed to 1 Gbps in December, essential for optimizing download times.
- Users Frustrated with GPT-4o Performance: After upgrading to GPT-4o, users expressed disappointment, noting frequent inaccuracies and lack of sourced responses, with one lamenting, ‘I felt the wise friend was long gone, only its dumb twin brother stayed.’
- Concerns about the SearchGPT API suggested that general access might take months, with users prioritizing functional improvements over API specifics.
- Challenges with Chatbot Memory Functions: Developers discussed difficulties in implementing function calls for chatbot memory creation, editing, and removal, currently hitting accuracy rates of around 60%. Clear guidance is deemed necessary for improving memory storage decisions.
- Suggestions included saving user preferences alongside important events, while emphasizing the need for specificity in memory input instructions.
- Issues with File Upload to OpenAI: A user encountered a 400 error while trying to upload a txt file to OpenAI, citing unsupported file extensions and referring to the OpenAI documentation.
- Despite following detailed documentation for file uploads using Python and FastAPI, the user faced challenges with vector store configurations linked to file upload failures.
Stability.ai (Stable Diffusion) Discord
- Stable Video 4D Shakes Up Video Generation: Stability AI introduced Stable Video 4D, a pioneering video-to-video generation model that creates dynamic multi-angle videos from a single input video in about 40 seconds.
- With the ability to generate 5 frames across 8 views, this tool enhances the creative process for users aiming for quality video production.
- Stable Assistant Gains New Powers: Stable Assistant now features Inpaint and Erase tools, allowing users to clean up generated content and iterate effortlessly within a 3-day free trial.
- These updates enable fine-tuning of output, catering to users seeking precision in their creative workflows.
- Debate Rages on Model Performance: Discussions heated up around model efficiency, with members claiming that a certain model outperforms SDXL while others noted the increasing competition from models like Kolors and Auraflow.
- The emphasis was placed on staying current with releases due to the rapidly shifting landscape of model performance.
- Mastering Lora Training for Better Outputs: Community members exchanged insights on the best practices for Lora training, emphasizing whether to use full or cropped images for different features.
- This discourse highlighted critical strategies for crafting detailed training datasets to enhance results effectively.
- Inpainting Techniques Explored in Detail: Users explored various inpainting methods, with recommendations to leverage img2img processes and pertinent tutorial resources for optimal results.
- The community reinforced using context-rich prompts as essential for successfully integrating objects into scenes.
Eleuther Discord
- Flash Attention Optimizes VRAM but Not Time: Flash Attention helps achieve linear VRAM usage, particularly during inference, but it does not lessen time complexity, which remains quadratic. One member observed that using Flash Attention with a long cache and a single query could actually slow down performance due to reduced parallelization.
- The impact of strategies like KV-Cache was discussed in terms of linear increases with sequence length, affecting VRAM without a significant change in compute time.
- Debate on Inference Costs for Model Providers: Members argued that inference for models like Mistral should be available for free at scale, emphasizing the efficiency of utilizing either single layers or MoE frameworks. Concerns were raised that inefficiencies in batch inference could undermine the benefits of MoE due to heightened complexity.
- Discussions touched on the minimal understanding of Meta’s operational tactics, challenging the operational efficiency that seems to be neglected in favor of optimization of lines of code.
- Scrutiny on Meta’s Scaling Laws: Users questioned if Meta’s scaling laws are affected by data superposition, suggesting non-linear scaling of optimal data amounts via exponential functions. This led to dialogue about calculating and understanding optimal data quantities in relation to model performance.
- Generalization of Chinchilla to 20 tokens per parameter was mentioned, revealing that scaling perceptions seem distorted yet rational at a deeper level.
- Explore the Awesome Interpretability Repository: The Awesome Interpretability in Large Language Models GitHub repository serves as an essential compilation for researchers focused on LLM interpretability. It functions as a key resource for digging into the complexities of large language model behaviors.
- Participation in the NDIF initiative allows access to Llama3-405b for audacious experiments, where participants will receive substantial GPU resources and support—a novel opportunity for meaningful research collaboration documented here.
- MMLU Evaluation on External APIs: A member is seeking guidance on testing MMLU performance with external APIs reflective of OpenAI’s setup, especially regarding log_probs in the model evaluation process. A related GitHub PR was mentioned that introduces a superclass aimed at API modularity.
- Concerns about calculating necessary VRAM for model evaluations arose, emphasizing the understanding of VRAM capabilities’ implications on experimental outcomes.
CUDA MODE Discord
- NCCL Overlap Challenges: A user raised concerns about achieving computation overlap with NCCL during the backward pass in their training setup using NCCL Issue #338. They noted that implementing what was suggested in lectures proved to be more complex than expected.
- This highlights ongoing challenges in effectively utilizing NCCL for optimized GPU workloads in training.
- Flute Matrix Multiplications Introduced: A member shared the repository for Flute, focused on fast matrix multiplications for lookup table-quantized LLMs. This aims to enhance performance in LLM processing applications.
- This tool could potentially streamline operations for models requiring efficient matrix handling, crucial for large-scale deployments.
- Analyzing Triton Kernels with CUDA Tools: You can analyze triton kernels just like other CUDA kernels using tools like Nsight Compute for detailed profiling. Nsight Compute provides comprehensive analysis capabilities to optimize GPU throughput.
- This profiling tool is essential for developers aiming to enhance performance and efficiency in GPU applications.
- Memory Limitations with FP16 Execution: A user expressed frustration regarding insufficient memory to run the model at fp16 precision, highlighting a common issue faced by developers. This prompted discussions on exploring alternative solutions to optimize memory usage.
- Addressing this issue is crucial for improving the feasibility of deploying large models in memory-constrained environments.
- Exploring Quantization Techniques with BnB: Another user recommended investigating quantization techniques using the bitsandbytes (BnB) library as a potential workaround for memory issues. This sparked confusion, with some questioning the concept of quantization itself.
- Understanding the implications of quantization is vital for leveraging model efficiencies, especially in large language models.
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) Discord
- DeepMind AI achieves Silver at IMO 2024: A recent discussion centered around Google DeepMind AI earning a silver medal at the IMO 2024, according to Google’s blog stating it meets ‘silver-medal standard.’
- Skeptics questioned the criteria’s clarity, suggesting Google may have influenced challenges to showcase its AI’s performance.
- Runway AI’s training data sources exposed: A leak revealed that Runway’s AI video generation tool was trained on scraped YouTube content and pirated films, which has raised ethical concerns.
- The controversy sparked intense discussion, hinting at heated debates over the implications for content creators.
- OpenAI enters search market with SearchGPT: OpenAI announced testing for SearchGPT, aimed at delivering quick answers and will initially involve 10,000 users.
- Feedback from this testing is expected to shape integrations into ChatGPT, generating excitement for improvements in AI search features.
- Recommendations for Books on Modern Architectures: In the search for resources on Diffusion and Transformers, a community member sought book recommendations for an ML course, highlighting the need for more focused reading materials.
- One suggestion was the book from rasbt, Building LLMs from scratch, but members are looking for more comprehensive titles on modern architectures.
- Understanding LLAMA 3.1 Annealing: Discussion focused on the LLAMA 3.1 technical report, particularly how lowering the learning rate to 0 aids in training without overshooting optimal points.
- This tactic could enhance model performance on leaderboards through meticulous pretraining strategies.
Latent Space Discord
- OpenAI’s SearchGPT Prototype Takes Off: OpenAI announced the launch of the SearchGPT prototype, designed to enhance search capabilities beyond current options, starting with a select user group for feedback.
- This initial phase aims to gather insights before integrating the prototype into ChatGPT for real-time operations.
- AI Shines at the International Mathematical Olympiad: A hybrid AI system developed by Google DeepMind secured silver medal level performance at the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO), solving 4 out of 6 problems using AlphaProof and AlphaGeometry 2.
- This achievement highlights significant progress in AI’s capability to tackle complex mathematical challenges, although it took longer than human competitors.
- OpenAI’s Rule-Based Rewards for Safer AI: OpenAI released Rule-Based Rewards (RBRs) aimed at improving AI safety by aligning behavior without requiring extensive human data collection.
- This approach allows for quicker adjustments to safety protocols with fewer manually labeled examples, promoting a more adaptable safety model.
- LLMs Step Up as Judges with Grading Notes: Databricks introduced Grading Notes to improve the reliability of LLMs in judgment roles by creating structured evaluation rubrics.
- The incorporation of these notes enhances domain-specific applications by providing clear guidelines for LLMs in specialized assessments.
- Synthetic Data in AI Training Faces Criticism: Concerns were raised in a recent paper about the over-reliance on synthetic data for AI training, warning that it could lead to model collapse after multiple generations.
- Experts emphasize maintaining diversity in training inputs to uphold information quality and mitigate performance degradation.
LlamaIndex Discord
- Structured Extraction Capabilities Launch: A new release enables structured extraction capabilities in any LLM-powered ETL, RAG, or agent pipeline, fully supporting async and streaming functionalities.
- Users can now define a Pydantic object and attach it to their LLM using
as_structured_llm(…)for streamlined implementation.
- Users can now define a Pydantic object and attach it to their LLM using
- Introducing LlamaExtract for Efficient Data Extraction: An early preview of LlamaExtract, a managed service for extracting structured data from unstructured documents, was revealed.
- This service infers a human-editable schema from documents, enabling user-defined criteria for structured extraction.
- OpenAI Calls Duplication Confusion: Users raised concerns about seeing duplicate OpenAI calls in
MultiStepQueryEngine, leading to discussions about logging issues with Arize.- Clarifications confirmed that these are not actual duplicates and progress continues on structured text extraction.
- RAG Chatbot Update Plans Shared: A user shared plans to upgrade their earlier RAG chatbot built with LlamaIndex, including a link to the GitHub repo for developers.
- They highlighted their eagerness to enhance the chatbot’s functionality now that RAG is much more popular.
- Monitoring Llama Agents Article Gains Praise: Members discussed an article titled Monitoring Llama Agents: Unlocking Visibility with LlamaIndex and Portkey, found here.
- One member remarked that it’s a nice article, emphasizing its significance to the community.
Cohere Discord
- Cohere compares well against OpenAI: Cohere provides language model solutions focused on natural language processing via API, allowing developers to create tools like conversational agents and summarizers. For comprehensive information, visit the Cohere API documentation.
- Their pricing is usage-based, eliminating the need for subscriptions, which differentiates it from other competitors in the market.
- Guidance for Writing Research Papers: Members discussed tips on writing research papers, emphasizing the role of university advisors for newcomers in academia. They pointed to the Cohere For AI community as a resource for collaborative support.
- The community offers essential guidance, helping to bolster the early stages of academic research for new authors.
- Understanding Langchain’s optional_variables: Clarifications about ‘optional_variables’ in Langchain’s ChatPromptTemplate surfaced, highlighting its function to permit non-required variables in prompts. This flexibility is crucial for creating adaptive user queries.
- However, confusion arose regarding how it differs from ‘partial_variables’, which also offers handling of optional metadata in prompt designs.
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) Discord
- Mistral Large 2 sets new benchmarks: Mistral Large 2 is reported to outperform 405 billion parameter models with a 123 billion parameters and a 128k context window, making it suitable for long context applications.
- This model supports multiple languages and coding languages, designed for efficient single-node inference, raising excitement about its performance potential.
- Exploring Multi-token Predictions: Members expressed curiosity about multi-token predictions, noting its potential in making byte-level models more feasible and efficient during training.
- There’s enthusiasm about possible annotations in datasets to specify token predictions, aligning thoughts with methodologies discussed in related papers.
- Training Data Modification Strategies: The discussion revolved around improving the efficiency of training by masking simpler words that don’t add value, akin to concepts from the Microsoft Rho paper.
- Members considered strategies to augment training data, like analyzing perplexity spots and enhancing context with tags to boost training effectiveness.
- Confusion Over Mistral Releases: There was confusion about the release details of Mistral Large vs Mistral Large 2, with members questioning the open-source status and the improvement claims.
- Some expressed concern over the relative performance metrics compared to existing models like Claude 3.5 and whether this model would eventually be open-sourced.
- Challenges loading 405B with FSDP and Zero3: A user reported difficulties getting the 405B model to load using FSDP or Zero3 with QLoRA.
- They expressed uncertainty about the specific issues causing these loading failures.
tinygrad (George Hotz) Discord
- Kernel Sharing Enhances GPU Efficiency: Members discussed the potential of peer-to-peer (p2p) kernel sharing to improve GPU efficiency after searching for optimal kernels.
- Previous discussions highlighted the effectiveness of p2p searches and sharing tinygrad caches.
- Need for Multiple Backpropagation Support: The community emphasized the necessity for a consistent method to backpropagate multiple times in tinygrad to implement neural network potentials.
- While some felt combining losses for backward calls would suffice, many sought a solution that retains the computation graph for complex gradient calculations.
- Random Tensor Generation Gives Repeated Results: A user reported issues with get_random_sum() returning the same output repeatedly due to TinyJit’s output overwriting behavior.
- It was advised that using
.numpy()before repeat calls would resolve this, ensuring unique outputs.
- It was advised that using
- Optimization in NumPy Conversion Process: A user reported cutting the NumPy conversion time from 6 seconds to 3 seconds by removing
.to('CLANG')in the tensor conversion method.- While questions about correctness arose, they verified that the resulting NumPy array remained accurate.
OpenInterpreter Discord
- Mistral-Large-Instruct-2407 offers speed: Mistral-Large-Instruct-2407 (128B) is approximately 3x smaller than the 405B model, resulting in reduced inference time.
- This reduction might appeal to those looking for efficient models.
- Llama 3.1 output token maximum inquiry: A member inquired about the maximum output tokens for Llama 3.1, indicating a need for more information in the community.
- Understanding these limits could optimize users’ experience with Llama 3.1.
- Concerns over outdated Ubuntu installation: Discussions arose about the installation instructions for Ubuntu potentially being outdated.
- It was noted that the current instructions do not work anymore.
- Fine-tuning GPT-4o-mini for optimization: A question was raised about fine-tuning GPT-4o-mini for better performance within the Open Interpreter framework.
- This discussion reflects an interest in capitalizing on the free fine-tuning quota available.
- Deepseek coder shows promising update: There was excitement over the recent update for the Deepseek coder, with promising performance specs shared.
- The affordability of Deepseek at 14-28 cents per mil was highlighted as a significant advantage.
Torchtune Discord
- Llama 3.1 approaches testing completion: Members indicated they’re finalizing tests for the Llama 3.1 patch, focusing on integrating 405B QLoRA on a single node. One participant flagged difficulties in saving checkpoints for such a large model.
- The current efforts reflect significant advancements, but challenges remain, especially in memory management while dealing with heavier models.
- Explore multi-GPU production challenges for Llama 3/3.1: Inquiries arose about distributed generation for Llama 3/3.1 70B, with pointers that current capabilities don’t support it natively; members suggested checking a repo for workarounds. Additionally, single GPU fitting was problematic, and users were directed towards quantizing the model to int4.
- Ongoing discussions indicated that while multi-GPU inference support isn’t prioritized, development is underway in the torchchat library.
- Snowflake enhances fine-tuning memory management: A member highlighted a blog post outlining memory optimizations for finetuning Llama 3.1, noting peak usage of 66GB on A100s using bfloat16. They shared that the lack of FP8 kernels forced this choice.
- The insights seem to set the stage for more efficient AI deployment as they share techniques for working with large model architectures.
- RFC proposes Transformer mod upgrades for cross attention: An RFC proposal seeks to modify TransformerDecoderLayer for cross attention in multimodal applications. It projects considerable implications for existing custom builders due to changes detailed in a pull request.
- Members were warned about the need for updates, emphasizing the comprehensive nature of the changes to maintain compatibility.
- Experimentation with distributed generation scripts: A user suggested that the existing generate.py could be adapted into generate_distributed.py for those adept with FSDP integration techniques. They recommended leveraging distributed finetuning recipes for smoother transitions.
- This approach could streamline multi-GPU implementations and enhance collaborative efforts as they aim to maximize efficiency in distributed environments.
LAION Discord
- Mistral Large 2 sets new AI benchmarks: Mistral Large 2 features a 128k context window and supports over a dozen languages, boasting 123 billion parameters for enhanced AI applications.
- Single-node inference capabilities allow for extensive throughput in long-context tasks.
- DFT Vision Transformer reshapes image processing: The new DFT Vision Transformer employs a Fourier transform, MLP, and inverse Fourier transform in each block to enhance image quality without bottlenecking data.
- This architecture also integrates image-wide norm layers efficiently, maintaining detailed information throughout.
- Complex numbers take center stage: The DFT Vision Transformer operates entirely with complex number parameters, enhancing computational dynamics within the network.
- This allows for an effective merging with rotary position encoding, refining overall performance.
- Rotary Position Encoding improves training speed: Switching to rotary position encoding resulted in a marked improvement in the loss curve’s decline rate, showing positive effects on training.
- Participants found this enhancement quite satisfying, confirming the method’s efficacy.
- Streamlined design boosts performance: The DFT Vision Transformer features a straight pipeline structure through equally sized blocks, completing with a global average pool and a linear layer.
- This ensures the image is never downsampled, preserving all information throughout processing.
DSPy Discord
- SymbolicAgentLearner merges RAG with symbolic learning: A member developed a SymbolicAgentLearner using DSPy that integrates Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and symbolic techniques for question answering and citation generation.
- The SymbolicLearningProcedure class enables multi-hop retrieval and auto-added citations, significantly enhancing information richness.
- Plans for a shared GitHub repository: In response to interest, it was mentioned that plans are in place to create a new public GitHub repository to share developments with the broader community.
- Currently, the existing code repository remains private, but this change aims to increase accessibility and collaboration.
- litellm proxy achieves flawless integration: Members reported using a litellm proxy across all models, noting it works like a charm for integrating with DSPy by redirecting OpenAI’s
api_base.- This solution simplifies model interactions, enhancing the usability of DSPy.
- Function calling across models requires extra effort: A member successfully enabled function calling across various models, though it requires additional workaround steps.
- Specific methods employed were discussed but not detailed, highlighting the effort needed for cross-model functionality.
- DSPy’s new approach to news categorization: A newly implemented news categorization system uses DSPy and OpenAI’s GPT-3.5-turbo to classify articles as ‘fake’ or ‘real’ via a Chain of Thought mechanism.
- The method employs ColBERTv2 for retrieval and MIPRO for optimization, showcasing a custom F1 score for effectiveness in evaluating misinformation.
LangChain AI Discord
- LangChain Agents struggle with consistency: Users voiced frustration with LangChain agents that utilize open-source models, citing inconsistent performance and improper tool selection.
- Multiple testers reported similarly disappointing results when evaluating local LLMs.
- Community explores Multi Agents functionality: A user sought guidance on implementing multi agents, spurring the community to discuss specific functionalities of interest.
- This exchange prompted further questions about the potential applications and configurations of these agents.
- Inquiry to use ConversationSummary with Database Agents: A user wondered if they could integrate ConversationSummary with their own database agent, asking for implementation advice.
- They showed openness to suggestions, especially if direct usage presented challenges.
- LangChain and Ollama drop a useful video: A member highlighted a YouTube video called ‘Fully local tool calling with Ollama’ that discusses local LLM tools and their usage.
- The video aims to clarify tool selection and maintains that agents can function consistently if set up correctly; watch it here.
- LangGraph looks for persistent options: A user requested updates on potential enhancements to LangGraph persistence beyond existing SqliteSaver options.
- Community members shared interest in alternative storage solutions that could improve data handling.
AI Stack Devs (Yoko Li) Discord
- Excitement for AI Raspberry Pi: In a recent exchange, a user expressed enthusiasm over the AI Raspberry Pi project, prompting curiosity about its specifics.
- The request for more details suggests potential interest in its capabilities and applications within low-cost AI deployment.
- Inquiry for More Details: A member requested further information, stating, this is cool, tell us more regarding the AI Raspberry Pi discussions.
- This indicates an active engagement in the community around innovative AI projects using Raspberry Pi, likely looking to explore technical intricacies.
The Alignment Lab AI Discord has no new messages. If this guild has been quiet for too long, let us know and we will remove it.
The LLM Finetuning (Hamel + Dan) Discord has no new messages. If this guild has been quiet for too long, let us know and we will remove it.
The LLM Perf Enthusiasts AI Discord has no new messages. If this guild has been quiet for too long, let us know and we will remove it.
The MLOps @Chipro Discord has no new messages. If this guild has been quiet for too long, let us know and we will remove it.
The Mozilla AI Discord has no new messages. If this guild has been quiet for too long, let us know and we will remove it.
The DiscoResearch Discord has no new messages. If this guild has been quiet for too long, let us know and we will remove it.
The AI21 Labs (Jamba) Discord has no new messages. If this guild has been quiet for too long, let us know and we will remove it.
PART 2: Detailed by-Channel summaries and links
{% if medium == ‘web’ %}
Unsloth AI (Daniel Han) ▷ #general (657 messages🔥🔥🔥):
Data Privacy and GDPRUsing Discord Logs for AI TrainingBTEC Education SystemValue of Software Engineering vs Data ScienceImpact of AI on Job Security
- Data Privacy and GDPR: The discussion highlighted concerns about using Discord logs for AI training, emphasizing that even public messages may require permission for reuse due to privacy laws, especially GDPR in the EU.
- There was a consensus that while public data may seem fair game, utilizing it without consent could lead to potential violations of privacy rights.
- Using Discord Logs for AI Training: There was a debate around the morality and legality of training models on Discord chat logs, especially with sensitive or personal information that could lead to privacy breaches.
- Participants noted the importance of not trivializing the issue, with emphasis on the difference between public and private data contexts.
- BTEC Education System: The BTEC system was discussed in terms of its place alongside traditional education routes, with a brief overview provided about how it operates within the UK education framework.
- Participants shared personal experiences with the BTEC system, revealing that it assigns more emphasis on practical assignments than exams.
- Value of Software Engineering vs Data Science: There was a conversation about career choices between software engineering and data science, with varied opinions on which field is more appealing or lucrative.
- One participant expressed their preference for software engineering while acknowledging the financial benefits often associated with data science positions.
- Impact of AI on Job Security: Concerns were raised regarding AI potentially taking jobs, particularly in software engineering, with opinions varying on the immediacy and impact of such changes.
- The sentiment among participants suggested a mix of acceptance towards AI’s role in the workforce and worries about the pace at which legislators might adapt to these changes.
Links mentioned:
- GitHub Accelerator Showcase 2024 | The next wave of AI projects: Get ready to dive into the next wave of AI innovation! 🌐✨ Witness open-source AI projects in action. Our Showcase highlights project demos, the inspiring jo...
- Tweet from OpenAI (@OpenAI): We’re testing SearchGPT, a temporary prototype of new AI search features that give you fast and timely answers with clear and relevant sources. We’re launching with a small group of users for feedba...
- [Blue Archive] [AI Tendou Alice] Chipi Chipi Chapa Chapa (Dubidubidu): AI singing tool 歌聲音色轉換模型: so-vits-svc 4.1: https://github.com/svc-develop-team/so-vits-svcCharacter Voice: ブルアカ 天童アリス(CV:田中美海)Original Music: Christell - Du...
- Nuh Uh Beocord GIF - Nuh Uh Beocord No - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Imagen 3: Imagen 3 is our highest quality text-to-image model, capable of generating images with even better detail, richer lighting and fewer distracting artifacts than our previous models.
- Release PyTorch 2.4: Python 3.12, AOTInductor freezing, libuv backend for TCPStore · pytorch/pytorch: PyTorch 2.4 Release Notes Highlights Tracked Regressions Backward incompatible changes Deprecations New features Improvements Bug Fixes Performance Documentation Developers Security Highlights We...
Unsloth AI (Daniel Han) ▷ #off-topic (2 messages):
Template Construction for SlackSlack Channel Posting
- Struggling with Template for Slack Conversations: A member expressed difficulty in constructing a template for fine-tuning the LLama model during Slack conversations.
- They are seeking guidance on which template might be best suited for this purpose.
- Need for Targeted Channel Posting: Another member noted that it’s sufficient to post in the specific Slack channel instead of broadcasting the message to all channels.
- This emphasizes the importance of keeping discussions relevant and contained.
Unsloth AI (Daniel Han) ▷ #help (104 messages🔥🔥):
Max Sequence Length in SFTTrainerLlama 3 Fine-Tuning IssuesInference Challenges with Fine-Tuned ModelsMulti-Turn Conversation Dataset FormattingModel Implementation on Websites
- Understanding Max Sequence Length in SFTTrainer: A user asked about the
max_seq_lengthinSFTTrainer, confirming it’s the maximum tokens processed during fine-tuning.- Another user noted that they are fine-tuning Llama 3 with a large prompt, potentially causing issues.
- Challenges in Fine-Tuning Llama 3 Models: Users faced various issues when fine-tuning Llama 3, including Out-Of-Memory (OOM) errors and inference quality concerns.
- Participants suggested cleaning dataset formats and using instruct models for better responses.
- Inference Issues with Fine-Tuned Llama 3 Models: One user encountered nonsensical responses when performing inference on a fine-tuned model despite successful training.
- It was suggested that issues may stem from the dataset formatting or prompt templates used during training.
- Formatting Multi-Turn Conversations: A user sought advice on formatting datasets for multi-turn conversations, sharing their dataset structure.
- Suggestions included ensuring the dataset’s cleanliness and consistency with the mapping template for expected outputs.
- Running Models Locally and WSL Recommendations: Users discussed the complications of running models locally, particularly with Windows, leading to WSL recommendations for better performance.
- Challenges with package installations like xformers were noted, suggesting the need for prebuilt wheels.
Links mentioned:
- llama-tokenizer-js playground: no description found
- Home: Finetune Llama 3.1, Mistral, Phi & Gemma LLMs 2-5x faster with 80% less memory - unslothai/unsloth
- Google Colab: no description found
- Google Colab: no description found
- Google Colab: no description found
- Google Colab: no description found
- Llama 3 | Model Cards and Prompt formats: Special Tokens used with Llama 3. A prompt should contain a single system message, can contain multiple alternating user and assistant messages, and always ends with the last user message followed by ...
- Google Colab: no description found
Unsloth AI (Daniel Han) ▷ #research (10 messages🔥):
Inference speed comparisonTask management with LLMsBatching in inferenceAutoregressive inference process
- Inference speed debate arises: A user questioned why inference is significantly slower than training, citing rates of only 30-100 tokens/sec during inference.
- Another member dismissed the claim, suggesting tools like vllm aphrodite can improve inference speeds.
- Batching essential for improved performance: A member pointed out that the key to achieving higher inference speeds lies in batching data effectively.
- It was noted that using HF transformers might lead to slower performance if batching is not implemented.
- Autoregressive process slows inference: A member explained that autoregessive inference processes lead to slow performance as each token requires a new model computation sequentially.
- The breakdown explained how the model generates responses token by token, illustrating inefficiencies in direct inference methods.
- Inquiry on LLMs for task management: A user sought advice on utilizing LLMs for distributing tasks within a management algorithm.
- Responses included warnings against excessive messaging, implying limited patience in the discussion.
LM Studio ▷ #💬-general (298 messages🔥🔥):
LM Studio UpdatesModel PerformanceGPU vs RAM UsageCoding ModelsLocal Model Limitations
- Updates on LM Studio Versions: Multiple users discussed the latest version of LM Studio, noting that 0.2.28 is required for proper support of Llama 3.1, which is not yet available via the auto-updater.
- Users were advised to download the latest version manually from the LM Studio website to access new features and improvements.
- Model Performance and Resource Usage: Conversations revealed that running the Llama 3.1 model effectively on systems with different hardware configurations, such as GPUs with sufficient VRAM, can greatly influence performance.
- Users reported varying performance metrics, emphasizing the importance of ensuring models are loaded onto the GPU memory instead of RAM.
- Best Local Models for Limited Specs: Users discussed recommendations for local language models suitable for machines with limited resources, such as Mistral and WizardLM.
- Models like DeepSeek were mentioned as feasible options for those seeking coding capabilities while considering hardware limitations.
- Impact of System Specs on Inference Speed: The relationship between system specifications and inference speed was highlighted, with some users achieving speeds as low as 0.21 tok/s on specific hardware configurations.
- Despite low performance numbers, participants expressed satisfaction with the results, showcasing the capabilities of local models in relation to their specs.
- Community Engagement and Support: Community members actively engaged in troubleshooting and offering support for each other’s experiences with LM Studio and hardware setups.
- Collaborative problem-solving and sharing of insights on model capabilities and potential issues fostered a supportive environment for learning and experimentation.
Links mentioned:
- Mcmahon Crying He Was Special GIF - Mcmahon Crying He was special WWE - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- update quant for llama3.1 by yagil · Pull Request #87 · lmstudio-ai/model-catalog: no description found
LM Studio ▷ #🤖-models-discussion-chat (85 messages🔥🔥):
LLaMA Model Data MixNaming Preferences in AIModel Performance ComparisonsGPU Support in LM StudioDolphin Model Issues
- LLaMA Model Data Mix Overview: The pretraining dataset for LLaMA models reportedly contains 50% general knowledge, 25% mathematical reasoning, 17% code, and 8% multilingual tokens.
- Source of this information includes a data mix summary.
- Naming Trends in AI Responses: A discussion unfolded regarding the frequent use of names like Zorvath, Elara, and Seraphina in AI-generated content for characters.
- One hypothesis floated was that this trend may stem from a prolific writer whose themes heavily influenced AI training datasets.
- Model Performance Comparisons: Users compared the performance of models like LLaMA 3.1 8B and Yi 1.5, noting that LLaMA requires multishot summarization strategies unlike Yi 1.5 which handles long contexts better.
- Additionally, LLaMA was favored for tasks involving JSON outputs among smaller models.
- GPU Support Limitations in LM Studio: It’s confirmed that LLaMA 3.1 does not support GPU offloading on LM Studio v0.27 leading to extremely slow performance on CPUs.
- Upgrading to LM Studio v0.28 is necessary to utilize newer models effectively and gain full GPU support.
- Issues with Dolphin Model: Users reported problems loading the Dolphin 2.9.3 model due to unsupported features in LM Studio, resulting in errors about unknown pre-tokenizer types.
- The model does not function correctly across various llama.cpp based software, indicating it was likely untested before release.
Links mentioned:
- 👾 LM Studio - Discover and run local LLMs: Find, download, and experiment with local LLMs
- no title found: no description found
- cognitivecomputations/dolphin-2.9.3-mistral-nemo-12b-gguf · "llama.cpp error: 'error loading model vocabulary: unknown pre-tokenizer type: 'dolphin12b''": no description found
- microsoft/Phi-3-vision-128k-instruct · Should Phi-3V provide support in llama.cpp?: no description found
- Embed - The Cosmic Union: Dreamcatchers - Wattpad: no description found
- Feature Request: Proper Llama 3.1 Support in llama.cpp · Issue #8650 · ggerganov/llama.cpp: Prerequisites I am running the latest code. Mention the version if possible as well. I carefully followed the README.md. I searched using keywords relevant to my issue to make sure that I am creati...
LM Studio ▷ #⚙-configs-discussion (1 messages):
melkanea: i got +5600 if you count cuda cores individually
LM Studio ▷ #🎛-hardware-discussion (144 messages🔥🔥):
ML Inference with Various HardwareP40 GPU ExperienceRTX 3090 vs M3 Max for InferencePerformance of Apple Silicon for AIDual GPU Configurations
- Exploring GPU Options for LLM Inference: Users discussed the pros and cons of different GPUs for running LLM models, noting the P40’s limitations in performance and heat management in comparison to newer cards like the RTX 3090.
- With 4 P40s, one user reported achieving 3.75 tokens/s with Llama 3.1 70B, while others highlighted the efficiency of M3 Max for inference tasks.
- Challenges and Solutions with P40 Setup: Concerns were raised about the P40’s high temperature and cooling needs, with users recommending custom cooling solutions to mitigate heat issues.
- One user successfully implemented custom cooling ducts, keeping their P40s functional even under heavy loads despite initial overheating problems.
- Comparative Performance: RTX 3090 and M3 Max: Discussions highlighted the potential of the M3 Max for AI tasks, especially in a comfortable ecosystem, contrasting with the high power and heat of gaming GPUs like the RTX 3090.
- Users shared performance metrics, suggesting that a dual 3090 setup might be a cheaper option if faster inference is desired, despite the potential for higher power consumption.
- Apple Silicon for AI Tasks: The M3 Max was praised for its quiet operation and efficient power usage while running LLM inferences, making it a compelling alternative to traditional GPUs.
- Users expressed satisfaction with DiffusionBee and the overall ease of using the Apple ecosystem for daily tasks and AI inference.
- Potential Issues with Combining GPUs: Concerns about the compatibility of running RTX and P40 GPUs together were discussed, pointing to user experiences that varied widely in stability and performance.
- Some users confirmed successful operations using both GPUs without additional driver issues, while others advised caution when integrating older hardware.
LM Studio ▷ #🧪-beta-releases-chat (27 messages🔥):
Beta 1 CPU issuesRenderer crash reportsNew UI feedbackModel comparisonUpcoming Beta 2 release
- Beta 1 struggles with CPU performance: Users reported experiencing CPU spikes and sluggish typing in Beta 1 after typing a certain amount of text in chats.
- One user also encountered a Renderer crash and plans to report it through official channels.
- Feedback on new UI’s responsiveness: A user remarked that the new UI feels snappy, suggesting a positive response to the recent updates.
- General enthusiasm for the UI’s performance was expressed by multiple members.
- Debate on quantized model efficiency: A discussion unfolded about using a 70 billion parameter model on a GPU with 24GB of VRAM, weighing the benefits of quantized vs unquantized models.
- Users raised points about the potential for quality degradation with quantization, with contrasting opinions on the efficacy of large quantized models like the 120B Goliath.
- Technical issues with Beta 0.2.29: A user reported problems starting Version 0.2.29, prompting suggestions for troubleshooting and reinstalling LM Studio.
- Another user mentioned similar issues with v26, which resolved after an update to v27, indicating possible version-related bugs.
- Beta 2 release date announced: Anticipation builds as Beta 2 is expected to drop tomorrow, promising new goodies and bug fixes.
- Participants expressed eagerness to see the enhancements in the next beta iteration and discussed possibly missing the previous release.
LM Studio ▷ #amd-rocm-tech-preview (17 messages🔥):
Linux AppImage updatesGPU offloading with ROCmCompatibility with 7800XTCommand line for ROCmOpenCL performance
- Linux AppImage upgrade to 0.2.28 works seamlessly: A user transitioned from Linux 0.2.27 to 0.2.28 appimage and confirmed that the llama 3.1 model worked out of the box on their 7800XT.
- Another user, who deleted 0.2.27, confirmed functionality with the newer version despite initial GPU detection errors.
- Uncertainty about ROCm extensions for 0.2.28: There was discussion regarding whether 0.2.28 requires ROCm extensions, with one user noting they used a script for 0.2.27 but did nothing for 0.2.28.
- A consensus emerged that the requirements from 0.2.27 likely apply without needing additional steps for the latest version.
- Successful ROCm usage on other GPUs: ROCm reported to work effectively with an RC6600XT as well, indicating broad compatibility among different models.
- Another user suggested starting HSA_OVERRIDE_GFX_VERSION=10.3.0 lm-studio via command line for those with compatibility issues.
- OpenCL offers adequate performance for now: One user noted that while they couldn’t get ROCm to work, OpenCL performance is decent enough for their needs.
- They indicated they would wait for Vulkan developments before further pursuing ROCm.
LM Studio ▷ #model-announcements (1 messages):
Mistral Large
- Mistral Large Model Release: Mistral Large has officially launched, crafted with imatrix for enhanced size management, scaling up to 70GB.
- The model promises excellent performance, inviting users to explore its capabilities via the Hugging Face page.
- Mistral Model Size and Capabilities: The Q4_K_M model configuration of Mistral Large enables it to maintain a very large size while still achieving optimal performance.
- Users are encouraged to experiment with this powerful model and enjoy the benefits it offers.
LM Studio ▷ #🛠-dev-chat (3 messages):
Using Llama 3.1VS Code ExtensionsCodestral Setup
- Guidance on Using Llama 3.1: Members discussed how to use Llama 3.1 in Cursor or VS Code, suggesting that extensions may be available for local LLM integration.
- One user prompted the discussion, seeking specific guidance from the community.
- Setting up VS Code Autocomplete: It was shared that Continue now supports tab autocomplete in VS Code and JetBrains IDEs.
- Members were encouraged to provide feedback and suggestions through the Discord channel.
- Recommendation for Codestral Setup: For the best autocomplete experience, it is recommended to use Codestral, accessible via the Mistral API.
- To set it up, users need to obtain an API key and integrate it into their
config.json.
- To set it up, users need to obtain an API key and integrate it into their
Link mentioned: Tab Autocomplete (beta) | Continue: Continue now provides support for tab autocomplete in VS Code and JetBrains IDEs. We will be greatly improving the experience over the next few releases, and it is always helpful to hear feedback. If …
HuggingFace ▷ #announcements (1 messages):
Llama 3.1 Release
- Llama 3.1 has arrived!: The much-anticipated Llama 3.1 is now available, bringing enhancements to the community’s favorite AI chat models. For more details, check out the official blogpost.
- Explore the new capabilities and models through this link, and dive into the community’s involvement via Hugging Quants.
- How to utilize Llama 3.1: Interested users can learn how to effectively implement Llama 3.1 by following the instructions in the Hugging Face recipes on GitHub.
- To try it out directly, visit the Meta-Llama 3.1 chat model for hands-on experience.
Link mentioned: HuggingChat: Making the community’s best AI chat models available to everyone.
HuggingFace ▷ #general (421 messages🔥🔥🔥):
Hugging Face Community DiscussionsModel Performance ComparisonsTraining and Fine-tuning LLMsAudio Denoising ResearchChina's Regulatory Impact on AI Models
- Hugging Face Access in China: Community members discussed the challenges of accessing Hugging Face in China, noting that while the site is blocked, some developers use VPNs to access models.
- Suggestions included the potential need for Hugging Face to negotiate with Chinese regulators to restore access and discussions on localized content.
- Performance Issues with Llama Models: Users expressed concerns about the performance of Llama 3.1 compared to previous models, with several feeling it scored lower in instruction tasks than expected.
- Some users noted they would prefer smaller models or API alternatives for efficiency in their work.
- Audio Processing and Model Optimization: One user shared a project incorporating audio denoising using neural networks, emphasizing the need for effective optimization for real-time performance.
- Discussion centered around the effectiveness of using linear neural networks for audio tasks despite their simplicity.
- Fine-tuning Large Language Models (LLMs): Several users discussed various approaches to fine-tuning LLMs, sharing code snippets and the need for efficient architecture in their implementations.
- There was a particular interest in applying MCTS (Monte Carlo Tree Search) methods for improving reasoning capabilities in smaller LLMs.
- Resources for Local Model Inference: A user inquired about setting up a local instance for using models like Whisper, seeking guidance on documentation and configurations.
- Suggestions included looking into Hugging Face’s private model spaces and exploring additional community resources for setting up inference APIs.
Links mentioned:
- 🧑🎓 How to use Continue | Continue: Using LLMs as you code with Continue
- Tweet from Vaibhav (VB) Srivastav (@reach_vb): Here’s how much GPU VRAM you’ll need to run L3.1 405B - 810 GB in fp/bf16, 405 GB in fp8/ int8, 203 GB in int4 HW - 4 x H/ A100 to 8 x H/ A100 (depending on quantisation used) 70B - 140 GB in fp/bf1...
- no title found: no description found
- Du hast kein Herz: Till Lindemann · Song · 2023
- Till Lindemann Spinning GIF - Till lindemann Spinning - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Troll Face Cube GIF - Troll Face Cube Funny - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Cuh Guh GIF - Cuh Guh Buh - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- What GIF - What - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Sigh Of Relief GIF - Spongebob Squarepants Nickelodeon - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Dpowe GIF - Dpowe - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Cat Eating Eatin Gamer Gunk GIF - Cat Eating Eatin Gamer Gunk Gamer Gunk - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Rammstein Ausländer audio: no description found
- Troll Lol GIF - Troll Lol Gta - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Tweet from Cognitive Computations (@cognitivecompai): llama 3.1 score lower than llama 3?
- Don't ask to ask, just ask: no description found
- HuggingFaceTB/SmolLM-1.7B-Instruct · Hugging Face: no description found
- lmsys/chatbot_arena_conversations · Datasets at Hugging Face: no description found
- AMD delays its Ryzen 9000 launch due to unspecified quality issue — new launch in August; chipmaker pulls back all units shipped globally for quality checks [Updated]: AMD hits the brakes on its Zen 5-powered Ryzen 9000 processors.
- ModelScope 魔搭社区: ModelScope——汇聚各领域先进的机器学习模型,提供模型探索体验、推理、训练、部署和应用的一站式服务。在这里,共建模型开源社区,发现、学习、定制和分享心仪的模型。
- GitHub - wootwootwootwoot/ComfyUI-RK-Sampler: Batched Runge-Kutta Samplers for ComfyUI: Batched Runge-Kutta Samplers for ComfyUI. Contribute to wootwootwootwoot/ComfyUI-RK-Sampler development by creating an account on GitHub.
- GitHub - mlfoundations/open_clip: An open source implementation of CLIP.: An open source implementation of CLIP. Contribute to mlfoundations/open_clip development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Introducing HuggingFace blog for Chinese speakers: Fostering Collaboration with the Chinese AI community: no description found
- Contributing: Native WebGPU implementation based on wgpu-core. Contribute to gfx-rs/wgpu-native development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Ai じゃ ない: Synthfunk/Vaporwave inspired track
- HuggingFaceFW/fineweb · Datasets at Hugging Face: no description found
- Dahmer: Provided to YouTube by CDBabyDahmer · 6snotNadietepregunto℗ 2022 Daniel TotaReleased on: 2022-04-01Auto-generated by YouTube.
- 100 gecs - 757 {OFFICIAL AUDIO}: 10,000 gecs available now: https://100gecs.lnk.to/10000gecsIDFOLLOW 100 GECS:https://twitter.com/100gecshttps://soundcloud.com/100gecshttps://www.instagram.c...
HuggingFace ▷ #cool-finds (12 messages🔥):
Dolphin 2.9.3 Model ReleaseAI Solves Mathematical OlympiadK-Nearest Neighbors AlgorithmAI Job Security Discussion
- Dolphin 2.9.3 Mistral Nemo Released: The new Dolphin 2.9.3 Mistral Nemo 12b model has been curated and trained by Eric Hartford and Cognitive Computations, featuring enhancements from the Mistral-Nemo-Base-2407 model.
- This model boasts a 128K context and utilized an 8192 sequence length during fine-tuning.
- AI Achieves Silver Medal in Math Olympiad: Google DeepMind announced a breakthrough AI that can solve International Mathematical Olympiad problems at a silver medalist level, combining AlphaProof and the improved AlphaGeometry 2.
- More details are available in their announcement thread, showcasing the potential of AI in formal reasoning.
- K-Nearest Neighbors Overview: This article provides an overview of the K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) algorithm, a supervised machine learning technique useful for regression and classification.
- KNN is non-parametric, meaning it does not assume any underlying data distribution, making it a versatile choice in various fields.
- Job Security in the Age of AI: Bernard Marr discusses job security in relation to AI, exploring which professions may remain unaffected as technology evolves.
- His insights are reflected in his extensive writings and influence in the technology sector.
Links mentioned:
- Fullbound - A dream tool for every recruiter: no description found
- Tweet from Google DeepMind (@GoogleDeepMind): We’re presenting the first AI to solve International Mathematical Olympiad problems at a silver medalist level.🥈 It combines AlphaProof, a new breakthrough model for formal reasoning, and AlphaGeome...
- K-Nearest Neighbor (KNN) Algorithm Overview: Using supervised machine learning, the K-Nearest Neighbors (KNN) technique is used to solve regression and classification issues. This…
- What Job Is Most Safe From AI?: As artificial intelligence continues to reshape industries, understanding which jobs remain secure is crucial. While AI's impact on the job market is undeniable, not all roles are equally vulnera...
- cognitivecomputations/dolphin-2.9.3-mistral-nemo-12b · Hugging Face: no description found
- AI models collapse when trained on recursively generated data - Nature: Analysis shows that indiscriminately training generative artificial intelligence on real and generated content, usually done by scraping data from the Internet, can lead to a collap...
HuggingFace ▷ #i-made-this (5 messages):
W2V2-BERT Model for UkrainianNext Word AutoCompleteCommunity Engagement
- Fine-tuned W2V2-BERT model for Ukrainian: A model was fine-tuned on Ukrainian using the YODAS2 dataset with 400k samples, now available on Hugging Face.
- Users can also join the Discord server for discussions related to Data Science and AI, and are invited to the Telegram Speech Recognition Group.
- Next Word AutoComplete and Phrase Inference Model: A new autocomplete component for tokenization, built on a 240k word phrase data model, is being offered for integration, as seen on this demo.
- The developer has been working on this model for over 6 months and encourages community feedback and collaboration via GitHub.
Links mentioned:
- AutoComplete - Wiki Phrases Tokenizer : no description found
- Yehor/w2v-bert-2.0-uk-v2 · Hugging Face: no description found
- Speech-to-Text for Ukrainian v2 - a Hugging Face Space by Yehor: no description found
HuggingFace ▷ #reading-group (8 messages🔥):
Open Source Bounty ProgramsDiffusion ModelsFinegrain BountyTinygrad Bounties
- Explore Open Source Bounty Programs: A member mentioned that while implementing projects from scratch may not be necessary, there are several open-source bounty programs available for implementing diffusion models.
- These programs facilitate contributions from developers while also providing potential compensation for completed work.
- Finegrain Bounty Universe Welcomes Contributors: One participant shared insights about the Finegrain bounty platform, which encourages contributors by offering payment for successfully merged pull requests.
- The program details indicate various statuses for bounties and provide clear guidelines for participation and submission.
- Tinygrad Bounties Recognized: A member acknowledged their familiarity with Tinygrad bounties, noting the inspiration it has provided to others in the community.
- This discussion around known bounty programs affirms their relevance and encourages exploration of these opportunities.
- Success Stories from Bounty Programs: Discussion revealed that some members have even been hired through their participation in bounty programs, illustrating their effectiveness.
- This highlights the potential for career advancement through engagement with open source projects.
Links mentioned:
- Finegrain Bounties: Bounties <a href="https://github.com/finegrain-ai/refiners">Refiners</a> is our open-source (MIT) adapters library Dive into the Finegrain Bounty Universe: Code, Conquer, Cash-i...
- Bounties - Google Drive: no description found
HuggingFace ▷ #core-announcements (1 messages):
Quantized DiffusersMemory OptimizationOrig PixArt Sigma Checkpoint Reduction
- Operate with Quantized Diffusers through Quanto: A new feature allows operation directly with quantized Diffusers models via Quanto, significantly improving performance.
- This change leads to a 50% reduction in memory usage, showcased in this GitHub PR.
- Significant Size Reduction for Orig PixArt Sigma Checkpoint: The Orig PixArt Sigma checkpoint size has been reduced from 2.44GB to 587MB, enabling easier access and faster processing.
- This optimization is a notable enhancement in model management, highlighted in the aforementioned GitHub PR.
Link mentioned: feat: support diffusion models. by sayakpaul · Pull Request #255 · huggingface/optimum-quanto: What does this PR do? Fixes #252
HuggingFace ▷ #computer-vision (7 messages):
Labeling PlatformsRoad Detection from Satellite ImagesUnderstanding LLaVa
- Labeling Platforms Discussion: Several members discussed alternatives for annotating images, particularly emphasizing Labelstudio and CVAT as potential solutions for those needing self-hosted options.
- Labelstudio was recommended for its usability, while caveats about installation difficulties were shared, especially with Docker.
- Challenges with Satellite Image Analysis: There was a query about using transformer-based models to detect roads from satellite images, prompting community input on existing methods.
- One user inquired about any specific models available, indicating a keen interest in practical applications.
- Seeking Clarity on LLaVa: A member expressed difficulty understanding the concept of SeparatorStyle in LLaVa, particularly regarding its implications for various language backbones.
- A request for a detailed explanation on this topic highlights ongoing learning and curiosity within the community.
HuggingFace ▷ #NLP (21 messages🔥):
Embedding Model Fine-tuningRAG System PerformanceEmbedding Numerical Data ChallengesCollaborative LLM ProjectsLlama 3.1 with Inf2 Guides
- Fine-tuning Embedding Models for Better Performance: A member expressed the need to fine-tune their embedding model as current performances are lacking on real data, despite being adequate for synthetic data.
- They believe a fine-tuned model could improve their results significantly, particularly as they plan to test larger model options.
- Challenges with Embedding Numerical Data in RAG Systems: Another member shared their experience using a qdrant vector database where they struggled with RAG’s inefficiency in retrieving numerical data accurately.
- Despite trying hybrid search techniques, they found that searching only for textual keywords did not yield satisfactory results for number retrieval.
- Call for Collaboration on LLM Projects: A member reached out to find others interested in collaborating on LLM projects, feeling that solo work has become boring.
- This highlights a desire in the community for collaborative efforts to share knowledge and enhance project outcomes.
- Inquiry About Llama 3.1 and Inf2 Servers: A user inquired about any available guides for using Llama 3.1 with Inf2 servers, indicating a need for resources in this area.
- This reflects ongoing interest in leveraging advanced LLM frameworks within different computational environments.
HuggingFace ▷ #diffusion-discussions (2 messages):
Diffusion techniques in biological sequence generationUpdates on ComfyUIMediaPipe integrationTensorRT performanceWorkflow changes in ComfyUI
- Diffusion techniques for biological sequences: A user inquired about the typical process for noise addition in diffusion techniques for generating biological sequences from their data points and features.
- They specifically asked whether noise should be added to the original data, the data with calculated features, or after applying embedding layers.
- ComfyUI sees major updates: A user shared their experience implementing new features in ComfyUI, which included a fully functional video2video mode with community support.
- They mentioned significant efforts to improve the application and that old workflows are now void due to these changes.
- MediaPipe replaces Insightface: The update regarding ComfyUI highlighted a shift from Insightface to MediaPipe, which is preferred due to its Apache-2.0 license.
- This transition allows users more flexibility compared to the previously non-commercial license of InsightFace’s models.
- Mixed results with TensorRT support: The user shared their experiences attempting to leverage TensorRT support but reported minimal benefits on their hardware or due to their inexperience.
- Despite this, they successfully optimized and streamlined other functionalities, achieving ‘realtime’ speeds within ComfyUI’s framework.
Link mentioned: Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
Nous Research AI ▷ #datasets (1 messages):
jsarnecki: https://github.com/mlfoundations/MINT-1T
Nous Research AI ▷ #interesting-links (9 messages🔥):
Hermes 2 Theta 70BMistral Large 2Reddit's indexing policy changeCondé Nast legal actionWiki Phrases Tokenizer
- Hermes 2 Theta 70B Surpasses Llama-3: Nous Research announced the release of Hermes 2 Theta 70B, surpassing benchmarks set by Llama-3 Instruct and achieving performance comparable to GPT-4.
- The model introduces capabilities like function calling and feature extraction, enhancing AI application versatility.
- Mistral Large 2 Revolutionizes AI: On July 24, 2024, Mistral AI revealed Mistral Large 2, featuring 123 billion parameters and a 128,000-token context window.
- This model excels in code generation and mathematics, outperforming Llama 3.1 and nearly matching GPT-4.
- Reddit Blocks Unpaid Search Engines: Reddit’s update to block most search engines except Google has sparked controversy, linked to a $60 million deal with Google.
- The policy change prevents unauthorized indexing, raising concerns about future open internet access.
- Condé Nast Takes Legal Action Against Perplexity: Condé Nast has sent a cease-and-desist letter to Perplexity, demanding cessation of content use from its publications in AI responses.
- This legal action escalates tensions between traditional media and AI-powered search engines, following a significant valuation of Perplexity.
- Next Word AutoComplete and Phrase Inference Model: A new autocomplete component for tokenization using a 240k word phrase data model has been introduced with a LIVE DEMO.
- The project, under active development for over 6 months, invites integration and community contributions via GitHub.
Links mentioned:
- AutoComplete - Wiki Phrases Tokenizer : no description found
- MOMAland: A Set of Benchmarks for Multi-Objective Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning: Many challenging tasks such as managing traffic systems, electricity grids, or supply chains involve complex decision-making processes that must balance multiple conflicting objectives and coordinate ...
- _Think-Lab Revised: Use the power of ScratchPad-Think for every day web searches. Export refined search queries in JSON format. The scratchpad is a powerful tool that helps you maintain coherence and accuracy, especially...
- Hermes 2 Theta 70B Surpasses Llama-3 Instruct: Nous Research has announced the release of Hermes 2 Theta 70B, a powerful new AI model developed in collaboration with Arcee AI and Charles Goddard....
- Mistral Large 2: Revolutionizing AI: On July 24, 2024, Mistral AI unveiled Mistral Large 2, a powerful new language model boasting 123 billion parameters and a 128,000-token context window,...
- Reddit Blocks Unpaid Search Engines: Reddit's recent decision to block most search engines from indexing its content, except for Google, has sparked controversy and raised questions about the...
- Condé Nast Takes Legal Action Against AI Search Engine Perplexity: According to reports from The Information, publishing giant Condé Nast has sent a cease-and-desist letter to AI search engine Perplexity, demanding it stop...
Nous Research AI ▷ #announcements (1 messages):
Nous Research subredditUpcoming AMA
- Nous Research launches a subreddit: A new subreddit has been created for the Nous Research community to engage in discussions about the latest AI research and projects.
- Members are encouraged to join and start threads to share insights and ideas.
- AMA on the horizon with Nous leaders: An AMA is planned in the coming weeks with two key members to answer community questions on Reddit.
- Details will be shared soon, inviting members to participate and submit their questions.
Link mentioned: Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
Nous Research AI ▷ #general (246 messages🔥🔥):
Nous Research UpdatesLLaMA Model PerformanceQuantization and Precision in AISynthetic Data GenerationOpenAI Features and Releases
- LLaMA Models Show Mixed Performance: Users reported that the LLaMA 3.1 instruct model appears worse than its predecessor LLaMA 3.0 on various benchmarks, impacting performance on knowledge-related tasks.
- Concerns were raised regarding RoPE’s effect on performance, with indications that disabling RoPE leads to better outcomes, particularly in smaller models.
- Discussion on GPU Usage and Efficiency: A user inquired about estimations for H100 GPU usage compared to A10G during heavy fine-tuning, highlighting the challenge of navigating GPU availability.
- The conversation included considerations of how to quantify token processing speeds to assess performance improvements.
- Precision Techniques in Model Training: There was a thorough discussion on quantization, particularly the nuances between fp16, bf16, and fp8, and their impact on model training and inference.
- Users noted that while model training typically favors lower precision for efficiency, certain configurations can lead to degraded performance.
- Synthetic Data Gains Adoption: One user noted that their pipeline for synthetic data generation significantly improved their model performance, particularly in Brazilian Portuguese.
- This highlights an interest in exploring alternative methods to enhance model capabilities through generated datasets.
- OpenAI’s Feature Developments: A user questioned the maturity of OpenAI’s SearchGPT developments compared to previous features such as Sora and GPT-4o, noting a lack of public updates.
- Conversations suggested a cautious stance on anticipated releases, echoing sentiments about previous hype without substantial follow-through.
Links mentioned:
- The Illustrated Transformer: Discussions: Hacker News (65 points, 4 comments), Reddit r/MachineLearning (29 points, 3 comments) Translations: Arabic, Chinese (Simplified) 1, Chinese (Simplified) 2, French 1, French 2, Italian, ...
- Tweet from Cognitive Computations (@cognitivecompai): llama 3.1 score lower than llama 3?
- casperhansen/mistral-large-instruct-2407-awq · Hugging Face: no description found
- google/gemma-2-9b · Hugging Face: no description found
- Tweet from Clémentine Fourrier 🍊 (@clefourrier): @paulml_fr Hi! For the ift-model, problem's the MATH score: their model answers systematically using CoT instead of following the few shot examples format - it almost never follows expected temp...
- HyperFeeder/audioScripts/ttsLocalScript.sh at master · normand1/HyperFeeder: The Autonomous Podcast Generator. Contribute to normand1/HyperFeeder development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
Nous Research AI ▷ #ask-about-llms (33 messages🔥):
Hermes release on Llama 3.1H100 GPUs vs Gaming GPUsData Synthesis in AIImage-to-Text FinetuningConsumer Grade Models
- Hermes Llama 3.1 release speculation: A member inquired about a Hermes release for Llama 3.1 8B, expressing confidence that work is underway despite no current availability.
- Teknium hinted at ongoing internal tests, suggesting developments might be close.
- H100 GPUs not suitable for gaming: There was a discussion regarding whether H100 GPUs could replace gaming GPUs, with members confirming that they are unsuitable for gaming due to lack of display outputs.
- One member humorously pointed out that owning such hardware is a challenge, noting that even they were ‘negative net-worth’.
- Issues with data synthesis in AI models: Concerns were raised about data synthesis, with members noting that many models do it poorly, impacting training outcomes.
- Recommendations such as reviewing the materials on Wizardlm, Orca, and Alpaca papers were shared for further understanding.
- New finetuning update for image-to-text integration: A newcomer inquired if the recent 4o-mini finetuning update allows for image-to-text finetuning, reflecting a growing interest in multimodal capabilities.
- This indicates a broader trend toward integrating various data types in AI training processes.
- Running large models on consumer hardware: Members explored how to run large AI models on consumer-grade hardware, with suggestions for upcoming competition in the GPU market.
- Insights included potential drops in inference costs as AMD prepares to challenge NVIDIA’s dominance.
Link mentioned: AI models collapse when trained on recursively generated data - Nature: Analysis shows that indiscriminately training generative artificial intelligence on real and generated content, usually done by scraping data from the Internet, can lead to a collap…
Nous Research AI ▷ #rag-dataset (2 messages):
Grounded RefusalsMeta Team Intelligence
- Realization of Grounded Refusals: A member expressed surprise at not having considered grounded refusals in their discussions previously.
- This reflects a moment of realization about the complexity and nuances involved in the topic.
- Feeling Outshined by the Meta Team: Another member remarked on how they feel that the Meta team is smarter than them in their approaches.
- This acknowledgment indicates an appreciation for the team’s capabilities and insights.
Nous Research AI ▷ #world-sim (1 messages):
kentrid: No code available for it, I guess?
Nous Research AI ▷ #reasoning-tasks-master-list (78 messages🔥🔥):
Moral Reasoning TasksSyllogism ReasoningTask StructuringDataset Collaboration
- Exploring Moral Reasoning Tasks: Members discussed the idea of creating a subsection for complex moral queries such as the trolley problem to evaluate reasoning capabilities in AI models.
- One suggestion proposed detailing how a self-driving car should prioritize safety in unavoidable collision scenarios, prompting further inquiries about reasoning processes.
- Standardizing Task Formats: Efforts began to restructure reasoning tasks into individual markdown documents, allowing for better organization and documentation clarity.
- Discussions included formatting considerations for headers, citations, and the possibility of linking tasks in a primary index document.
- Dataset Collaboration Opportunities: A member shared a curated dataset resource focused on reasoning tasks and expressed willingness to merge efforts with the Nous Research team.
- This initiative highlights the potential for collaborative research in AI reasoning by gathering existing benchmarks and papers for shared use.
- Improving Task Documentation: A proposed final list of fields for each task documentation included clear categories for description, modality, and citation type.
- Members also discussed the benefit of using tables for organization and the possibility of creating markdown and HTML pages for the main task index.
- AI Performance in Mathematical Reasoning: Discussion referenced a recent achievement by AlphaGeometry 2, which showcased silver medal performance in problem-solving at the International Mathematical Olympiad.
- The model’s hybrid approach combined a language model with reinforcement learning techniques, illustrating advances in AI’s mathematical reasoning abilities.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Séb Krier (@sebkrier): Some models can't work out if 9.11 is larger than 9.9, ours get silver medal level performance at the International Mathematical Olympiad! AlphaGeometry 2 is a neuro-symbolic hybrid system which...
- sample.md: GitHub Gist: instantly share code, notes, and snippets.
- GitHub - neurallambda/awesome-reasoning: a curated list of data for reasoning ai: a curated list of data for reasoning ai. Contribute to neurallambda/awesome-reasoning development by creating an account on GitHub.
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #general (20 messages🔥):
Open Source Git Tool - stack-prPosits and MLIRGame Development and AI Overlap
- Modular Releases New Git Tool - stack-pr: Modular announced the release of a new open-source tool called stack-pr for managing stacked pull requests (PRs) on GitHub, aimed at simplifying the integration process for developers.
- Stacked PRs allow for smaller, more manageable contributions, enhancing code reviews and maintaining smoother updates as PRs are reviewed.
- Interest in Posits for AI: Discussions emerged around the usefulness of posits for AI applications, with references to various implementations like Gosit and the llvm-xposit.
- Members noted that while MLIR could integrate posits, the transition from traditional floating-point systems could present significant challenges.
- Potential Overlap Between Game Dev and AI: Members humorously suggested that game development and AI might share a surprising overlap, with playful mentions of a potential ‘kiss’ between the two fields.
- One member shared a fleshed-out game idea that could explore this overlap, but lamented the challenges of being both a non-game developer and lacking funding.
Links mentioned:
- Modular: Announcing stack-pr: an open source tool for managing stacked PRs on GitHub: We are building a next-generation AI developer platform for the world. Check out our latest post: Announcing stack-pr: an open source tool for managing stacked PRs on GitHub
- GitHub - artecs-group/llvm-xposit: The LLVM Project is a collection of modular and reusable compiler and toolchain technologies. This repository contains the Xposit RISC-V custom extension for posit arithmetic.: The LLVM Project is a collection of modular and reusable compiler and toolchain technologies. This repository contains the Xposit RISC-V custom extension for posit arithmetic. - artecs-group/llvm-x...
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #💬︱twitter (2 messages):
Modular updatesModular community engagement
- Modular announces exciting updates: Modular shared a tweet highlighting new features and improvements, encouraging users to explore the latest functionalities at Modular’s official Twitter.
- The post received positive feedback from the community, indicating strong interest in enhancements.
- Engagement with Modular’s community: Another tweet by Modular emphasized the importance of community involvement, inviting feedback and suggestions for future updates at Modular’s latest Tweet.
- This call to action inspired members to share their ideas, highlighting a collaborative atmosphere.
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #✍︱blog (5 messages):
stack-pr toolFeedback on stack-prBenefits of stacked PRs
- Introducing the stack-pr tool for GitHub: A new tool called stack-pr has been released to simplify the management of stacked pull requests on GitHub, enabling developers to break changes into smaller, manageable PRs.
- This tool is in early development and the community is invited to contribute with feedback and questions on this blog post.
- Discussion on using stack-pr vs. simple labels: One member expressed concern that using the stack-pr tool seems more complicated than their usual method of labeling branches while waiting for merges.
- Another member countered that while it takes time to get used to stack-pr, it effectively prevents blocking by allowing continuous commits during reviews.
- Benefits of splitting big changes into multiple PRs: The stack-pr tool allows for breaking large changes into smaller PRs, improving the code review process by enabling parallel reviews of individual PRs.
- As each PR is reviewed and merged, the remaining ones automatically update, which streamlines integration without bottlenecks.
Link mentioned: Modular: Announcing stack-pr: an open source tool for managing stacked PRs on GitHub: We are building a next-generation AI developer platform for the world. Check out our latest post: Announcing stack-pr: an open source tool for managing stacked PRs on GitHub
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #ai (1 messages):
Meta's commitment to open AILlama 3.1 model advancementsOpen intelligence accessibilitySynthetic data generation
- Meta champions open AI access: Meta is committed to openly accessible AI and shared Mark Zuckerberg’s letter outlining the benefits of open source for developers, Meta, and the world.
- The letter emphasizes that open source fosters collaboration and innovation in the AI community.
- Introducing Llama 3.1 with 128K context length: Meta’s latest models, including Llama 3.1 405B, expand context length to 128K and support eight languages, showcasing their commitment to open intelligence.
- This new model is unique, providing capabilities that rival top closed source models.
- Llama 3.1 empowers new workflows: The Llama 3.1 405B model allows the community to unlock new workflows, prominently featuring capabilities in synthetic data generation and model distillation.
- These advancements aim to enhance the potential applications of AI, giving developers enhanced flexibility and control.
- Continued development of Llama ecosystem: Meta is dedicated to expanding the Llama framework by providing additional components that work seamlessly with the model.
- Their goal is to equip developers with the tools necessary to create transformative AI applications.
Link mentioned: no title found: no description found
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #mojo (97 messages🔥🔥):
Mojo regex supportTenka package managerSDL window creationIterator traitsInfrared 2D primitives
- Mojo lacks a regex library: A member confirmed that Mojo does not currently have a regex library and shared a related discussion link for further context.
- The absence of this library raises concerns among developers about functionality and convenience.
- Tenka package manager launched: A member announced the release of Tenka v0.1, a package manager for Mojo, and invited contributions and feedback.
- Challenges were noted regarding compatibility of package versions across environments, leading to discussions about potential solutions.
- Creating SDL windows in Mojo: A user celebrated successfully creating a window via SDL in Mojo after troubleshooting linking paths.
- Discussion around the proper use of variables in definitions indicated that advancements are being made in the community.
- Iterator traits and associated types: Members discussed the foundational issues preventing the implementation of a generic iterator API in Mojo, particularly the need for associated types.
- Concerns about traits with fields were expressed, with suggestions on using traits to enhance iterator functionality.
- Advancing Infrared’s 2D primitives: A developer mentioned adding initial features to Infrared, with the realization that many 2D shapes might relate to point pairs geometrically.
- They expressed interest in uncovering deeper mathematical abstractions behind these 2D primitives and their implications.
Links mentioned:
- Associated types - Rust By Example: no description found
- Issues · modularml/mojo: The Mojo Programming Language. Contribute to modularml/mojo development by creating an account on GitHub.
- GitHub - Ryul0rd/sdl-bindings: Contribute to Ryul0rd/sdl-bindings development by creating an account on GitHub.
- [stdlib] Iterator proposal by martinvuyk · Pull Request #3018 · modularml/mojo: Closes #2629
- Pacman Example: Vega - A Visualization Grammar. Vega is a visualization grammar, a declarative format for creating, saving, and sharing interactive visualization designs. With Vega, you can describe the visual appear...
- [Feature Request] Introduce Iterator Trait · Issue #2629 · modularml/mojo: Review Mojo's priorities I have read the roadmap and priorities and I believe this request falls within the priorities. What is your request? I would like to have iterator trait like trait Iterato...
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #nightly (198 messages🔥🔥):
SIMD ComparisonsEqualityComparable TraitSIMD Behavior for ListsPerformance and API DesignFunction Overloading and Return Types
- Discussions on SIMD Comparisons: The community is debating the handling of SIMD comparisons, with interests in maintaining both element-wise and total comparison results to cater to different use cases like
any()andall().- There is consensus that the behavior of SIMD should not sacrifice performance for compatibility with lists, especially for use cases related to hash tables and database indexing.
- EqualityComparable Trait and Overloading: The group is exploring whether
Eqimplementations should be introduced to SIMD types to support polymorphic behavior without overwhelming the standard library with numerous traits.- Suggestions include having separate functions for returning boolean versus SIMD logic to better satisfy trait requirements without further complicating the implementation.
- Performance Focus Over API Complexity: There is a strong emphasis on ensuring SIMD remains efficient without breaking its functionality to conform to list behavior, arguing for dedicated vector types when necessary.
- The resolution indicates a preference for maintaining low overhead and direct use of SIMD rather than overloading or altering existing features to cater to list compatibility.
- Proposals for Improved SIMD Functionality: Proposals are surfacing to create additional types like
AnyCmpSIMDandAllCmpSIMD, specifically tailored to clarify and control comparison behaviors for SIMD types.- These types aim to bridge the gap between expected mathematical behavior and practical coding needs in SIMD implementation, while avoiding a cluttered trait system.
- Future Directions in SIMD and Traits: The conversation suggests that iterative improvements and formal recognition of behaviors for function traits like
FnAnyandFnAllmight be needed as future directions.- Participants are keen on ensuring that custom types could integrate seamlessly with SIMD operations, while awaiting advancements in iterator extensions within the framework.
Links mentioned:
- SIMD | Modular Docs: Represents a small vector that is backed by a hardware vector element.
- [Proposal] Reduce the workload of stdlib's maintainers with `stdlib-extensions` · modularml/mojo · Discussion #3233: This discussion is here to have a place to talk about the folloowing proposal: pull request markdown document We are especially interested in the opinion of frequent contributors, as well as the st...
- [stdlib] SIMD conformance to EqualityComparable by helehex · Pull Request #2412 · modularml/mojo: This allows SIMD to conform to EqualityComparable, without losing any of the original behavior. It uses the 4th overload resolution rule to give the new methods lower precedence, while still confor...
- [stdlib] Constrain `simd.bool()` to `size == 1` by helehex · Pull Request #2502 · modularml/mojo: Use explicit reduce_or()/reduce_and() instead see #2412
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #mojo-marathons (6 messages):
Mojo ImplementationSpam Messages
- Open Sourcing Mojo Matrix Multiplication: A member announced the open sourcing of their matrix multiplication implementation in Mojo, inviting others to share their benchmark results on their machines. More details can be found in the Discord message.
- This release aims to facilitate collaboration and discussion around performance metrics among users.
- Concerns Over Spam Activity: Conversation highlighted issues with spam messages proliferating across many channels, causing disruption. A member acknowledged the problem but noted that others were currently offline to address it.
- Community engagement is needed to tackle this issue effectively as users seek resolution.
Link mentioned: Discord - Group Chat That’s All Fun & Games: Discord is great for playing games and chilling with friends, or even building a worldwide community. Customize your own space to talk, play, and hang out.
Perplexity AI ▷ #announcements (1 messages):
Scheduled DowntimeDatabase Maintenance
- Heads-up for Scheduled Downtime: There is a scheduled 10-minute downtime on <t:1722060000:R> for database maintenance.
- The team appreciates your patience and understanding, and expresses gratitude for your support.
- Database Maintenance Appreciation: The team acknowledges the inconvenience caused by the scheduled downtime and thanks users for their support.
- This maintenance is crucial to ensure ongoing performance and reliability.
Perplexity AI ▷ #general (305 messages🔥🔥):
Mistral vs. Llama modelsPerplexity's API usageSearchGPT's anticipated launchEducation system concernsSubscription and discount issues
- Debate over model capabilities: Users discussed the performance of Mistral and Llama models, with opinions varying on their reasoning and writing abilities, particularly highlighting 3.5 Sonnet’s strength in writing compared to GPT-4o.
- Some users expressed doubts about benchmarks and perceived inconsistencies, while others pointed to 4o’s coding advantages.
- Trust in Perplexity’s model claims: Concerns were raised about Perplexity’s use of models like OpenAI’s GPT-4o, with users questioning how to verify that the API version used is the original.
- Arguments pointed out the importance of transparency, while some suggested that the responses from Perplexity models closely match those obtained directly from OpenAI.
- Expectations for SearchGPT: The community speculated on the upcoming release of SearchGPT and whether it would be free or subscription-based, emphasizing how competition could benefit users.
- Users indicated an interest in trying it out if it proves to be free, contrasting it with their current experience using Perplexity.
- Critical thinking in education: Discussion around the impact of AI like ChatGPT on education highlighted concerns about decreased critical thinking and reliance on memorization.
- Some users argued that AI has exposed flaws in the education system, suggesting that open-book assessments and practical applications should be prioritized.
- Discount code issues on Perplexity: A user inquired about why their discount code for Perplexity was not working while it functioned for a friend’s account.
- The query pointed to potential account-specific issues or discrepancies in eligibility that needed clarification.
Links mentioned:
- Mistral Unveils Large 2: Mistral AI has unveiled its latest large language model, Mistral Large 2, boasting significant advancements in multilingual capabilities, reasoning, and...
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- Google Is the Only Search Engine That Works on Reddit Now Thanks to AI Deal: Google is now the only search engine that can retrieve recent results from Reddit, thanks to a $60 million agreement between the two companies that allows...
- GitHub - nuprl/MultiPL-E: A multi-programming language benchmark for LLMs: A multi-programming language benchmark for LLMs. Contribute to nuprl/MultiPL-E development by creating an account on GitHub.
- _Think-Lab Revised: Use the power of ScratchPad-Think for every day web searches. Export refined search queries in JSON format. The scratchpad is a powerful tool that helps you maintain coherence and accuracy, especially...
- Perplexity: Perplexity is a free AI-powered answer engine that provides accurate, trusted, and real-time answers to any question.
Perplexity AI ▷ #sharing (11 messages🔥):
Mistral Large 2 ReleaseReddit Blocks Unpaid Search EnginesCondé Nast Legal Action Against PerplexityHydrogen vs Atomic BombsFirst Nations Funding Opportunities
- Mistral Large 2 Sets New AI Standards: On July 24, 2024, Mistral AI introduced Mistral Large 2, a language model with 123 billion parameters and a 128,000-token context window, enhancing capabilities in code generation, mathematics, and multilingual tasks.
- It shows promising performance, outperforming competitors like Llama 3.1 70B by an average of 6.3% in the Multilingual MMLU benchmark.
- Reddit Limits Search Engine Access: Reddit’s recent update blocks most search engines from indexing its content except for Google, tied to a $60 million annual deal with the tech giant.
- This policy change has raised concerns regarding open internet access and the implications for data scraping and AI training.
- Condé Nast Takes Stand Against AI Search: Condé Nast has sent a cease-and-desist letter to AI search engine Perplexity, accusing it of using content from its publications without permission.
- This legal action highlights the escalating tensions between traditional media and AI-powered platforms regarding content usage.
- Hydrogen vs Atomic Bombs: Understanding the Differences: Hydrogen bombs utilize nuclear fusion, combining hydrogen isotopes for a more powerful explosion compared to atomic bombs, which use nuclear fission to split heavy atoms.
- This fundamental difference leads to significant variations in their explosive power and destructive effects.
- Funding Opportunities for Indigenous Businesses: The Aboriginal Business Investment Fund (ABIF) provides crucial financial support for Indigenous-owned businesses in Canada, with grants ranging from $150,000 to $750,000.
- Federal and provincial programs, including the Indigenous Growth Fund, are aimed at bolstering economic development initiatives and complementing technology innovation.
Links mentioned:
- YouTube: no description found
- Mistral Large 2: Revolutionizing AI: On July 24, 2024, Mistral AI unveiled Mistral Large 2, a powerful new language model boasting 123 billion parameters and a 128,000-token context window,...
- Meta Drops 405B Parameter Model: Meta has unveiled its most advanced AI language model to date, Llama 3.1 405B, boasting 405 billion parameters and capabilities that rival leading proprietary...
- Mistral Large 2: Revolutionizing Language Models with Unprecedented Capabilities: Here's my review of the output using the scratchpad format: <scratchpad> [Key information extracted from the prompt] Review task for an article about Mistral...
- Mistral Unveils Large 2: Mistral AI has unveiled its latest large language model, Mistral Large 2, boasting significant advancements in multilingual capabilities, reasoning, and...
- Reddit Blocks Unpaid Search Engines: Reddit's recent decision to block most search engines from indexing its content, except for Google, has sparked controversy and raised questions about the...
- Legal Trials of Inanimate Objects: Throughout history, legal systems have grappled with the unusual practice of putting inanimate objects on trial for causing harm or death to humans. From...
- Comparing Hydrogen and Atomic Bombs: Hydrogen bombs and atomic bombs are both types of nuclear weapons, but they differ significantly in their underlying reaction, explosive power, and...
- Condé Nast Takes Legal Action Against AI Search Engine Perplexity: According to reports from The Information, publishing giant Condé Nast has sent a cease-and-desist letter to AI search engine Perplexity, demanding it stop...
- First Nations Funding Opportunities: The Aboriginal Business Investment Fund (ABIF) and similar programs offer crucial financial support for Indigenous-owned businesses and economic development...
Perplexity AI ▷ #pplx-api (3 messages):
Microsoft Copilot StudioLlama 3.1 models API
- Microsoft Teams Upload Error with Perplexity Connector: A member reported an unspecified error message encountered when uploading a Perplexity Connector exported as a ZIP file into Microsoft Teams.
- They inquired if anyone has successfully implemented the connector and whether there might be solutions available.
- Interest in Additional Llama 3.1 Models for API: A user asked about the possibility of adding the other Llama 3.1 models (8B and 70B) to the API.
- This inquiry was met with agreement from another member, highlighting interest in extending available model options.
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) ▷ #announcements (5 messages):
Llama 405B price cutMiddle-out transform changesDatabase traffic surgeLlama 3.1 price reductionDatabase performance issues
- Llama 405B gets a 10% price cut: The price of Llama 405B has been reduced by 10% as announced by OpenRouterAI.
- This pricing adjustment is part of ongoing competitive strategies in the market.
- Middle-out transform to be turned off by default: The middle-out transform will be turned off by default starting August 1, moving away from its historical default setting to provide better control for users.
- Users heavily relying on this feature are encouraged to update their requests accordingly, as found in the documentation.
- Traffic surge causing database strain: The platform experienced a 5x traffic surge which strained the database, necessitating a scheduled downtime at 10:05 PM ET for upgrades.
- Post-upgrade, services were reported to be back online promptly.
- 14% price cut for Llama 3.1-8b-instruct: A 14% price cut has been announced for the meta-llama/llama-3.1-8b-instruct model, continuing the recent trend in aggressive pricing adjustments.
- This price change raises questions about where the pricing competition will eventually stabilize, especially following the recent product launch.
- Database performance issues arise again: Some database issues have resurfaced, leading to potential degradation in performance during the troubleshooting phase.
- The team is actively addressing these issues to ensure smooth operations.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from OpenRouter (@OpenRouterAI): 🍕 Price cut: Llama 405B pricing reduced by 10%
- Meta: Llama 3.1 8B Instruct by meta-llama: Meta's latest class of model (Llama 3.1) launched with a variety of sizes & flavors. This 8B instruct-tuned version is fast and efficient. It has demonstrated strong performance compared to ...
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) ▷ #general (215 messages🔥🔥):
Llama 3.1 PerformanceInference Engine IssuesPrice Competition Among ProvidersModel QuantizationOpenRouter Provider Accountability
- Llama 3.1 exhibits variable performance: Users reported inconsistent outputs from the Llama 3.1 model, with responses sometimes being entirely off-topic or nonsensical, especially when under heavy context loads.
- Switching providers improved the output quality for some users, suggesting that inference engine performance is critical.
- Concerns over inference engine quality: Discussion highlighted that many open-source inference engines might degrade model quality, leading to gibberish responses when parameters or contexts are pushed to their limits.
- The community speculated about potential issues with specific vendors and their deployment practices, which could be leading to poor output quality.
- Providers engage in price competition: There are ongoing discussions about providers undercutting prices to attract more users, sometimes at the cost of model quality and performance.
- This pricing behavior raises concerns about accountability and the consistency of the models being offered on OpenRouter.
- Model quantization techniques: Users discussed the transition to lower precision quantization methods like FP8 for Llama 3.1, analyzing the implications on performance and quality.
- There was a consensus that while good quality FP8 can be nearly equivalent to FP16, problems may arise depending on the implementation of inference engines.
- OpenRouter’s role in ensuring vendor quality: A lack of clear accountability on OpenRouter was cited, with concerns that vendors could misrepresent the models they host, particularly regarding the quantization methods used.
- The community discussed the need for better verification processes to ensure providers deliver models that meet expected performance standards.
Links mentioned:
- Meta: Llama 3.1 8B Instruct by meta-llama: Meta's latest class of model (Llama 3.1) launched with a variety of sizes & flavors. This 8B instruct-tuned version is fast and efficient. It has demonstrated strong performance compared to ...
- The Era of 1-bit LLMs: All Large Language Models are in 1.58 Bits: Recent research, such as BitNet, is paving the way for a new era of 1-bit Large Language Models (LLMs). In this work, we introduce a 1-bit LLM variant, namely BitNet b1.58, in which every single param...
- mistral-large: Mistral Large 2 is Mistral's new flagship model that is significantly more capable in code generation, mathematics, and reasoning with 128k context window and support for dozens of languages.
- GitHub - princeton-nlp/SWE-agent: SWE-agent takes a GitHub issue and tries to automatically fix it, using GPT-4, or your LM of choice. It solves 12.47% of bugs in the SWE-bench evaluation set and takes just 1 minute to run.: SWE-agent takes a GitHub issue and tries to automatically fix it, using GPT-4, or your LM of choice. It solves 12.47% of bugs in the SWE-bench evaluation set and takes just 1 minute to run. - princ...
- GitHub - BuilderIO/micro-agent: An AI agent that writes (actually useful) code for you: An AI agent that writes (actually useful) code for you - BuilderIO/micro-agent
- CofeAI/Tele-FLM-1T · Hugging Face: no description found
- MythoMax 13B by gryphe: One of the highest performing and most popular fine-tunes of Llama 2 13B, with rich descriptions and roleplay. #merge
- LLM Rankings | OpenRouter: Language models ranked and analyzed by usage across apps
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) ▷ #일반 (1 messages):
Mistral Large 2
- Mistral Large 2 showcases multilingual prowess: Mistral Large 2 excels in various languages, including English, French, German, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Dutch, Russian, Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Arabic, and Hindi.
- Mistral Large 2’s impressive language model: The performance of Mistral Large 2 makes it a noteworthy player in the field of multilingual language processing.
OpenAI ▷ #annnouncements (1 messages):
SearchGPTAI search features
- Introducing SearchGPT Prototype: OpenAI is testing SearchGPT, a new prototype that provides fast and timely answers with clear and relevant sources, intended to enhance search capabilities.
- This prototype will initially roll out to a small group of users for feedback before integration into ChatGPT, with more details available at OpenAI’s SearchGPT page.
- Feedback Loop for SearchGPT: Users will have the opportunity to provide feedback on SearchGPT during its testing phase, which is essential for refining the search experience.
- The feedback gathered will influence how SearchGPT is developed and integrated into the main ChatGPT platform.
OpenAI ▷ #ai-discussions (177 messages🔥🔥):
Mistral Model DownloadMacBook Pro PerformanceInternet Speed UpgradesVoice Features in AILlama 3.1 Accessibility
- Mistral Model Download Times: Users discussed lengthy download times for the Mistral Large model, with one user reporting it took 2.5 hours at their current internet speed.
- Another user highlighted achieving 18 tk/s on their MacBook Pro with the same model, indicating that performance is satisfactory despite slow download speeds.
- MacBook Pro Performance Enthusiasm: Conversations highlighted the MacBook Pro M2 Max’s capabilities, particularly with 96GB RAM, making it suitable for running various models locally.
- Users compared their setups, noting the differences in performance and the excitement around future upgrades like the M4 Max.
- Anticipation for Fast Internet: Several users expressed eagerness for faster internet connections, with one anticipating an upgrade to 1 Gbps fiber in December.
- Others shared their current speeds, with some having recently upgraded from 50 to 750 Mbps, enhancing their model download times.
- Voice Features in AI Tools: Discussion surrounded new AI voice features, with some users looking forward to access while others noted that not everyone has received the upgrade yet.
- One user humorously referenced the rollout frustrations, indicating that some features are still delayed for many users.
- Llama 3.1 Access on Different Platforms: Users explored ways to access and utilize the Meta Llama 3.1 model given the restrictions based on geographic location.
- Recommendations included using platforms like Groq or OpenWebUI for API access, emphasizing the need for affordable solutions for younger users new to AI.
Links mentioned:
- mistralai/Mistral-7B-v0.3 · Hugging Face: no description found
- EleutherAI/gpt-neo-125m · Hugging Face: no description found
OpenAI ▷ #gpt-4-discussions (8 messages🔥):
Feedback on GPT-4oSearchGPT API Availability
- Users express frustration with GPT-4o: Many users lament that after upgrading to GPT-4o, the model increasingly provides incorrect information and fails to reference sources directly, leading to confusion.
- One user mentioned the model often just repeats the user’s questions instead of providing accurate answers, stating ‘I felt the wise friend was long gone, only its dumb twin brother stay.’
- SearchGPT API still in question: There is speculation on whether SearchGPT will be available via API, but users feel it’s more important first to establish general access.
- One user suggested it could be months before broader availability, emphasizing the need for functionality over API discussions.
OpenAI ▷ #prompt-engineering (7 messages):
Memory Function CallsGuidance for Memory StorageSpecificity in EventsTypes of Information to Store
- Memory Function Calls Implementation: A user seeks to implement function calls for a chatbot to create, edit, and remove user memories, aiming for improved performance.
- Currently, the bot only stores memories about 60% of the time.
- Need for Clear Guidance: A member emphasized the importance of providing the chatbot with precise instructions on when and how to save memories.
- Suggesting that more concrete examples will aid the model in making accurate memory decisions.
- Storing Favorite and Worst Things: It was suggested that the bot should explicitly save information about users’ favorite and least favorite items, like food and games.
- Users mentioned the value of remembering important future events, such as birthdays and release dates.
- Specificity vs. Abstraction in Guidance: A user pointed out the need for specificity in the instructions to the bot, noting that vague input leads to inaccurate assumptions.
- The use of open variables was suggested to improve how the bot handles various memory events.
OpenAI ▷ #api-discussions (7 messages):
Function calls for chatbot memoriesGuidance for memory storageEvent types for memory savingSpecificity in user memory requirements
- Function calls for chatbot memories: A developer is working on function calls for their chatbot to create, edit, and remove user memories, but struggles with memory accuracy.
- Current memory storage success is around 60%, prompting a need for improved instructions.
- Need for more guidance in memory storage: A suggestion was made to provide the model with specific instructions on how to determine when and what to save as memories.
- This guidance could enhance the model’s ability to decide on valuable information to remember.
- Examples of memory types to store: One member suggested directly instructing the model to save users’ favorite and least favorite items like food, books, and games.
- They emphasized the importance of saving useful details for future interactions, such as events, age, and names.
- Clarification on event types for memory: The discussion included ambiguities around what constitutes an ‘event’, with mentions of calendar events like birthdays and holidays.
- Members noted the importance of broad categories for events, while also highlighting the need for specificity without limiting the scope.
- Importance of specificity in inputs: A participant advised on being specific, yet allowing for abstraction in the types of events to be saved in the memory.
- Using open variables was suggested as a means to better capture the diverse nature of possible events.
OpenAI ▷ #api-projects (2 messages):
Error uploading files to OpenAIPython code for file uploadVector stores configuration
- Error uploading files to OpenAI: A user reported receiving a 400 error when attempting to upload a txt file to OpenAI, stating that files with extensions [none] are unsupported.
- The user shared detailed error information and referred to the OpenAI documentation for supported file types.
- Python code for file upload: The user’s Python code for uploading files included using FastAPI and the OpenAI client, but resulted in an error message during execution.
- They mentioned trying all available documentation without success, indicating persistence in troubleshooting the upload issue.
- Vector stores configuration: The user attempted to configure vector stores using IDs from uploaded files within their provided Python code, but faced errors in both file uploads and vector store creation.
- There seems to be a focus on ensuring proper file handling and configuration setup in their code process.
Stability.ai (Stable Diffusion) ▷ #announcements (1 messages):
Stable Video 4DDynamic multi-angle video generationTechnical report release
- Introducing Stable Video 4D for Multi-Angle Generation: We are excited to announce Stable Video 4D, our first video-to-video generation model that transforms a single video into dynamic novel-view videos with eight different angles.
- This model enables users to tailor outputs by specifying camera angles, thus enhancing creativity in video production.
- Rapid Frame Generation with Stable Video 4D: Stable Video 4D generates 5 frames across 8 views in approximately 40 seconds, significantly improving efficiency in video processing.
- This innovative approach offers unprecedented versatility for users aiming to create high-quality videos quickly.
- Future Applications in Various Fields: Currently in research phase, Stable Video 4D aims to enhance applications in game development, video editing, and virtual reality.
- Ongoing improvements are expected, focusing on further enhancing the model’s capabilities and applications.
- Comprehensive Technical Report Released: In conjunction with the announcement of Stable Video 4D, a comprehensive technical report detailing methodologies, challenges, and breakthroughs has been released.
- Users can access the report for in-depth insights into the model’s development here.
- Availability on Hugging Face: The Stable Video 4D model is now available on Hugging Face, providing users easy access to this cutting-edge technology.
- This open access aims to foster experimentation and further development in the community.
Link mentioned: Stable Video 4D — Stability AI: We are pleased to announce the availability of Stable Video 4D, an innovative model that allows users to upload a single video and receive dynamic novel-view videos of eight new angles/views, deliveri…
Stability.ai (Stable Diffusion) ▷ #general-chat (147 messages🔥🔥):
Updates on Stability AI ProjectsUsage of Stable DiffusionDiscussion on Models and PerformanceLora Training TechniquesInpainting Techniques
- Stability AI expands capabilities of Stable Assistant: Stability AI announced new features for the Stable Assistant including Inpaint and Erase, allowing users to refine generated content and enhance their creative workflow.
- These tools enable endless iterations and the removal of unwanted elements, available for a free 3-day trial here.
- Mixing Stable Diffusion with Discord: A user inquired about using Stable Diffusion in Discord, expressing confusion over its use compared to Midjourney.
- It was suggested that users check the relevant Discord channels for updates and potential features linked to Stable Diffusion integration.
- Debate on Model Performance: There was a discussion about various models, with some asserting that a particular model performs better than SDXL, highlighting the importance of timing for new releases.
- Models like Kolors and Auraflow were mentioned for their promise, albeit users noted a crowded market with many alternatives available.
- Understanding Lora Training: Users discussed best practices for training Loras, focusing on whether full images or cropped ones should be used for specific features like eyes and mouths.
- The conversation illuminated strategies for Lora prompts, reinforcing the importance of detail in training datasets for enhanced results.
- Inpainting Techniques with Stable Diffusion: Users explored methods for inpainting, with suggestions to utilize img2img processes and tutorial resources to refine results.
- The principle of using prompts with context was shared as a means to successfully inpaint objects into scenes effectively.
Links mentioned:
- Image Viewer: no description found
- Tweet from Stability AI (@StabilityAI): Today, we’ve expanded Stable Assistant’s capabilities by introducing two new features: 🖌️ Inpaint: Replace the specified area with new content, generating endless iterations. 🫥 Erase: Remove unwa...
- Tweet from Elman Mansimov (@elmanmansimov): Images from Text: how it started (2015) how it is going (2021)
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
Eleuther ▷ #general (83 messages🔥🔥):
Flash Attention vs Traditional AttentionVRAM Usage in InferenceChunking in Attention MechanismsComparisons of Attention AlgorithmsMultiple-Choice Datasets and APIs
- Flash Attention Optimizes VRAM but Not Time: Members discussed that Flash Attention helps in linear VRAM usage during inference, but does not reduce time complexity, which remains quadratic.
- One noted that using FA with a long cache and a single query can actually be slower due to less parallelization across sequence dimensions.
- Google Paper vs Flash Attention: There was a disagreement on the credit given to the Google paper for developing Flash Attention, with members arguing it doesn’t have linear space usage with respect to sequence length.
- The discussion highlighted the subtle differences in the algorithms that impact memory and computation.
- Influence of Key-Value Cache on Performance: A key point raised was that the KV-Cache size increases linearly with sequence length, a factor that impacts VRAM but not compute time significantly.
- Members clarified that while Flash Attention improves memory efficiency, its computational overhead remains unchanged.
- Chunking Strategies for Attention Mechanisms: Several members discussed how Flash Attention implements chunking to reduce memory bandwidth and improve efficiency, shifting to smaller matrices.
- This method contrasts with naive implementations, as it enables better performance on hardware, leading to effective parallel processing.
- Multiple-Choice Dataset API Integration: A new member inquired about testing multiple-choice datasets in a non-English language using various AI services, seeking templates for parsing output.
- They expressed having API keys but struggling with coding, indicating the need for community support in implementing efficient testing methodologies.
Links mentioned:
- Context is Everything: Why Maximum Sequence Length Matters - Cerebras: GPU Impossible™ sequence lengths on Cerebras systems may enable breakthroughs in Natural Language Understanding, drug discovery and genomics.
- Context is Everything: Why Maximum Sequence Length Matters - Cerebras: GPU Impossible™ sequence lengths on Cerebras systems may enable breakthroughs in Natural Language Understanding, drug discovery and genomics.
Eleuther ▷ #research (51 messages🔥):
Inference Costs for ModelsMoE EfficiencyMeta Research StrategyAlphaProof BreakthroughxAI's Market Position
- Discussing Inference Costs for Model Providers: Members proposed that inference for models like Mistral should be free at scale, arguing for the efficiency of using either single layers or MoE across clusters.
- Concerns were raised that if batch inference is not used effectively, it could reduce advantages of MoE due to increased complexity.
- Meta’s Research Strategy Under Scrutiny: Discussion revealed that Meta’s approach involves utilizing various external research, pouring substantial resources into optimizing lines of code rather than leveraging broader model structures.
- One member cited a lack of understanding in Meta’s operational tactics, questioning their rationale against adopting more efficient methodologies.
- AlphaProof Success in Theorem Proving: The chat noted AlphaProof, an application built on AlphaZero and LLMs, managed to solve 4 IMO problems, achieving silver-medalist level according to DeepMind.
- Excitement surrounding this breakthrough emphasized the potential ramifications for competitive mathematical methodologies with LLM integration.
- xAI’s Position Changes Amidst Competition: Conversations reflected skepticism around xAI’s narrative, with members indicating that its initial advantage may diminish due to effective competition from DeepMind’s advancements.
- Discussion highlighted Musk’s financial influence but questioned the long-term efficacy of xAI, focusing on the smart utilization versus reckless spending of resources.
- Protein Language Models Presentation: One member announced their participation in ICML’s ML4LMS Workshop, showcasing research on how protein language models can reveal facets of viral mimicry.
- The announcement brought attention to emerging intersections between biology and AI, indicating a growing focus within machine learning communities.
Links mentioned:
- PERSONA: A Reproducible Testbed for Pluralistic Alignment: The rapid advancement of language models (LMs) necessitates robust alignment with diverse user values. However, current preference optimization approaches often fail to capture the plurality of user o...
- EM Distillation for One-step Diffusion Models: While diffusion models can learn complex distributions, sampling requires a computationally expensive iterative process. Existing distillation methods enable efficient sampling, but have notable limit...
- Tweet from Julian Schrittwieser (@Mononofu): Our latest work AlphaProof, building on AlphaZero, LLMs and the @leanprover theorem prover, combined with AlphaGeometry 2 managed to solve 4 IMO problems and achieve silver-medalist level! 🚀 More at...
- AI models collapse when trained on recursively generated data - Nature: Analysis shows that indiscriminately training generative artificial intelligence on real and generated content, usually done by scraping data from the Internet, can lead to a collap...
- Prism: mapping interpretable concepts and features in a latent space of language | thesephist.com: no description found
Eleuther ▷ #scaling-laws (9 messages🔥):
Meta scaling lawsData scaling functions
- Meta’s Scaling Laws Under Scrutiny: A user questioned whether the scaling laws from Meta are influenced by data superposition, suggesting that optimal data amounts do not scale linearly.
- This prompted discussions on the calculation of optimal data amounts using an exponential function.
- Chinchilla’s Token Calculation Generalization: The conversation mentioned generalizing Chinchilla to 20 tokens per parameter, noting that optimal values did not change significantly according to their function.
- This led to an acknowledgment that while scaling seems distorted, the reasoning appears logical.
- Demand for Inverse Data Analysis: One participant expressed that while the findings are interesting, an inverse analysis would be more beneficial, focusing on more data per parameter over size.
- This insight calls for further investigation into how increasing data better optimizes performance relative to model size.
Eleuther ▷ #interpretability-general (2 messages):
Awesome Interpretability RepositoryNDIF Llama3-405b Access Opportunity
- Explore the Awesome Interpretability Repository: The Awesome Interpretability in Large Language Models GitHub repository provides a comprehensive collection of resources focused on interpretability in LLMs.
- This repository serves as a valuable hub for researchers exploring the nuanced understanding of large language models.
- NDIF Offers Llama3-405b Access for Experiments: The National Deep Inference Fabric (NDIF) is inviting AI researchers to apply for access to the Llama3-405b model for groundbreaking experiments via the new programming interface described on their website.
- Participants will receive terabytes of GPU resources and support while contributing innovative research, moving beyond conventional benchmarking.
Links mentioned:
- National Deep Inference Fabric: NDIF is a research computing project that enables researchers and students to crack open the mysteries inside large-scale AI systems.
- GitHub - ruizheliUOA/Awesome-Interpretability-in-Large-Language-Models: This repository collects all relevant resources about interpretability in LLMs: This repository collects all relevant resources about interpretability in LLMs - ruizheliUOA/Awesome-Interpretability-in-Large-Language-Models
Eleuther ▷ #lm-thunderdome (2 messages):
Evaluating MMLU on External APIsCalculating VRAM Requirements
- Evaluating MMLU on External APIs: A member is seeking assistance with evaluating MMLU on external APIs similar to OpenAI’s schema, which includes log_probs.
- They referenced a GitHub PR that introduces a superclass for API models, aiming for modularity and improved request handling.
- How to calculate VRAM requirements for model evaluation: A query was raised about the methods for calculating the necessary VRAM to evaluate a model effectively.
- This is a common concern as VRAM needs can significantly impact performance during model assessments.
Link mentioned: Refactor API models by baberabb · Pull Request #2008 · EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness: This PR introduces a new superclass for API request models, providing: Modularity for downstream classes Overloadable methods for request transformation, API requests and response parsing Tokeniza…
CUDA MODE ▷ #general (2 messages):
NCCL PerformanceFlute Matrix Multiplications
- NCCL Overlap Challenges: A user raised concerns about achieving computation overlap with NCCL during the backward pass in their training setup using NCCL Issue #338. They noted that while the lecture on NCCL suggested it was feasible, implementing it proved to be more complex than expected.
- Introduction of Flute for LLMs: Another user shared the repository for Flute, a project focused on fast matrix multiplications specifically designed for lookup table-quantized LLMs and its applications. This tool aims to optimize the performance of LLM processing.
Links mentioned:
- computation overlapped with nccl get much slower · Issue #338 · NVIDIA/nccl: I used the environment from https://github.com/NVIDIA/DeepLearningExamples/tree/master/MxNet/Classification/RN50v1.5 to train resnet-50 with multiple GPUs (with horovod using nccl), and found the d...
- GitHub - HanGuo97/flute: Fast Matrix Multiplications for Lookup Table-Quantized LLMs: Fast Matrix Multiplications for Lookup Table-Quantized LLMs - HanGuo97/flute
CUDA MODE ▷ #triton (1 messages):
CUDA profiling toolsNsight ComputeTriton testing helpers
- Analyze Triton Kernels with CUDA Tools: You can analyze triton kernels just like other CUDA kernels using tools like Nsight Compute for detailed profiling.
- Nsight Compute offers guided analysis to optimize CUDA kernels, including GPU throughput and warp state statistics.
- Get Started with Nsight Compute: For those interested in optimizing GPU performance with CUDA or OptiX, NVIDIA Nsight Compute is an essential tool that supports both an interactive UI and command-line usage.
- There is also an overview video showcasing how guided analysis in Nsight Compute aids in making CUDA kernel optimizations.
- Triton Testing Helpers Available: Triton provides several built-in helpers for benchmarking performance, including triton.testing.
- This feature includes functions like
do_benchandperf_reportto facilitate performance measurement with a concise API.
- This feature includes functions like
Links mentioned:
- NVIDIA Nsight Compute: An interactive profiler for CUDA and NVIDIA OptiX.
- triton.testing — Triton documentation: no description found
CUDA MODE ▷ #torch (1 messages):
andreaskoepf: PyTorch 2.4 was released: https://pytorch.org/blog/pytorch2-4/
CUDA MODE ▷ #cool-links (1 messages):
AlphaProofAlphaGeometry 2Mathematical reasoningAGI potential in math
- AlphaProof and AlphaGeometry 2 advance math reasoning: Breakthrough models AlphaProof and AlphaGeometry 2 are designed to solve advanced reasoning problems in mathematics, achieving a silver medal level in competitions.
- These models signify a step toward developing AGI with enhanced mathematical reasoning capabilities, potentially unlocking advancements in science and technology.
- Challenges of current AI in math: Despite progress, current AI systems still face challenges in general math problem-solving due to limitations in reasoning skills and available training data.
- Previous models have provided insights into novel algorithms and addressed open problems, but ongoing development is needed for broader mathematical applications.
Link mentioned: AI achieves silver-medal standard solving International Mathematical Olympiad problems: Breakthrough models AlphaProof and AlphaGeometry 2 solve advanced reasoning problems in mathematics
CUDA MODE ▷ #jobs (3 messages):
ML/AI Career RoadmapProgramming and Math Background
- Seeking Guidance on ML/AI Career Roadmap: A member is looking for help in designing a roadmap to secure full-time positions and internships in ML/AI and shared a Google Document with details.
- They mentioned they are open to any suggestions and can dedicate long hours to meet their goals.
- Exploring Programming and Math Backgrounds: Another member inquired about the programming and math background of those pursuing ML/AI roles.
- This seeks to understand the foundational skills necessary for success in the field.
Link mentioned: ML Roadmap: 3 months - (sept, oct, nov) roadmap Statistics: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MXaJ7sa7q-8&list=PL0KQuRyPJoe6KjlUM6iNYgt8d0DwI-IGR&t=11s (1 week) Linear Algebra - https://www.youtube.com/wat…
CUDA MODE ▷ #beginner (6 messages):
Quantization techniques for modelsMemory issues with fp16 execution
- Memory Limitations with FP16 Execution: A user expressed frustration regarding insufficient memory to run the model at fp16 precision, highlighting a common issue faced by developers.
- This prompted suggestions for exploring alternative solutions to optimize memory usage.
- Exploring Quantization with BnB: Another user recommended investigating quantization techniques using the bitsandbytes (BnB) library as a potential workaround for the memory issue.
- This recommendation sparked confusion, with a user questioning the concept of quantization.
- Understanding Quantization for Model Efficiency: In response to the confusion, it was explained that quantization reduces memory usage by representing data with fewer bits, which benefits large language models (LLMs).
- The discussion included various quantization methods, such as AWQ, GPTQ, and AQLM, detailing their roles in optimizing model performance.
Link mentioned: Quantization: no description found
CUDA MODE ▷ #torchao (1 messages):
marksaroufim: <@1213148470664495114>
CUDA MODE ▷ #ring-attention (18 messages🔥):
Blockwise Attention ImplementationKV Cache SplittingRing Attention in Llama 3Pipeline ParallelismLlama 3.1 Features
- Blockwise Attention Implementation Confusion: A user questioned where to split the input sequence into blocks for blockwise attention in the Llama 3 architecture, specifically after projecting the input into Q, K, and V.
- Another member clarified that splitting is typically done at the input level, maintaining that it’s generally a non-issue whether it occurs before or after projection.
- KV Cache Passing in Ring Attention: A user inquired how the model would handle attention across tokens after the input sequence is split and noted the lack of a KV cache at that point.
- A member responded that the ‘ring’ approach involves passing KV shards among workers, ensuring each one accesses the complete necessary attention data.
- Layered Processing with Ring Attention: Questions arose about processing chunks of input through all 28 layers of Llama 3 and passing computed KV to multiple GPUs for parallel processing.
- It was emphasized that full attention scores must be computed at every layer, necessitating ring attention to function at each attention layer.
- Combining Pipeline and Context Parallelism: A user discussed implementing both pipeline parallelism and context parallelism (ring attention) across GPUs, clarifying how layers would be distributed among them.
- Members confirmed that managing KV chunks over multiple layers is essential and that these methods could coexist effectively within the same system.
- Using Llama 3 for Inference with Long Context Models: A user expressed difficulties with the KV cache size when implementing Ring Attention for inference with long context models, highlighting memory constraint issues on single devices.
- The conversation included a note that while Llama 3.1 may handle longer contexts natively, the user is still working with Llama 3.
CUDA MODE ▷ #off-topic (6 messages):
Slider Game LaunchGame Comparison with Baba Is YouNew Member IntroductionBusiness Model Discussion
- Slider Launches as a Free Puzzle Game: Slider is a new free-to-play puzzle game that just got published and is worth checking out.
- The creator mentioned that the game is easier than Baba Is You, as players can tell when they are making progress.
- Game Difficulty Comparison: A member commented on the difficulty of Baba Is You, saying they weren’t smart enough to beat it, but they would check out Slider.
- The game’s creator reassured them that Slider is easier and allows clearer tracking of progress.
- Welcome to a New Member!: A new member introduced themselves in the chat, expressing excitement about joining.
- This friendly greeting contributed to a welcoming atmosphere in the community.
- Discussion on Business Models in the Gaming Space: A member speculated about the potential adoption of the Adam Newman business model, which involves attracting VC money with questionable practices.
- They clarified that while they find this scenario possible, they do not actually suspect any specific company of doing so.
CUDA MODE ▷ #irl-meetup (2 messages):
ICML ConferenceCoffee Meet-up
- ICML Arrival and Coffee Invite: @muhtasham just arrived at the ICML and expressed interest in grabbing coffee tomorrow.
- Could connect with anyone else attending, fostering networking opportunities during the conference.
- Delayed Response from Erik: Erik responded, acknowledging a delay in getting back and confirming he’s still at the conference.
- This highlights the busy environment at ICML, where attendees are engaged in activities.
CUDA MODE ▷ #llmdotc (96 messages🔥🔥):
FP8 Training ChallengesOutlier Detection in TrainingmuP and Unit ScalingModel Performance ImprovementsGitHub Pull Requests
- Challenges in FP8 Training: A member reported that their FP8 124M run isn’t converging to the same loss as the BF16 baseline, potentially only matching GPT2’s performance.
- This struggle reflects broader concerns about training stability and outcomes when utilizing FP8 compared to BF16.
- Outlier Detection Mechanism in Focus: Discussing skipped updates due to outliers, it was highlighted that including outliers in the moving average impacts the outcome negatively and can lead to convergence issues.
- A new approach to outlier detection was introduced via a PR (pull request #711) that aims to exclude outliers from the moving average calculation.
- Exploration of muP and Unit Scaling: Members discussed the potential benefits of the Unit Scaling approach in the context of muP, suggesting that it might alleviate some training pitfalls seen with FP8.
- Although there’s skepticism about whether Unit Scaling will solve all issues, its lead author’s proximity may enable further collaboration.
- Performance Improvements in Training: There are ongoing efforts to implement performance improvements, particularly for matmul operations that benefit larger models significantly.
- One member shared their plan to introduce another performance improvement shortly, emphasizing its greater impact on larger models.
- GitHub Pull Requests Progress: Progress was made in merging PRs to streamline model initialization and address platform compatibility, with excitement about upcoming changes.
- Collaborative efforts to review and polish PRs continue, with members encouraging each other to check for potential race conditions and conflicts.
Links mentioned:
- u-$μ$P: The Unit-Scaled Maximal Update Parametrization: The Maximal Update Parametrization ($μ$P) aims to make the optimal hyperparameters (HPs) of a model independent of its size, allowing them to be swept using a cheap proxy model rather than the full-si...
- IEEE-754 Floating Point Converter: no description found
- Restore from master weights (& allow restoring from a checkpoint of different precision) by ademeure · Pull Request #702 · karpathy/llm.c: This is fully deterministic for new checkpoints where the new rng_state_last_update is saved, so that stochastic rounding from master weights is done with the exact same seeds (while restoring the ...
- Build software better, together: GitHub is where people build software. More than 100 million people use GitHub to discover, fork, and contribute to over 420 million projects.
- Outlier detection: catch more outliers by not updating moving average with skipped updates by ademeure · Pull Request #711 · karpathy/llm.c: This is an improvement to the znorm/zgrad update skipping mechanisms (-sl and -sg) to avoid skipping updates for outliers. Note that znorm will still be updated if zgrad is an outlier that causes t...
- Model init cleanup by ngc92 · Pull Request #694 · karpathy/llm.c: consolidate model parameter allocation to a single source location made gradient buffer accumulation eager moved encoder determinism helper buffers so that they are eagerly allocated by forward -> ...
- jrahn/gpt2_350M_edu_hermes · Hugging Face: no description found
CUDA MODE ▷ #rocm (1 messages):
andreaskoepf: https://x.com/AMD/status/1816168883587538946
CUDA MODE ▷ #lecture-qa (2 messages):
Lecture 24 SlidesGitHub Repository Updates
- Inquiry about Lecture 24 Slides Availability: A member inquired whether the slides for Lecture 24: Scan at the Speed of Light will be available soon.
- This request highlights a continued interest in educational materials related to CUDA Mode lectures.
- Call for GitHub Slides Update: Another member asked a peer if they had their slides handy and to update the GitHub repository with a pull request.
- This reflects ongoing collaboration and contributions within the community to keep educational resources up-to-date.
Link mentioned: GitHub - cuda-mode/lectures: Material for cuda-mode lectures: Material for cuda-mode lectures. Contribute to cuda-mode/lectures development by creating an account on GitHub.
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #news (11 messages🔥):
DeepMind AI achievementsRunway AI training data leaksOpenAI's SearchGPT prototype
- DeepMind AI achieves Silver at IMO 2024: A discussion emerged around whether a Google DeepMind AI truly earned a silver medal at the IMO 2024, referencing Google’s own blog stating it meets ‘silver-medal standard.’
- Concerns were raised about the clarity of the criteria, with skeptics suggesting Google might have adjusted challenges to highlight its AI’s performance.
- Runway AI’s training data sources exposed: A leak revealed that Runway’s praised AI video generation tool was trained on scraped content from YouTube and pirated films, raising ethical questions.
- The revelation caused a stir in the community, with comments indicating this discourse could become quite heated.
- OpenAI enters search market with SearchGPT: OpenAI announced the testing of SearchGPT, a prototype aimed at providing fast answers and relevant sources, which will be trialed by 10,000 users.
- They plan to gather feedback for integration into ChatGPT, fueling excitement about potential enhancements in AI search capabilities.
Links mentioned:
- Runway Ripped Off YouTube Creators: A leaked internal document shows Runway’s celebrated Gen-3 AI video generator collected thousands of YouTube videos and pirated movies for training data.
- Did a Google Deepmind AI really get Silver on IMO 2024?: Resolved YES. The Verge posted an article claiming this which is now deleted. Possibly The Verge just accidentally broke the press embargo? If anyone has the full text that would be appreciated. htt...
- Tweet from Andrew Curran (@AndrewCurran_): OpenAI is entering the search market. 10,000 test users will get early access. Quoting OpenAI (@OpenAI) We’re testing SearchGPT, a temporary prototype of new AI search features that give you fast a...
- AI achieves silver-medal standard solving International Mathematical Olympiad problems: Breakthrough models AlphaProof and AlphaGeometry 2 solve advanced reasoning problems in mathematics
- Video sourcing - Jupiter.xlsx: Keywords from REDACTED (Cleaned 3d,Yes,[COLUMN CONTENTS REDACTED BY 404 MEDIA] aerial,Yes alien,Yes animation,Yes anime,Yes apocalypse,Yes apollo,Yes astronaut,Yes beach,Yes bear,Yes beard,Yes bed,Ye...
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #ml-questions (9 messages🔥):
Books on Modern ArchitecturesLLAMA 3.1 AnnealingFoundations of Computer Vision Book
- Recommendations for Books on Modern Architectures: A member sought recommendations for books on modern architectures like Diffusion and Transformers, needing resources for an ML course.
- I just snagged some copies of rasbt’s “Building LLMs from scratch” but was looking for more focused titles on the mentioned architectures.
- Understanding LLAMA 3.1 Annealing: Discussion focused on the LLAMA 3.1 technical report, particularly on the concept of annealing and reducing the learning rate to 0 during training.
- One member explained that this low learning rate helps prevent overshooting optimal points and might enhance leaderboard performance through careful pretraining.
- Suggestions for Additional Reading Materials: A member suggested the new book Foundations of Computer Vision, which covers modern computer vision topics if budget allows.
- There were also mentions of Chris Bishop’s new deep learning book and Kevin Murphy’s probabilistic ML books that might include relevant discussions.
Link mentioned: Understanding Deep Learning: no description found
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #ml-drama (19 messages🔥):
Student Open Letter ContestNew York Times OpinionsB2B Pricing CompetitionGPT-4 Magnet LinkParker Conrad and Rippling
- Student Open Letter Contest Raises Eyebrows: A member shared a New York Times article about a ‘student open letter contest’, sparking surprise about its coverage.
- Why is this on New York Times? questioned another member, showing skepticism about the paper’s opinion pieces.
- Criticism of New York Times Opinions: Several members criticized the New York Times’ opinion section with one remarking that it is ‘shit’ and expressing confusion over its article choices.
- The discussion highlighted a general discomfort with mainstream media narratives.
- B2B Pricing Dynamics: A member remarked on how surprising it is that a certain company is somewhat on par with Databricks, to which another clarified that it’s due to their B2B pricing strategy and lack of competition.
- This led to a broader discussion about business strategies and market positions.
- Desire for Access to GPT-4: A user humorously expressed a longing for a magnet link to GPT-4, reflecting a desire for easy access to resources in the AI community.
- Another member chimed in about a future scenario where they would download an xjdr magnet link without hesitation.
- Parker Conrad’s Reputation: Questions arose about Parker Conrad, identified as the founder of Rippling, with one member noting they never got a good vibe from his companies.
- The conversation hinted at a mix of curiosity and skepticism surrounding his entrepreneurial journey.
Link mentioned: Tweet from Alex Cohen 🤠 (@anothercohen): Update: Holy shit Quoting Alex Cohen 🤠 (@anothercohen) Y’all want to see a dead body?
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #random (50 messages🔥):
GPT-4o Training Data InsightsImportance of Prompt DiversityGalactica LLM RetrospectiveSearchGPT TestingChallenges in Dataset Diversity
- GPT-4o Training Data Insights with BPE Tokenizer: A paper was mentioned discussing what the BPE tokenizer reveals about training data for models like GPT-3.5 and GPT-4o, focusing on token distributions across languages and domains.
- The paper proposes serious hypotheses about the data mixture used in these models based on token analysis.
- Prompt Diversity and Its Importance: Members discussed the critical role of prompt diversity in relation to the quantity and quality of preference-scored responses.
- They highlighted that while some diversity comes from sampling distributions, acquiring genuinely new prompts remains a significant challenge.
- Galactica LLM Leads to Future Developments: In an upcoming interview, insights about the Galactica LLM and its lead, Ross Taylor, will be sought, particularly regarding past challenges and potential future work.
- The community expressed interest in how the project evolved from challenges faced in L2 to reaching SoTA in L3.
- SearchGPT Testing Announced by OpenAI: OpenAI has announced a small testing group for SearchGPT, a new AI search feature aimed at providing fast, relevant answers.
- Users speculated on factors like access and related features, leading to humorous comments about potential bribery for access.
- Challenges in Creating Diverse Datasets: The difficulty in acquiring diverse datasets was discussed, emphasizing that even paid prompts often lack true diversity in formats and content.
- Members shared techniques for evaluating diversity, such as classifying prompts according to a human knowledge taxonomy, but acknowledged logistical challenges and perverse incentives in dataset collection.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Jimmy Apples 🍎/acc (@apples_jimmy): There’s something in the air. A schizo vibe of hope. Lets get mathy.
- Tweet from Ross Taylor (@rosstaylor90): Was not expecting a hastily written, early morning Galactica retrospective to bounce so much - given it happened 3000 years ago in AI time. To close the topic, here’s a great talk below by Sean Murra...
- Tweet from Alexander Doria (@Dorialexander): Uh that’s a paper for me: what BPE tokenizer reveals of training data. With serious hypothesis on GPT-3.5, GPT-4o, Claude, data mixture per languages/domains based on token distributions. https://open...
- Tweet from TestingCatalog News 🗞 (@testingcatalog): ChatGPT will get a separate entry point for SearchGPT on top of the main sidebar 👀
- Tweet from OpenAI (@OpenAI): We’re testing SearchGPT, a temporary prototype of new AI search features that give you fast and timely answers with clear and relevant sources. We’re launching with a small group of users for feedba...
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #memes (39 messages🔥):
Perplexity's OverhypeZuckerberg vs OpenAI StrategiesWeb Browsing Capabilities of LLMsResearch Queries and Agent Efficiency
- Perplexity faces criticism for being overhyped: Members expressed skepticism regarding Perplexity, highlighting its reliance on top results and inadequate performance for complex searches, leading to allegations of it being overvalued.
- One user noted that using Google directly often yields better and faster results than relying on Perplexity.
- Zuckerberg’s approach vs OpenAI’s: Discussion contrasted Zuckerberg’s wide-reaching op-ed strategy with OpenAI’s more focused targeting of DC insiders, showcasing differences in audience engagement.
- One member humorously noted the ongoing ‘cagefight’ between tech leaders, suggesting heightened competition amid differing publishing tactics.
- Web Browsing capabilities are essential for LLMs: Members discussed the limitations of LLM’s web browsing abilities, underscoring the need for more profound search processes to yield useful results beyond the first page of search results.
- A user lamented that while web browsing is expected to enhance capabilities, it often leads to slower processing and higher inference costs.
- The potential for improved research agents: Users suggested that a sophisticated search agent capable of deep diving into results could provide substantial value, though this would inherently raise costs significantly.
- There was a consensus that current offerings like Perplexity fail to utilize deeper search methods or iterate effectively for complex inquiries.
Link mentioned: Tweet from kif (@kifleswing): In ChatGPT’s recent search engine announcement, they ask for “music festivals in Boone North Carolina in august” There are five results in the example image in the ChatGPT blog post : …
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #rlhf (1 messages):
Pluralistic AlignmentSynthetic PersonasPersona Hub
- Introducing PERSONA Paper on Pluralistic Alignment: Synth Labs announced a new paper titled PERSONA: A Reproducible Testbed for Pluralistic Alignment, evaluating how language models align with diverse user values using 1,586 synthetic personas and 317,200 preference pairs.
- These personas reflect real-world diversity, integrating traits based on the US census along with idiosyncratic features.
- Comparison to Persona Hub: A discussion arose comparing this new paper to the recently discussed Persona Hub project, though it remains unclear how similar they actually are.
- A user mentioned that according to goose man, the two concepts are actually distinct.
Link mentioned: Tweet from SynthLabs (@synth_labs): 🚨New paper🚨 PERSONA: A Reproducible Testbed for Pluralistic Alignment We evaluate how LMs align with diverse user values using 1,586 synthetic personas & 317,200 preference pairs Personas reflect…
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #reads (2 messages):
Future of AI ControlOpenAI Rule-Based Reward Paper
- Urgent Questions on AI Control: Sam Altman emphasizes that the future of AI hinges on whether the U.S. will foster a globally beneficial technology or allow authoritarian regimes to gain power. He notes that there is no third option and urges for a strategic decision on this matter.
- With continued progress in AI, Altman warns that authoritarian governments are poised to invest heavily to catch up and potentially overtake the U.S., hinting at the stakes involved.
- Discussion on OpenAI’s Rule-Based Reward Paper: A member inquired if anyone had read the OpenAI Rule-Based Reward paper, likening it to OpenAI’s CAI approach.
- Some members noted that another contributor has indeed read it and engaged in a discussion, suggesting shared interest in its implications.
Link mentioned: Opinion | Sam Altman: AI’s future must be democratic - The Washington…: no description found
Latent Space ▷ #ai-general-chat (127 messages🔥🔥):
SearchGPT LaunchAI at IMORule-Based RewardsLLM as JudgeSynthetic Data Concerns
- SearchGPT launched by OpenAI: OpenAI announced the launch of a prototype called SearchGPT aimed at improving search capabilities beyond current offerings.
- The prototype will initially be tested with a small group of users for feedback before being integrated into ChatGPT for real-time operations.
- AI achieves Silver Medal at IMO: Google DeepMind presented a hybrid AI system that achieved a silver medal level performance at the International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) by fully solving 4 out of 6 problems.
- This program combined AlphaProof for formal reasoning and AlphaGeometry 2, showcasing significant advancements in AI’s mathematical problem-solving capabilities.
- OpenAI’s Rule-Based Rewards for AI Safety: OpenAI introduced Rule-Based Rewards (RBRs) to align AI behavior without extensive human data collection, aiming to enhance system safety.
- The RBR approach utilizes fewer manually labeled examples while allowing for adaptive responses to changing safety policies.
- Grading Notes for LLM as Judge: Databricks introduced Grading Notes to enhance the reliability of LLMs as judges in specialized domains, functioning as evaluation rubrics.
- These notes support domain-specific AI applications by providing structured guidelines for LLM evaluations.
- Concerns about Synthetic Data in AI Training: A recent paper raised concerns about the risks of relying too heavily on synthetic data for AI training, indicating that it may lead to model collapse over successive generations.
- Experts in the field emphasize the importance of diverse training inputs to maintain information quality and prevent degradation in model performance.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Jim Fan (@DrJimFan): LLMs are alien beasts. It is deeply troubling that our frontier models can both achieve silver medal in Math Olympiad but also fail to answer "which number is bigger, 9.11 or 9.9"? The latter ...
- - YouTube: no description found
- Tweet from Matei Zaharia (@matei_zaharia): How can you make LLM-as-judge reliable in specialized domains? Our applied AI team developed a simple but effective approach called Grading Notes that we've been using in Databricks Assistant. We ...
- Tweet from Aidan McLau (@aidan_mclau): >be google >build cool ai! >ai does well on math. >yay! >be openai >wait for google to drop cute math model >launch fire competing search engine that could potentially blow up go...
- Tweet from Alexandr Wang (@alexandr_wang): 1/ New paper in Nature shows model collapse as successive model generations models are recursively trained on synthetic data. This is an important result. While many researchers today view synthetic ...
- Tweet from Noam Brown (@polynoamial): Very impressive result from @GoogleDeepMind! They convert hard math problems into the formal reasoning language Lean, and then use an AlphaZero-style approach to find solutions. This, combined with th...
- Tweet from Aditya P. Advani (@aditya_advani): @latentspacepod @lvdmaaten @swyx @vibhuuuus @picocreator @eugeneyan In the spirit of rapid-fire recaps, my Open Source Arxiv2Paper generator ELDO made this 2 min video for the club's viewing pleas...
- Tweet from Hassan Hayat 🔥 (@TheSeaMouse): Several things interesting about the paper 1. They only needed to manually label about 500 examples (gold data) 2. The behavior policy is just a prompt We're starting to see how synthetic data ...
- Tweet from Lilian Weng (@lilianweng): Rule-based rewards (RBRs) use model to provide RL signals based on a set of safety rubrics, making it easier to adapt to changing safety policies wo/ heavy dependency on human data. It also enables us...
- Tweet from Deedy (@deedydas): Google just dropped an elite AI mathematician. It's a neuro-symbolic system that formalizes problems into Lean, a formal language, with a fine-tuned Gemini and uses AlphaZero-style search to solv...
- Tweet from Ji-Ha (@Ji_Ha_Kim): If anyone is interested, OpenAI did work similar to the new AlphaProof 2 years ago, at a smaller scale, and has written a paper on it. https://openai.com/index/formal-math/
- Tweet from Julia Kempe (@ICML) (@KempeLab): How to leverage AI-synthesized data without catastrophic degradation? Rank-and-prune feedback, from humans or even weaker models, provably restores and even surpasses original performance! See https:/...
- Tweet from morgan — (@morqon): openai’s search experiment has a dedicated side-tab for displaying link results, no burying the website (and no ads)
- Tweet from Chip Huyen (@chipro): Building a platform for generative AI applications https://huyenchip.com/2024/07/25/genai-platform.html After studying how companies deploy generative AI applications, I noticed many similarities in...
- Tweet from Kyle Wiens (@kwiens): Hey @AnthropicAI: I get you're hungry for data. Claude is really smart! But do you really need to hit our servers a million times in 24 hours? You're not only taking our content without payin...
- Tweet from Timothy Gowers @wtgowers (@wtgowers): Google DeepMind have produced a program that in a certain sense has achieved a silver-medal peformance at this year's International Mathematical Olympiad. 🧵 https://deepmind.google/discover/blo...
- Tweet from martin_casado (@martin_casado): I'm shocked. Just shocked that continually averaging a data corpus without exogenous inputs results in degraded information quality. Doomer ouroboros arguments were always silly. But they get d...
- Tweet from Timothy Gowers @wtgowers (@wtgowers): The main qualification is that the program needed a lot longer than the human competitors -- for some of the problems over 60 hours -- and of course much faster processing speed than the poor old huma...
- Tweet from kif (@kifleswing): In ChatGPT's recent search engine announcement, they ask for "music festivals in Boone North Carolina in august" There are five results in the example image in the ChatGPT blog post : ...
- Tweet from lmsys.org (@lmsysorg): We are thrilled to announce the milestone release of SGLang Runtime v0.2, featuring significant inference optimizations after months of hard work. It achieves up to 2.1x higher throughput compared to...
- Tweet from OpenAI (@OpenAI): We’ve developed Rule-Based Rewards (RBRs) to align AI behavior safely without needing extensive human data collection, making our systems safer and more reliable for everyday use. https://openai.com/i...
- Tweet from Sam Altman (@sama): we think there is room to make search much better than it is today. we are launching a new prototype called SearchGPT: https://openai.com/index/searchgpt-prototype/ we will learn from the prototype,...
- Tweet from prerat (@prerationalist): it's happening dot gif
- Tweet from Julian Schrittwieser (@Mononofu): Our latest work AlphaProof, building on AlphaZero, LLMs and the @leanprover theorem prover, combined with AlphaGeometry 2 managed to solve 4 IMO problems and achieve silver-medalist level! 🚀 More at...
- Tweet from Eliezer Yudkowsky ⏹️ (@ESYudkowsky): Paul Christiano and I previously worked hard to pin down concrete disagreements; one of our headers was that Paul put 8% probability on "AI built before 2025 IMO reaches gold level on it" and ...
- Tweet from OpenAI (@OpenAI): We’re testing SearchGPT, a temporary prototype of new AI search features that give you fast and timely answers with clear and relevant sources. We’re launching with a small group of users for feedba...
- Tweet from Hieu Pham (@hyhieu226): This is super impressive. Sure it's a silver, but an almost-gold silver. Look, the AI got 28 points, fully solving 4 problems, while the cutoff for gold is 29 points. If @GoogleDeepMind tried to...
- Tweet from Crémieux (@cremieuxrecueil): A new paper in Nature found that you cannot, in fact, train AIs on AI-generated data and expect them to continue improving. What happens is actually that the model collapses and ends up producing non...
- Tweet from Rylan Schaeffer (@RylanSchaeffer): For anyone interested in model collapse, I strongly urge people to look at our COLM 2024 paper https://arxiv.org/abs/2404.01413 Model collapse appears when researchers intentionally induce it in ways...
- Tweet from Google DeepMind (@GoogleDeepMind): We’re presenting the first AI to solve International Mathematical Olympiad problems at a silver medalist level.🥈 It combines AlphaProof, a new breakthrough model for formal reasoning, and AlphaGeome...
- Tweet from Jimmy Apples 🍎/acc (@apples_jimmy): There’s something in the air. A schizo vibe of hope. Lets get mathy.
- Tweet from Sam Altman (@sama): AI progress will be immense from here, and AI will be a critical national security issue. i wrote an op-ed for the washington post about why the U.S. need to maintain its lead in developing in AI, ra...
- Tweet from Datenschatz (@datenschatz): @casper_hansen_ If you believe OpenAI's video, SearchGPT offered the user two specific dates to watch nudibranchs in Half Moon Bay, while Perplexity vaguely suggests the 'winter season' to...
- Tweet from Michael Nielsen (@michael_nielsen): Remarkable: Quoting Timothy Gowers @wtgowers (@wtgowers) Google DeepMind have produced a program that in a certain sense has achieved a silver-medal peformance at this year's International Math...
- Tweet from Jeff Dean (@🏡) (@JeffDean): AI System Achieves Silver Medal-level score in IMO The International Mathematical Olympiad (IMO) is the oldest, largest & most prestigious competition for young mathematicians. Every year, countries...
- Tweet from Noam Brown (@polynoamial): 5 years ago we revealed Pluribus, the first superhuman multiplayer poker AI. It cost only $150 to train. Why did poker take longer than Go? And how did it end up being so cheap? The answer is a cautio...
- Tweet from Andrej Karpathy (@karpathy): Jagged Intelligence The word I came up with to describe the (strange, unintuitive) fact that state of the art LLMs can both perform extremely impressive tasks (e.g. solve complex math problems) while...
- Opinion | Sam Altman: AI’s future must be democratic - The Washington…: no description found
LlamaIndex ▷ #blog (2 messages):
Structured Data ExtractionLlamaExtractPydantic IntegrationLLM-powered ETL
- Launch of Structured Extraction Capabilities: A new release enables structured extraction capabilities in any LLM-powered ETL, RAG, and/or agent pipeline, including full support for async and streaming functionalities.
- Users can define a Pydantic object and attach it to their LLM using
as_structured_llm(…)for streamlined implementation.
- Users can define a Pydantic object and attach it to their LLM using
- Introducing LlamaExtract for Data Extraction: An early preview of LlamaExtract, a managed service for extracting structured data from unstructured documents, was introduced today.
- The service allows users to infer a human-editable schema from documents, enabling structured extraction based on user-defined criteria.
LlamaIndex ▷ #general (98 messages🔥🔥):
OpenAI Calls with MultiStepQueryEngineRAG Chatbot DevelopmentUpdating Knowledge Graph Node EmbeddingsDocument Summary Index ErrorsChunking and Triple Extraction Modifications
- OpenAI Calls with MultiStepQueryEngine: Users reported concerns about seeing duplicate OpenAI calls while using
MultiStepQueryEngine, leading to discussions about logging issues with tools like Arize.- Despite the confusion, it was clarified that there are not actual duplicate calls, and a member emphasized progress is still being made on structured text extraction.
- RAG Chatbot Development: A user shared motivations to upgrade a previously built RAG chatbot using LlamaIndex, along with a GitHub repo link for reference.
- They expressed interest in enhancing the functionality since they had previously built the chatbot before RAG gained significant popularity.
- Updating Knowledge Graph Node Embeddings: A discussion emerged about managing outdated knowledge graph node embeddings within the
PropertyGraphIndex, especially when documents change.- Users debated the relevance of the
refresh_ref_docsmethod and sought clarity on how to update these embeddings effectively.
- Users debated the relevance of the
- Document Summary Index Errors: There were reports of errors occurring during the operation of
DocumentSummaryIndex, particularly after recent changes in message size and complexity.- Programmable errors were discussed, with suggestions to ensure proper arguments were passed during execution while troubleshooting the sudden occurrence of a SystemExit error.
- Chunking and Triple Extraction Modifications: One user proposed an approach for integrating semantic chunking and triple extraction in the property graph code, aiming for enhanced context in entity extraction.
- By suggesting a combination of document chunks with metadata, they aimed to improve triple extraction while maintaining query efficiency through vector embeddings.
Links mentioned:
- GitHub - wadie999/Chat-Bot: Contribute to wadie999/Chat-Bot development by creating an account on GitHub.
- indices base refresh_ref_docs not working as expected · Issue #5772 · run-llama/llama_index: version 0.16.19 same refresh_ref_docs could not be recognized as the same. From the the debug the hash of original file can not be found. existing_doc_hash always return none and all file was inser...
- add back kwargs to Ollama by logan-markewich · Pull Request #14963 · run-llama/llama_index: Since adding an actual constructor to Ollama, we need kwargs to allow passing in parent class attributes
- Property Graph Index - LlamaIndex: no description found
- no title found: no description found
LlamaIndex ▷ #ai-discussion (4 messages):
Monitoring Llama AgentsRoute Planning with RAG
- Monitoring Llama Agents article praised: Members discussed an article titled Monitoring Llama Agents: Unlocking Visibility with LlamaIndex and Portkey which can be found here.
- A member noted that it’s a nice article, emphasizing its value.
- Exploring RAG for Route Planning: A member inquired if anyone had experimented with RAG on the route planning task.
- They found it interesting to use graphRAG for planning tasks based on complex databases.
Cohere ▷ #general (70 messages🔥🔥):
Cohere OverviewWriting Research PapersLangchain's ChatPromptTemplate
- Cohere provides language model solutions: Cohere is compared to OpenAI as a provider of large language models and focuses on natural language processing, with functionalities available via API documentation for developers.
- Their API allows the creation of applications such as conversational agents and summarization tools, and pricing is based on usage rather than subscription.
- Tips for Writing Research Papers Shared: Members discussed the importance of university advisors, particularly for those new to writing research papers, and highlighted resources like the Cohere For AI community for support.
- Cohere For AI offers opportunities for collaboration and guidance in academic research, enhancing the initial steps for new researchers.
- Clarification on Langchain’s optional_variables: The ‘optional_variables’ parameter in Langchain’s ChatPromptTemplate allows users to define non-required variables for more adaptable prompts.
- While ‘optional_variables’ serves a flexible purpose, questions arose about its distinction from ‘partial_variables’, which also addresses optional metadata.
Links mentioned:
- Cohere Enterprise Group: no description found
- Form: no description found
- The Cohere Platform - Cohere Docs: no description found
- Pricing: Access our models directly through our API to create scalable production workloads.
- Login | Cohere: Login for access to advanced Large Language Models and NLP tools through one easy-to-use API.
- Cohere For AI (C4AI): Cohere For AI is a non-profit research lab that seeks to solve complex machine learning problems. We support fundamental research that explores the unknown, and are focused on creating more points of ...
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) ▷ #general (31 messages🔥):
Mistral Large 2Multi-token predictionsTraining data efficiencyPerplexity issuesRelease confusion
- Mistral Large 2 sets new benchmarks: Mistral Large 2 is reported to outperform 405 billion parameter models with a 123 billion parameters and a 128k context window, making it suitable for long context applications.
- This model supports multiple languages and coding languages, designed for efficient single-node inference, raising excitement about its performance potential.
- Exploring Multi-token Predictions: Members expressed curiosity about multi-token predictions, noting its potential in making byte-level models more feasible and efficient during training.
- There’s enthusiasm about possible annotations in datasets to specify token predictions, aligning thoughts with methodologies discussed in related papers.
- Training Data Modification Strategies: The discussion revolved around improving the efficiency of training by masking simpler words that don’t add value, akin to concepts from the Microsoft Rho paper.
- Members considered strategies to augment training data, like analyzing perplexity spots and enhancing context with tags to boost training effectiveness.
- Confusion Over Mistral Releases: There was confusion about the release details of Mistral Large vs Mistral Large 2, with members questioning the open-source status and the improvement claims.
- Some expressed concern over the relative performance metrics compared to existing models like Claude 3.5 and whether this model would eventually be open-sourced.
- Performance Insights on Various Models: Discussion about the performance of 405b versus Nvidia’s models revealed insights on the infrastructure’s impact on inference speeds.
- Members noted disparities in hardware specifications that could influence the efficacy of models in practical applications.
Link mentioned: Large Enough: Today, we are announcing Mistral Large 2, the new generation of our flagship model. Compared to its predecessor, Mistral Large 2 is significantly more capable in code generation, mathematics, and reas…
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) ▷ #axolotl-dev (5 messages):
AdamW 8-bit optimizationFSDP and Zero3 challenges405B model loading issuesQLoRA efficiency
- AdamW 8-bit optimizations with DeepSpeed: A member shared their preference for using AdamW 8-bit and DeepSpeed Stage 2 on Docker for full finetunes.
- This setup seems to be effective based on their experience in the community.
- Challenges loading 405B with FSDP and Zero3: A user reported difficulties getting the 405B model to load using FSDP or Zero3 with QLoRA.
- They expressed uncertainty about the specific issues causing these loading failures.
- Theoretical load capacity for 405B on 8x80GB: It was noted that the 405B model theoretically should load on 8x80GB hardware, especially when using QLoRA.
- This serves as a reminder about the expected capabilities of the setup under ideal conditions.
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) ▷ #general-help (2 messages):
Training Configurations
- Query on Specifying max_steps in Training: A member questioned the rationale behind training by specifying the number of max_steps between max_step and num_epochs.
- Could you rephrase your question? was the reply received, indicating confusion over the original inquiry.
- Clarification Request on Training Logic: Another member asked for clarification on the question regarding training process, seeking a more explicit rephrasing.
- This discussion highlights the need for clear communication in technical queries to avoid misunderstandings.
tinygrad (George Hotz) ▷ #learn-tinygrad (37 messages🔥):
Kernel Sharing DiscussionTinygrad Cache SharingMultiple Gradients in TinygradRandom Tensor Generation IssueOptimization in NumPy Conversion
- Kernel Sharing Enhances GPU Efficiency: Members discussed the potential of sharing optimal kernels after spending GPU hours searching, noting that peer-to-peer (p2p) kernel sharing could leverage efforts across a network of users.
- Some participants acknowledged that previous discussions mentioned p2p searches and the ability to share tinygrad caches.
- Need for Multiple Backpropagation Support: The need for a consistent method to backpropagate multiple times was highlighted as a requirement for implementing neural network potentials in tinygrad.
- Some members expressed that while combining losses for backward calls should work, a better solution would involve retaining the computation graph to support more complex gradient calculations.
- Random Tensor Generation Gives Repeated Results: A user reported unexpected behavior with repeated calls to
get_random_sum()inside another function, yielding the same outputs due to TinyJit’s output overwriting.- It was advised that calling
.numpy()before repeating calls resolves the issue, ensuring unique outputs for each function call.
- It was advised that calling
- Optimization in NumPy Conversion Process: A user noted that they managed to halve the time taken for NumPy conversion from 6 seconds to 3 seconds by removing
.to('CLANG')in the tensor conversion method.- This modification raised questions about underlying correctness, yet the resulting NumPy array was verified to be accurate*.
Links mentioned:
- Issues · tinygrad/tinygrad: You like pytorch? You like micrograd? You love tinygrad! ❤️ - Issues · tinygrad/tinygrad
- Multiple gradients for force-matching problems by scdunne · Pull Request #5701 · tinygrad/tinygrad: In order to implement neural network potentials in tinygrad, we need to have a consistent way to backpropagate multiple times. This test shows a minimal example with a PyTorch implementation of thi...
- spinningup/spinup/algos/pytorch/ppo/ppo.py at 20921137141b154454c0a2698709d9f9a0302101 · openai/spinningup: An educational resource to help anyone learn deep reinforcement learning. - openai/spinningup
- Remove the toCPU copy by pgkt04 · Pull Request #2445 · tinygrad/tinygrad: Removes the copy from lib.py but copied in numpy instead
OpenInterpreter ▷ #general (14 messages🔥):
Mistral-Large-Instruct-2407Llama 3.1 output token maxUbuntu installation instructionsGPT-4o-mini fine-tuningDeepseek performance
- Mistral-Large-Instruct-2407 offers speed: Mistral-Large-Instruct-2407 (128B) is approximately 3x smaller than the 405B model, resulting in reduced inference time.
- This reduction might appeal to those looking for efficient models.
- Llama 3.1 output token maximum inquiry: A member inquired about the maximum output tokens for Llama 3.1, indicating a need for more information in the community.
- Understanding these limits could optimize users’ experience with Llama 3.1.
- Concerns over outdated Ubuntu installation: Discussions arose about the installation instructions for Ubuntu potentially being outdated.
- It was noted that the current instructions do not work anymore.
- Fine-tuning GPT-4o-mini for optimization: A question was raised about fine-tuning GPT-4o-mini for better performance within the Open Interpreter framework.
- This discussion reflects an interest in capitalizing on the free fine-tuning quota available.
- Deepseek coder shows promising update: There was excitement over the recent update for the Deepseek coder, with promising performance specs shared.
- The affordability of Deepseek at 14-28 cents per mil was highlighted as a significant advantage.
Link mentioned: Issues · OpenInterpreter/open-interpreter: A natural language interface for computers. Contribute to OpenInterpreter/open-interpreter development by creating an account on GitHub.
OpenInterpreter ▷ #O1 (6 messages):
Shipping updates for 01React Native/Expo app developmentWatchOS custom case for 01Interpreter on Rabbit device
- Big Shipping Announcement Coming Soon: There will be a big announcement in July regarding the shipping of the 01 and the open-sourcing of all manufacturing progress and materials.
- The team is grateful for the patience shown by the community, acknowledging the prolonged wait for updates.
- Fast and Reliable React Native App Update: The new version of the React Native/Expo app by Ben Xu is based on WebRTC, promising improved speed and reliability.
- The team has acquired their Apple Developer account and is preparing to publish the app on both the Play Store and iOS Store.
- WatchOS Custom Case for 01 in the Works: 01 for WatchOS is in development, with plans for a custom case to complement it.
- Excitement is high among the team regarding this new direction.
- Struggles of Using Interpreter on Rabbit Device: A user is trying to figure out how to make the Interpreter work on their Rabbit device, which they received a few weeks ago.
- They expressed frustration at the lack of useful functionality despite having purchased the device back in January.
Link mentioned: GitHub: Let’s build from here: GitHub is where over 100 million developers shape the future of software, together. Contribute to the open source community, manage your Git repositories, review code like a pro, track bugs and fea…
OpenInterpreter ▷ #ai-content (5 messages):
Database ComplexityBusiness Presentation NeedsSolutions by OpenInterpreterCase StudiesImplementation Overview
- Concerns about Database Complexity: A member expressed doubts about the effectiveness of a solution for complex databases due to joins across tables, suggesting the need for access to the full schema.
- Thanks for sharing and well done was also noted, showing appreciation for the contribution.
- Seeking Business Savvy Presentation: A community member inquired if there is a business-savvy presentation available for the interpreter, such as a PPT or PDF.
- They listed slides covering topics from the challenges businesses face to the solutions offered by OpenInterpreter.
- OpenInterpreter’s Solutions to Business Challenges: Slides highlighted how OpenInterpreter aims to solve major business challenges like high labor costs and scalability issues by simplifying coding and automating tasks.
- A focus was placed on increasing productivity and reducing dependency on skilled programmers.
- Success Stories of Implementation: The member proposed including case studies and testimonials in the presentation to showcase successful implementations of OpenInterpreter.
- They emphasized the importance of real-world examples to illustrate the effectiveness of the solutions.
- Implementation Steps Displayed: The presented slides included an implementation overview detailing steps for integration, training options, and timelines for adopting OpenInterpreter.
- This aims to guide stakeholders on how to effectively adopt and leverage the interpreter in their workflows.
Torchtune ▷ #general (6 messages):
Llama 3/3.1 70B Generation RecipeMulti-GPU InferenceQuantization TechniquesFSDP Integration
- Llama 3/3.1 70B generates script inquiry: A user asked if there is a generation recipe for Llama 3/3.1 70B that supports distributed generation across multiple GPUs.
- Another member pointed out that currently, distributed generation isn’t supported out of the box and suggested checking out this repo for more information.
- Single GPU fit issues: The user expressed concerns about fitting the Llama 3 70B model on a single GPU using bfloat16 and inquired about solutions.
- A member responded highlighting options like quantizing the model to int4 for single-GPU inference.
- Current state of multi-GPU support in Torchtune: Another participant noted that Torchtune hasn’t prioritized multi-GPU/distributed inference yet, but they are looking into it.
- They also mentioned that the development of multi-GPU inference support is ongoing in the torchchat library.
- Transitioning to distributed generation scripts: A member highlighted that the existing generate.py script can be converted into a generate_distributed.py recipe with some tweaks for those familiar with FSDP.
- They suggested that code from the distributed finetuning recipe could be leveraged to assist in this adaptation.
Torchtune ▷ #dev (9 messages🔥):
Llama 3.1 UpdatesMemory Management in Fine-TuningRFC for Cross AttentionMemory Optimizations with SnowflakeNew Transformations in Models
- Llama 3.1 progress nearing completion: Members discussed that they are wrapping up testing for the Llama 3.1 patch, with a focus on integrating 405B QLoRA on a single node.
- One noted that although the recipe works, saving an adapter’s checkpoint for such a large model is proving to be challenging.
- Snowflake walk-through for model fine-tuning: A member shared a blog post detailing optimizations for fine-tuning large models like Llama 3.1.
- They mentioned that their memory usage peaked around 66GB on A100s, and they are starting from the bfloat16 version due to the lack of FP8 kernels.
- Clarifications on FP8 and memory usage: A member sought clarification on whether FP8 is strictly applied to base weights, noting that their memory requirements should be lower due to NF4 quantization in their QLoRA recipe.
- This suggests that they expect optimizations to directly impact their memory efficiency positively.
- RFC for TransformerDecoderLayer modifications: A new RFC was shared aiming to support cross attention for multimodal architecture, necessitating changes to the TransformerDecoderLayer.
- Members were warned that existing custom model builders will need updates due to significant library changes outlined in the pull request.
Links mentioned:
- Fine-Tune Llama 3.1 405B on a Single Node using Snowflake’s AI Stack: Learn how Snowflake AI Research optimizes fine-tuning for massive LLMs like Meta Llama 3.1 405B using innovative memory management techniques for efficient AI deployment.
- [RFC] TransformerDecoderLayer Refactor by pbontrager · Pull Request #1224 · pytorch/torchtune: [RFC] TransformerDecoderLayer Refactor Refactor TransformerDecoder so it can be used for multimodal architectures. TLDR Replace TransformerDecoderLayer with TransformerSelfAttention and Transforme...
LAION ▷ #general (1 messages):
adiptamartu: is whisper speech model support bahasa indonesia language ? @here thanks for the info
LAION ▷ #research (10 messages🔥):
Mistral Large 2DFT Vision Transformer ArchitectureRotary Position EncodingComplex Number ParametersNormalization Techniques
- Mistral Large 2 pushes boundaries: Mistral Large 2 features a 128k context window and supports over a dozen languages, enhancing AI application building.
- It boasts 123 billion parameters and is designed for single-node inference with long-context applications, providing extensive throughput.
- Innovations in DFT Vision Transformer: A new architecture employing a Fourier transform, MLP, and inverse Fourier transform in each block has been developed, focusing on maintaining image quality.
- This design incorporates image-wide norm layers for normalization without causing any information bottlenecks.
- Utilizing Complex Number Parameters: The entire DFT Vision Transformer network operates with complex number parameters, enhancing its computational dynamics.
- This architecture allows for a clean integration of rotary position encoding, increasing efficiency and performance.
- Effect of Rotary Position Encoding: After switching to rotary position encoding, a notable improvement in the loss curve’s decline rate was observed.
- This change was described as satisfying, indicating the positive impact on the overall training process.
- Streamlined Architectural Structure: The DFT Vision Transformer features a straight pipeline through equally sized blocks, finishing with a global average pool and a linear layer.
- The design ensures that the image is never downsampled, consistently preserving all available information.
Links mentioned:
- Large Enough: Today, we are announcing Mistral Large 2, the new generation of our flagship model. Compared to its predecessor, Mistral Large 2 is significantly more capable in code generation, mathematics, and reas...
- GitHub - mlfoundations/MINT-1T: MINT-1T: A one trillion token multimodal interleaved dataset.: MINT-1T: A one trillion token multimodal interleaved dataset. - mlfoundations/MINT-1T
DSPy ▷ #papers (7 messages):
SymbolicAgentLearner DevelopmentGitHub Sharing Plans
- SymbolicAgentLearner combines RAG and symbolic learning: A member developed a SymbolicAgentLearner using DSPy that integrates Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and symbolic techniques to answer questions and create detailed paragraphs with citations.
- The core functionality includes a SymbolicLearningProcedure class that performs multi-hop retrieval and generates text with auto-added citations, enhancing information depth.
- Plans for a public GitHub repository: After an inquiry about a GitHub repository for shared projects, it was noted that the current code repository is private, but plans were mentioned to create a new public one.
- This move aims to make the developed gems and techniques accessible to others in the community.
DSPy ▷ #general (1 messages):
litellm proxyfunction calling across models
- litellm Proxy Works Flawlessly: A member suggested using a litellm proxy with all models and pointing OpenAI’s
api_baseto it, which works like a charm.- This workaround enables seamless integration with DSPy.
- Function Calling Cross Models with Extra Work: The member mentioned that they managed to get function calling working across models, but it requires a fair bit more workaround.
- Details on the specific methods used were not elaborated.
DSPy ▷ #examples (1 messages):
News categorizationGPT-3.5-turboMIPROColBERTv2F1 score
- DSPy powers news categorization program: A program implementing a news categorization system uses DSPy to classify articles as ‘fake’ or ‘real’ with a Chain of Thought approach using OpenAI’s GPT-3.5-turbo model and ColBERTv2 for retrieval.
- It utilizes MIPRO (Minimum Prompt Optimization) for prompt optimization and incorporates a custom F1 score calculation for evaluation.
- New advancements in news classification: The program introduces a new method for evaluating news articles by leveraging advanced models that enhance classification accuracy.
- Such implementations showcase the potential of integrating AI models in filtering misinformation.
LangChain AI ▷ #general (7 messages):
LangChain Agents Consistency IssuesWorking with Multi AgentsUsing ConversationSummary with Database AgentsLangChain and Ollama Video ReleaseLangGraph Persistence Options
- LangChain Agents face consistency problems: A user expressed frustration with LangChain agents using open-source models due to consistency issues and picking the wrong tools.
- Another member echoed the sentiment, stating all their tests showed similar results regarding local LLMs’ performance.
- Exploration of Multi Agents functionality: A user inquired about working with multi agents, looking for insights or guidance on implementation.
- The community member prompted further discussion by asking for specifics on what functionalities are being explored.
- Inquiry on ConversationSummary integration: A user asked if it’s possible to use ConversationSummary with their own database agent, seeking suggestions on how to achieve this.
- They expressed eagerness for feedback or alternative approaches if direct usage wasn’t supported.
- LangChain and Ollama’s promising new video: A member shared a YouTube video titled ‘Fully local tool calling with Ollama’ discussing the potential of tools with local LLMs.
- They noted that the video addresses common misconceptions about tool selection and consistent usage in agents.
- Updates on LangGraph persistence options: A user inquired about any updates on LangGraph persistence mechanisms beyond the SqliteSaver.
- They were looking for alternative solutions or improvements in data storage options within LangGraph.
Link mentioned: Fully local tool calling with Ollama: Tools are utilities (e.g., APIs or custom functions) that can be called by an LLM, giving the model new capabilities. However, LLMs need to be able to 1) sel…
AI Stack Devs (Yoko Li) ▷ #ai-raspberry-pi (1 messages):
felixultimaforeverromanempire: this is cool, tell us more
{% else %}
The full channel by channel breakdowns have been truncated for email.
If you want the full breakdown, please visit the web version of this email: [{{ email.subject }}]({{ email_url }})!
If you enjoyed AInews, please share with a friend! Thanks in advance!
{% endif %}