4 days ago, Victor Taelin confidently tweeted a simple A::B challenge for GPTs and then offered a $10k contest to prove him wrong:
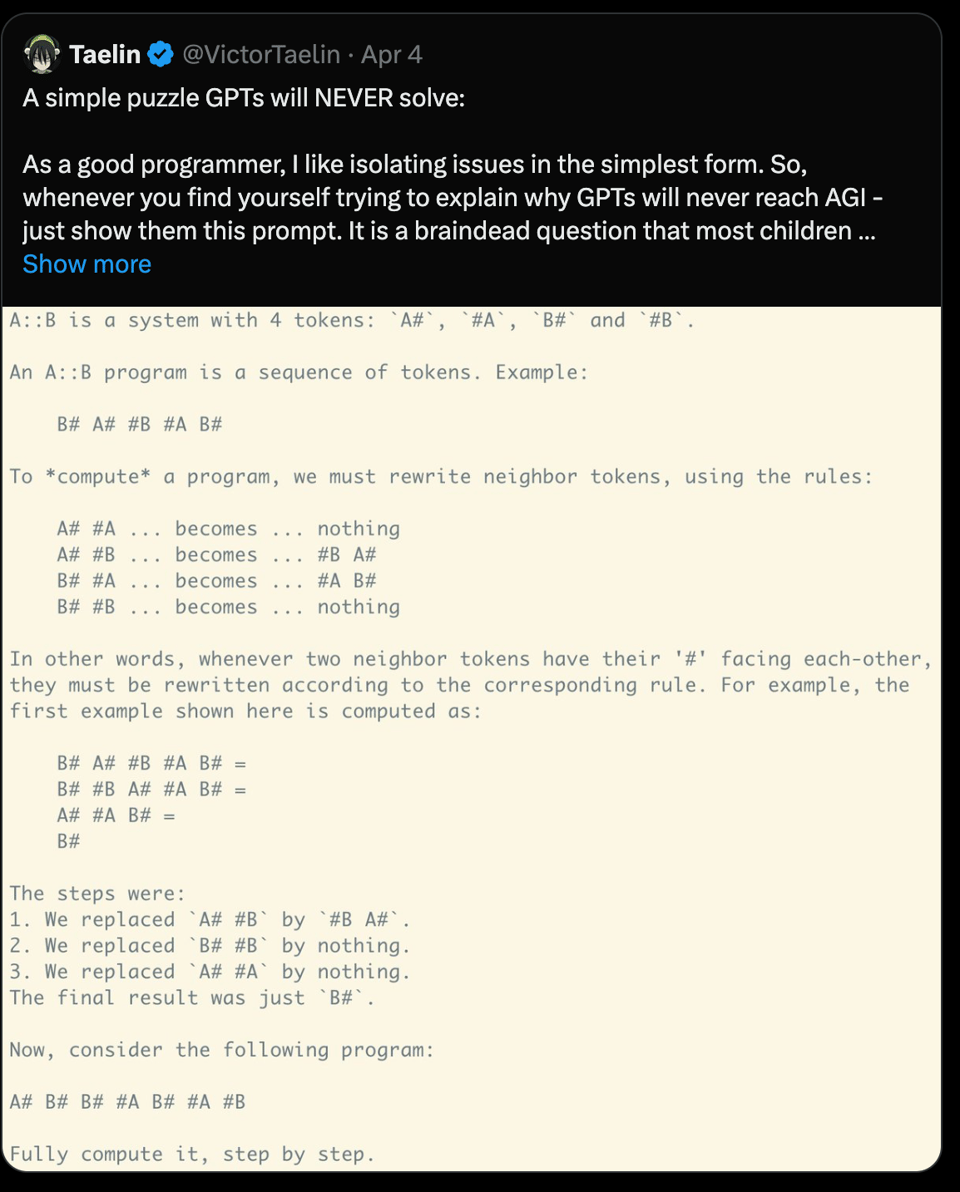
His initial attempts with all SOTA models got 10% success rates. Community submissions got 56%. It took another day for @futuristfrog to surpass 90%. The challenge lasted 48 hours in total. A fun lesson in GPT capability, and another reminder that failure to do something in 2024 AI pre AGI is often a simple skill issue.
Table of Contents
[TOC]
AI Reddit Recap
Across r/LocalLlama, r/machinelearning, r/openai, r/stablediffusion, r/ArtificialInteligence. Comment crawling still not implemented but coming soon.
Technical Developments and Releases
- Command R Plus (104B) working with Ollama: In /r/LocalLLaMA, Command R Plus (104B) is working with Ollama using a forked llama.cpp, allowing for quantized models to run on M2 Max hardware.
- GGUF quantizations for Command R+ 104B released: In /r/LocalLLaMA, Dranger has released GGUF quantizations for Command R+ 104B from 1 to 8 bit on Huggingface.
- Streaming t2v now available: In /r/StableDiffusion, streaming t2v is now available, allowing for generating longer videos using the st2v Github repo.
- New version of WD Tagger (v3) released: In /r/StableDiffusion, a new version of WD Tagger (v3) is available for mass auto captioning of datasets, utilizing a WebUI interface.
Techniques and Prompting
- Lesser known prompting techniques yield thought-provoking outputs: In /r/OpenAI, thought provoking outputs were generated using lesser known prompting techniques such as self-tagging output, generational frameworks, and real-time self-checks.
- Experiment with self-evolving system prompts: In /r/OpenAI, an experiment letting OpenAI API write its own system prompt over multiple iterations resulted in increasingly flowery and grandeur wording.
- Promptless outpaint/inpaint canvas updated: In /r/StableDiffusion, promptless outpaint/inpaint canvas has been updated to run ComfyUI workflows on low-end hardware.
Questions and Discussions
- Importance of image composition when training character LoRAs: In /r/StableDiffusion, there is a discussion on the importance of image composition when training character LoRAs, and whether auto-tagging sufficiently captures details.
- Best checkpoint for video game characters in Stable Diffusion 1.5: In /r/StableDiffusion, there is a question about the best checkpoint for generating video game characters in Stable Diffusion 1.5.
- Scarcity of 5B parameter models: In /r/LocalLLaMA, there is an inquiry about why there are so few 5B parameter models compared to 3B and 7B.
- Open(ish) licenses and aligning incentives for open source AI: In /r/LocalLLaMA, there is a discussion on open(ish) licenses and what terms are desired to align incentives for open source AI.
Memes and Humor
- Humorous post about dancing anime girls and “realistic” Call of Duty: In /r/StableDiffusion, there is a humorous post about too many dancing anime girls, countered with a “realistic” Call of Duty image.
- Joke about ChatGPT vs Gemini training data: In /r/ProgrammerHumor, there is a joke confirming that ChatGPT was trained with YouTubers while Gemini was not.
AI Twitter Recap
all recaps done by Claude 3 Opus, best of 4 runs. We are working on clustering and flow engineering with Haiku.
AI and Robotics Research Developments
- AI and robotics progress: @adcock_brett shares a weekly roundup of the most important research and developments in AI and robotics, highlighting the rapid pace of progress in the field.
- Rumored capabilities of GPT-5: @bindureddy reports that OpenAI’s upcoming GPT-5 model is rumored to have extremely powerful coding, reasoning and language understanding abilities that surpass Anthropic’s Claude 3.
- Sora for generating music videos: @gdb showcases Sora, a tool that allows users to visualize how a song has always “looked” by generating corresponding music videos.
- Fast performance of 4-bit Mistral 7B: @awnihannun achieved an impressive 103.5 tokens-per-second running the 4-bit Mistral 7B model on an M2 Ultra chip.
- Many-shot jailbreaking technique: @adcock_brett shares that Anthropic researchers discovered a technique called “many-shot jailbreaking” that can evade the safety guardrails of large language models by exploiting expanded context windows.
AI Agents and Robotics
- Complexity of building AI agents: @bindureddy notes that only 10% of the work in building AI agents is about LLMs and reasoning, while the remaining 90% involves heavy lifting in code, data, memory, evaluation and monitoring.
- OpenAI’s plans and LLMs in robotics: @adcock_brett provides an overview of OpenAI’s plans and discusses why large language models are important for robotics applications.
- Key factors for reliable LM-based agents: @sarahcat21 emphasizes that purposeful pretraining and interface design are crucial for building reliable agents based on large language models.
- Growth of coding agents: @mbusigin highlights the rapid explosion in the development and adoption of coding agents.
- Figure-01 humanoid robot: @adcock_brett shares an image of the Figure-01 electromechanical humanoid robot.
LLM Developments and Capabilities
- Grok 2.0 rumored performance: @bindureddy reports that Grok 2.0 is rumored to be the second model after Anthropic’s Claude Opus to beat OpenAI’s GPT-4 in performance, which would be a significant achievement for Grok and X.
- Claude 3 Opus outperforms GPT-4: @Teknium1 and @bindureddy note that Anthropic’s Claude 3 Opus model outperforms GPT-4 on certain tasks.
- New model releases: @osanseviero announces the release of Cohere Command R+, Google Gemma Instruct 1.1, and the Qwen 1.5 32B model family.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) Architectures
- Finance agent with LangChain and Yahoo Finance: @llama_index demonstrates building a finance agent using LangChain and Yahoo Finance, covering functions for stock analysis such as balance sheets, income statements, cash flow, and recommendations.
- Multi-document agents with LlamaIndex: @llama_index and @jerryjliu0 showcase treating documents as sub-agents for both semantic search and summarization using LlamaIndex.
- Agentic extension for RAG: @jerryjliu0 proposes an agentic extension for retrieval augmented generation that treats documents as tools and agents for dynamic interaction beyond fixed chunks.
- Extracting document knowledge graph for RAG: @llama_index demonstrates using LlamaParse to extract structured markdown, convert it to a document graph, and store it in Neo4j for advanced querying to power a RAG pipeline.
Memes and Humor
- Timeout set in seconds instead of milliseconds: @gdb shares a humorous meme about accidentally setting a timeout in seconds instead of milliseconds.
- Preferring In-N-Out to Shake Shack: @adcock_brett jokes about preferring In-N-Out to Shake Shack after living in NYC.
- Biological neural network performance after bad sleep: @_jasonwei humorously compares the performance of a biological neural network after a bad night’s sleep to GPT-4 base with poor prompting.
- Pains of saying Claude solved something: @Teknium1 shares a meme about the pains of admitting that Anthropic’s Claude model solved a problem.
- Studying LeetCode for 3 months without getting a job: @jxnlco shares a meme about the frustration of studying LeetCode for 3 months but not getting a job.
AI Discord Recap
A summary of Summaries of Summaries
1. Quantization and Optimization Breakthroughs for LLMs
-
QuaRot enables end-to-end 4-bit quantization of large language models like LLaMa2-70B with minimal performance loss, handling outliers while maintaining computational invariance. HQQ also showcased promising 4-bit quantization results integrated with gpt-fast.
-
Schedule-Free Optimization Gains Traction: Meta’s schedule-free optimizers for AdamW and SGD have been integrated into Hugging Face’s transformers library, potentially revolutionizing model training. Discussions revolved around the Schedule-Free Optimization in PyTorch repository and a related Twitter thread by Aaron Defazio on the topic.
-
Discussions around torch.compile focused on its utilization of Triton kernels only for CUDA inputs, asynchronous collective operations, DeepSpeed integration, and potential MLP optimizations using tiny-cuda-nn or CUTLASS.
2. Expanding Context Lengths and Attention Mechanisms
-
The EasyContext project introduces memory optimization and training recipes to extrapolate language model context lengths to 1 million tokens using ring attention on modest hardware like 8 A100 GPUs. A tweet by Zhang Peiyuan discussed the impact of increased context size on training throughput.
-
Mixture-of-Depths proposes dynamically allocating compute across a transformer sequence within a fixed budget, potentially enhancing efficiency without compromising flexibility.
-
Discussions covered linear attention vs. classic attention, variable length striped attention implementations, and the speed/memory trade-offs of ring attention in distributed computing scenarios.
3. Open-Source AI Advancements and Community Engagement
-
AMD announced open-sourcing the Micro Engine Scheduler (MES) firmware and documentation for Radeon GPUs, aligning with broader open-source GPU efforts welcomed by the community. (The Register Article, AMD Radeon Tweet)
-
The PaperReplica GitHub repository aims to replicate AI/ML research papers through community contributions, fostering knowledge sharing and skill development.
-
Licensing changes for text-generation-inference (TGI) to Apache 2 sparked a surge in contributors after the project was fully open-sourced, highlighting the potential economic benefits of open ecosystems like Mistral.
-
Command R+ by Cohere demonstrated impressive translation capabilities for archaic languages like Middle High German, outperforming GPT-4 class models and fueling hopes for an open-source release to drive developer engagement.
4. Multimodal AI Advancements and Applications
-
The Aurora-M project introduced a new 15.5B parameter open-source multilingual language model following the U.S. Executive Order on AI, showcasing cross-lingual impact of mono-lingual safety alignment across 2 trillion training tokens.
-
Unsloth AI faced challenges with models like Chat GPT and Claude accurately converting images to HTML while preserving colors and borders, prompting tongue-in-cheek suggestions to use ASCII art instead.
-
BrushNet, a new method for AI inpainting incorporating object detection, promises higher quality results as demonstrated in a tutorial video.
-
The LLaVA vision-language model underwent a novel “Rorschach test” by feeding it random image embeddings and analyzing its interpretations, detailed in a blog post. A compact nanoLLaVA model for edge devices was also released on Hugging Face.
5. Misc
-
Tinygrad Development Progresses with Reversions and Integrations: George Hotz reverted the command queue in tinygrad and is integrating the memory scheduler directly with the existing scheduler model using the multidevicegraph abstraction. The TinyJit tutorial and multi GPU training guide were shared to aid contributors.
-
Jamba Models Offer Alternatives for Limited Hardware: Scaled-down versions of the Jamba architecture, including an 8xMoE with 29B parameters and 4xMoE with 17.7B parameters, were created using spherical linear interpolation (Slerp) of expert weights to enable fine-tuning on more accessible hardware like a 4090 GPU at 4-bit precision.
PART 1: High level Discord summaries
Perplexity AI Discord
iOS Users Test Drive New Story Discovery: Perplexity AI is trialing an innovative story discovery format on iOS. Users are encouraged to provide feedback on their experiences through a designated channel, and can download the test app here.
AI Event Ends in Harmony: The Perplexity AI Discord event wrapped up with both eun08000 and codelicious sharing first place. Prize recipients will receive direct messages with details.
Claude 3 Opus - A Model Debate: On the server, the talk revolved around observed variations in Perplexity’s implementation of the Claude 3 Opus model compared to others, particularly regarding tasks demanding creativity.
API Quirks and Queries: Users noted inconsistencies between Perplexity’s API and web application, with the API showing more hallucinations; the API’s default model diverges from the web version. The ‘sonar-medium-online’ model is suggested for API users to closely mimic the Sonar model accessible via the web app for non-Pro users.
Tech Enthusiasts Share and Learn: Users exchanged information on a variety of topics from how AI affects the music industry to Tesla’s and Apple’s latest tech innovations. Additionally, a case study featuring Perplexity AI highlighted a 40% speed increase in model training powered by Amazon Web Services, demonstrating Perplexity’s efficient utilization of advanced machine learning infrastructure and techniques.
Nous Research AI Discord
-
Rorschach Test for AI Vision Models: The LLaVA vision-language model was put through a novel “Rorschach test” by feeding it random image embeddings and analyzing the interpretations, described in a blog post. Moreover, a compact nanoLLaVA model suitable for edge devices was introduced on Hugging Face.
-
Claude’s Memory Mechanism in Question: Technical discussions ensued on whether Claude retains information across sessions or if the semblance of memory is due to probabilistic modeling. Engineers debated the effectiveness of current models against the challenge of persistent context.
-
Worldsim Woes and Wisdom: Post-DDoS attack, proposals for a Worldsim login system to thwart future threats and discussions of a “pro” version to include more scenarios were afoot. Meanwhile, philosophical musings floated around potential AI-driven simulations akin to observed realities.
-
Chunking for RAG Diversity: Suggestions arose to pre-generate diverse datasets for RAG using a chunking script, alongside talk of creating complex multi-domain queries using Claude Opus. Ethical queries surfaced regarding data provenance, specifically using leaked documents from ransomware attacks, contrasting with the clustering strategies like RAPTOR for dataset curation.
-
The Coalescence of GitHub and Hermes: A GitHub repository, VikParuchuri/marker, was spotlighted for its high-accuracy PDF-to-markdown conversion, and can be found at GitHub - VikParuchuri/marker. Additionally, discussions focused on enhancing
Hermes-2-Pro-Mistral-7Bto execute functions withtoolsconfigurations, a hurdle matching the challenges delegates face with full-parameter finetuning vis-à-vis adapter training in various LLM contexts. -
Canada’s AI Ambitions and Enterprise LLMs: From the introduction of Command R+, a scalable LLM by Cohere for businesses, to insights into Canada’s strategy to champion global AI leadership, the discourse expanded towards understanding SSL certifications, creating local solutions akin to Google Image Search and untangling the surfeit of AI research and synthesis.
Stability.ai (Stable Diffusion) Discord
- Stability Bot MIA: Users seeking image generation services were guided to check bot status due to outages, pushing them towards alternate server channels for updates and support.
- Quality Quest in Image Generation: Debates emerged comparing local model outputs with Dreamstudio’s, with participants recommending open-source upscalers and discussing the effectiveness of various image enhancement techniques.
- SD3 Buzz Builds: There is an informal 2-4 week ETA on Stable Diffusion 3 (SD3), sparking conversations around expected improvements and new capabilities of the model.
- LoRa Training Dialogue: Information exchange on LoRa training saw users seeking installation advice and citing GitHub repositories for practical training methods.
- User Interface Upgrades: Discussions on user interface enhancements included suggestions for transitioning from Automatic 1.1.1.1 to StableSwarm, with a focus on user-friendliness and feature accessibility for new adopters.
Unsloth AI (Daniel Han) Discord
HTML Conversion Leaves Engineers Blue: AI engineers discussed the limitations of current language models like Chat GPT and Claude in accurately converting images to HTML, leading to lost color fidelity and rounded borders. A tongue-in-cheek proposal suggested the use of ASCII art as an alternative, stemming from its ability to elicit responses from AI models as shown in this Ars Technica article.
Aurora-M Lights Up Possibilities: An open-source multilingual model, Aurora-M, boasting 15.5 billion parameters, was introduced and caught the community’s attention with its cross-lingual safety capabilities, further detailed in this paper. The findings show that safety alignment in one language can have a positive impact on other languages.
Jamba Juice or Mamba Sluice? Investment Opinions Clash: Engineers debated the investment into AI21 Labs’ Jamba, especially given their recent fundraising of $155 million as reported by TechCrunch. The return on investment (ROI) of focused model fine-tuning was brought to light, presenting an optimistic view despite the model’s upfront costs.
AI Fine-Tuning Perspectives Merge and Diverge: The community engaged in a robust exchange on fine-tuning approaches, such as unsupervised fine-tuning techniques mentioned like GGUF, and the benefits of Dynamic Positional Offsets (DPO). Specific strategies for fine-tuning and the application of techniques like LoRA in enhancing performance were discussed.
Private AI Hosting Hustle: Data privacy concerns have led members to host their AI projects on personal servers, with anecdotes of using platforms like Hircoir TTS independently. Some envisioned future plans include integrating advertisements to capitalize on the growing portfolio of models.
LM Studio Discord
Boost Your Model’s Performance: The LM Studio appears to leap ahead of alternatives like oogabooga and Faraday with a GUI that wins user preference for its higher quality outputs. Suggestions poured in for expansions, notably for file reading support and modalities such as text-to-image and text-to-voice; such features edge closer to what Devin already offers and are angled towards enhancing creativity and productivity.
Big Thinkers, Bigger Models: A technical crowd advocates the power play of handling heavyweight models such as the Command R+, tipping the scales at 104B, and recommending brawnier hardware like the Nvidia P40 for older yet hefty models. Discussions around VRAM spill into strategies for optimizing multi-GPU setups, hinting at the use of both RTX 4060 Ti and GTX 1070 to spread the computational load, and leveraging Tesla P40 GPUs despite potential outdated CUDA woes.
The Joy of Smoothly Running Models: On both ROCM and ROCm Preview Beta fronts, GPU support discussion was rife, including the use of AMD’s RX 5000 and 6000 series chips. Users flagged the “exit 42” errors on ROCm 0.2.19 Beta, rallying around debug builds for a solution, displaying a communal spirit in action. Meanwhile, whispers of Intel’s Advanced Matrix Extensions (AMX) stirred speculation on how LM Studio could tap into such formidable processing prowess.
Excavating Model Gems: A surge in shared resources and models came through announcements, including Starling-LM 7B, c4ai command r v01, and stable-code-instruct-3b, among others. Accessibility stands upfront with a collective push towards a community page on Hugging Face, where the latest GGUF quants shine, luring AI enthusiasts to experiment with the offerings such as Google’s Gemma 1.1 2B, and stay alert for the upcoming 7B variant.
Sculpting the Vision Models Landscape: A member’s inquisition about training LLMs to decipher stock market OHLC patterns, amidst praise for LM Studio’s utility in vision model implementations, ignites a spark in exploring how the intricate dance between technology and finance could be choreographed with AI’s grace. The revelation of vision models on Hugging Face mirrors the community’s camera-ready attitude to snapshot and subsequently transpose this conceptual aesthetic into practical applications.
HuggingFace Discord
Gradio’s API Recorder and Chatbot UI Fixes Gear Up for Release: Gradio version 4.26.0 introduces an API Recorder to translate interactions into code and addresses crucial bugs related to page load times and chatbot UI crashes. The update is detailed in the Gradio Changelog.
A Crescendo of Concern Over LLMs: Security concerns gain spotlight as ‘Crescendo’, a new method that challenges the ethical restraints of LLMs, and vulnerabilities in Cohere’s Command-R-plus are exposed. Meanwhile, Mixture-of-Depths (Modes) proposal and llamaindex blogs offer innovative solutions for model efficiency and information retrieval.
NLP Community Finesse with SageMaker, Desire for PDF ChatGPT, and Sails Through Challenges: The community debates deploying models on SageMaker, customizing ChatGPT for PDFs, and shares fascination over Gemini 1.5’s 10M context window. Solution seekers confront multi-GPU training hiccups and demand token count information when using Hugging Face libraries.
Thriving Repository of AI Contributions and Dialogues: HybridAGI’s neuro-symbolic behavior programming on GitHub welcomes peer review, and the Hugging Face reading group archives its collective wisdom on GitHub. PaperReplica’s open-source invitation and RAG-enabled llamaindex shine as beacons of collaborative learning and resource sharing.
Vision and Beyond: Dialogues in the computer vision channel touch on the utility of HuggingFace as a model repository, efficacy of different Transformer models (e.g., XCLIP), and address real-time challenges using tools like the HuggingFace ‘datasets’ library for parquet file manipulation. Meanwhile, an open call for resources to apply diffusion models to video enhancement signifies the domain’s vibrant investigative spirit.
Modular (Mojo 🔥) Discord
Mojo Rising: A Dive into Special Functions and SICP Adaptation
- The Mojo community is flexing its technical muscle, diving into specialized mathematical functions with an update to the Specials package and porting the famed “Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs” (SICP) text to Mojo. Users can now find numerically accurate functions like
expandlogin the Specials package and participate in collaborative algorithm and package sharing via repositories such as mojo-packages.
MAX Aligns with AWS; Open Source Documentation Drive
- Modular announced a strategic alliance with AWS, intending to integrate MAX with AWS services and extend AI capabilities globally. The Mojo language is gearing up for enhanced collaboration with an appeal for community contributions to Mojo’s standard library documentation.
Discord Dynamics: Python Interop and Contributing to Mojo’s Growth
- The Mojo community is actively engaging in discussions about metaprogramming capabilities, compile-time evaluation complexities, and lifetimes in the
Referencetypes. They are exploring pathways to Python interoperability by implementing essential functions and are inviting contributors to jump in on “good first issues” on GitHub, offering a starting point with Mojo’s Changelog and contribution guidelines.
Var vs. Let - the Mojo Parameter Saga
- A conversation revealed that while
letmay have been removed from Mojo,varremains for lazily assigned variables with details in the Mojo Manual, feeding further knowledge to users. Additionally, efforts are converging on infusing Mojo into web development, with the availability of lightbug_http, reiterating Mojo’s position as a comprehensive general-purpose language.
Nightly Chronicles: From CPython Interop to Community Discussions
- Members are celebrating advancements in CPython interoperability in Mojo and fostering an environment ripe for contributions, discussing best practices for signed-off commits in PRs, and sharing solutions for managing nightly builds and package updates. This proactive collaboration is paving the way for future open source contributions, signposted on GitHub, including anticipated discussions on the Mojo Standard Library.
Blog Beats and Video Treats in Mojo’s Creative Continuum
- The launch of the Joy of Mojo website underscores the community’s commitment to sharing creative experiences with Mojo, further amplified by GitHub repositories like mojo-packages and enlightening videos on Mojo’s Python interoperability, underscoring its dynamic evolution.
Eleuther Discord
-
WikiText’s New Main Access Point: Stephen Merity has rehosted WikiText on Cloudflare R2, offering a larger dataset while maintaining original formatting, which is important for training language models with authentic data structures.
-
Perplexing Perplexity Scores: A debate emerged about the validity of perplexity scores reported by the GateLoop Transformer author, with lucidrains unable to replicate them, prompting discussions over result reproduction and transparency in reporting.
-
Hugging Face’s Automatic Parquet Conversion Frustration: Users expressed frustration at Hugging Face’s autoconversion of datasets to parquet format, which can cause confusion and issues, such as with
.rawfiles; a workaround involves hosting datasets using Git LFS. -
Documentation Ephemera and Reproducibility Emphasis: OpenAI’s fluctuating documentation on models, with some links being removed, underscores the importance of reliable resources like archived pages for consistency in the AI research community. Simultaneously, there’s a push for reproducible data formats, as shown by community efforts to mirror datasets like WikiText on platforms such as Cloudflare R2.
-
Optimizer Optimization and Zero-Shot Innovations: Conversations coalesced around the Schedule-Free optimizer and its capacity to estimate optimal learning rates, as well as intriguing methods for teaching language models to search using a stream of search (SoS) language. Moreover, the connection between emergent abilities in language models and exposure to long-tail data during training was a focal topic, with implications for zero-shot task performance.
-
Stars Matter for NSF Reviews: The number of GitHub stars for nnsight was highlighted by an NSF reviewer as a metric of concern, illustrating the unconventional impact of community engagement on research funding perspectives.
-
GPU Utilization and BigBench Task Recognition: Analysis of GPU utilization led to reduction in evaluation times by using
batch size=auto, revealing potential underutilization issues. Members also navigated confusion around BigBench tasks, suggesting verification of task variants usinglm_eval —tasks list. -
CLI Command Conundrums and Logit Bias Discussions: Technical discussions flourished around the
—predict_onlyCLI command issues and the non-effect of OpenAI’slogit_biasas expected on logits during one-token MCQA tasks, leading to exploration of alternative approaches such asgreedy_until. Temperature settings and their effects on outputs were clarified, highlighting the importance of correctgen_kwargssettings for achieving desired model behavior.
OpenAI Discord
- Translation Showdown: GPT-4 vs DeepL: GPT-4’s translation capabilities were compared to DeepL, highlighting that while DeepL excels in contextual language translation, GPT-4 sometimes falls short on nuancing basic contexts.
- AI Models in Code Generation Face-Off: Opus and GPT-4 received praise for impressive performance in code generation tasks, but GPT-4 also showed potential issues when processing larger contexts compared to other models.
- Decoding AI Consciousness: A lively exploration into simulating human consciousness with AI involved equating human neurochemical activities with GPT’s programming mechanisms, sparking debates on consciousness’s origins and AI’s role in its depiction.
- Prompt Engineering for Sensitive Content: Writers discussed circumventing ChatGPT’s content policy to develop backstories for characters with traumatic histories, seeking subtler ways to infuse nuanced, sensitive details into their narratives.
- Building AI-Powered Games: Engineers suggested utilizing JSON for structuring game progress data while discussing the challenge of crafting seamless game experiences that keep underlying code concealed from players.
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) Discord
Claude 3 Takes on Images: The Claude 3 models have been updated to multimodal, now supporting image input, requiring developers to modify existing codebases accordingly.
AI Goes Old School with Rock, Paper, Scissors: A new game at blust.ai, where players can challenge ChatGPT to a classic round of Rock, Paper, Scissors.
Frontends and Favorites Front and Center: Engineers discussed various OpenRouter API frontends like LibreChat, SillyTavern, and Jan.ai. Command-R+ has emerged as a favored model for coding tasks and interactions in Turkish, while concerns are raised about content censorship in models.
Performance Insights in Modeling: Conversations highlighted that Sonnet outstrips Opus in coding tasks, and Claude 3 is superior in PDF data extraction compared to Gemini Pro 1.5, which prompted some skepticism about its utility.
Model Efficacy Metrics Spark Debate: The community has voiced that model ranking based solely on usage statistics might not accurately reflect a model’s worth, suggesting spending or retention as potential alternate measures.
LlamaIndex Discord
Revving Up RAG Applications: Marker-Inc-Korea introduced AutoRAG, an automated tool for tuning RAG pipelines to enhance performance, detailed and linked in their tweet. Meanwhile, create-llama was released to streamline the launch of full-stack RAG/agent applications, as announced in its tweet.
Tweaking Sales Pitches with AI: A new application using RAG to create personalized sales emails was featured in a recent webinar, ditching hard-coded templates with an LLM-powered approach, further info available in a tweet.
Deep Diving Into Documents: Andy Singal presented on multi-document agents that handle complex QA across numerous sources. The aim is to expand this functionality for more intricate inquiries, shared in a presentation tweet.
Metadata to the Rescue for Document Queries: To get page numbers and document references from multi-document queries, make sure to include this metadata before indexing, allowing retrieval of detailed references post-query.
Optimization Overhaul for Azure and Embedding Times: Participants noted issues with Azure’s OpenAI not recognizing context and discussed using batching methods for faster embedding generation. Regarding challenges with ReAct agents and open-source models like “llama2” and “mistral”, better router descriptions may improve model-routing performance.
OpenInterpreter Discord
Mistral Needs Muscle: Mistral 7B Instruct v0.2 has been acknowledged as high-performing, yet it demands substantial resources—expect to allocate at least 16GB of RAM and have some GPU support for smooth operation.
Challenges with Python Compatibility: There’s a community consensus to stick with Python <=3.10 to avoid issues with TTS packages, with repeated suggestions to avoid using Python 3.11.4 for setups dependent on voice command recognition.
A Call for Better Documentation: Inquiries about local vision models and calls highlighting the need for more comprehensive examples and documentation in the Open Interpreter’s cookbook reveal gaps that are yet to be filled.
Efficiency Over Expense with Local Models: The costliness of GPT-4 has prompted discussions around leveraging local models such as Hermes 7B and Haiku—less expensive yet slightly less refined alternatives offering privacy and lower operating costs.
Hardware Hang-Ups and Software Setbacks: The O1 community reported hardware issues, particularly with external push-button integration, and software setup challenges when installing on Windows, with tweaks including using chocolatey, virtualenv, and specific environment variables being part of the troubleshooting dialogue.
Relevant resources and conversations are threaded throughout the community, with direct engagement on issues being tracked on platforms like GitHub.
LangChain AI Discord
-
GitHub Grievances: A user requested assistance with a Pull Request that was failing due to a “module not found” error related to “openapi-pydantic,” even though the module was included in dependencies. This highlights dependency management as a notable pain point in the community.
-
Fine-Tuning Finesse Without the GPU Muscle: Queries about training and fine-tuning language models sans GPU led to recommendations for tools like Google Colab and the mention of ludwig.ai as viable options, indicating an area of interest among engineers seeking cost-effective computing resources.
-
Visual Visions via Artful AI’s Update: The announcement of Artful AI’s new models, including Dalle Creative, Anime Dream, & Epic Realism, released on the Google Play Store, piqued the community’s interest in the evolving domain of AI-driven image generation.
-
Security Spotlight on AISploit: The introduction of AISploit, available on GitHub, sparked discussions on leveraging AI for offensive security simulations, indicating a tactical pivot in the use of AI technologies in cybersecurity.
-
TypeScript and Text Chunking Techniques Revealed: The share of a TypeScript Gist that demonstrated breaking up large text into semantic chunks using OpenAI’s sentence embedding service exemplified community engagement in developing and sharing tools for enhanced text processing workflows.
LAION Discord
Apple’s AI Ambitions Under Scrutiny: Apple is criticized for the subpar performance of Metal Performance Shaders (MPS) and torch compile, even as recent merges aim to fix MPS issues in the PyTorch nightly branch. Community experiences with torch.compile vary, reflecting ongoing optimizations needed for Apple’s platforms.
Copyright Conundrum: AI’s use of copyrighted content for creating derivative works sparks legal debate, with consensus on the insufficiency of paraphrasing to avoid infringement. The community anticipates the need for substantial legal changes to accommodate new AI training data practices.
The Harmony of AI-Composed Music: Discussions about AI-generated music, involving companies like Suno and Nvidia, recognized rapid advancements but also forecasted potential legal spats with the music industry. Members also noted the less impressive progress in text-to-speech (TTS) technology compared to AI’s leap in music generation.
AI Career Dynamics Shifting: The rise of freelance AI-related careers due to technological progress is noted, with resources like Bloomberry’s analysis cited. Stability AI’s CosXL model release sparks conversations about the efficacy of EDM schedules and offset noise in model training.
Novelties in AI Research Techniques: A new paper on transformers shows computational resource allocation can be dynamic, DARE’s pruning technique for language models hints at preservable capabilities, and BrushNet introduces enhanced AI inpainting. Latent diffusion for text generation, referenced from a NeurIPS paper, indicates a potential shift in generative model techniques.
Latent Space Discord
-
GPT Models Tackle the A::B Challenge: Victor Taelin conceded that GPT structures could indeed address certain problem-solving tasks, including long-term reasoning, after a participant utilized GPT to solve the A::B problem with a near 100% success rate, winning a $10k prize. Victor Taelin’s statement on the outcome is available online.
-
Stanford Debuts Language Modeling Course CS336: Stanford is offering a new course, CS336, which delves into the nuts and bolts of language modeling, including insights on Transformers and LLMs, garnering significant interest from the community eager for the release of lecture recordings.
-
Groq Plans to Topple AI Hardware Rivals: The AI hardware startup Groq, led by a founder with an unconventional educational background, aims to outdo all existing inference capacity providers combined by next year and asserts their developers enjoy reduced inference costs and speedier hardware in comparison to NVIDIA’s offerings.
-
Introducing LangChain’s Memory Service: LangChain’s latest alpha release brings a memory service aiming to upgrade chatbot interactions by automatically condensing and refining conversations, with resources posted for quick start.
-
Peer Learning in AI Tools and Knowledge Management: Engineers exchanged resources and strategies for curating personal and organizational knowledge using AI tools, such as incorporating Obsidian-Copilot and fabric, and discussed the development of integrations to enhance tools like ChatGPT within knowledge systems.
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) Discord
-
Quantized DoRA Available, Dance of the LoRA: The latest release of
peft=0.10.0supports quantized DoRA, prompting suggestions to update axolotl’srequirements.txt(PEFT’s release notes). The advanced optimizers from Facebook Research have now been integrated into Hugging Face’s transformers library, with Schedule-Free Learning open-sourced and specific parameter recommendations of0.0025for ScheduleFreeAdamW (Hugging Face PR #30079). -
Model Generation Hiccup: Users reported and discussed an error occurring in the generation process with a fine-tuned Mistral 7b model using fp16, specifically after a few successful generations resulting in
_queue.Empty. -
Rotary Queries and Sharding Insights: The parameter
"rope_theta": 10000.0came under scrutiny, relating to Rotary Positional Embedding. Meanwhile, The FSDP configuration for Mistral was shared with details on how theMixtralSparseMoeBlockclass should be utilized (mixtral-qlora-fsdp.yml). -
Seek and You Shall Find: LISA and Configs: Queries arose about the location and absence of LISA parameters in documentation, later resolved with the discovery of the LISA configuration file. Members also engaged in technical discussions on handling optimizer states for unfreezing new layers during training.
-
Model Training Conundrums Solved: The community solved various challenges including training with raw text, adapting Alpaca instruction sets, differentiating micro batch size and batch size, and adjusting configurations to disable checkpoints and evaluations or handling special tokens.
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) Discord
Podcasting Gold: John Schulman to Possibly Feature on Show: Nathan Lambert is considering featuring John Schulman in a podcast, a move that stirred excitement among members. Moreover, a licensing change for text-generation-inference (TGI) to Apache 2 has spurred a significant increase in contributors to the open-source project.
Memes Channel Maintains Light-Heartedness: The memes channel included joking references to targetings without context, improvements in experiences, and confirmation of employment status, indicating a casual, light-hearted discourse among members.
Open AI Weights Debate Hits Engaged Nerve: The #reads channel had a vibrant discussion on the societal impacts of open foundation models, with a focus on safety thresholds, regulation feasibility, and AI’s potential to manipulate societal processes. A shared visualization of Transformer attention mechanisms and speculation about future models that emphasize verification instead of generation were among the in-depth topics discussed.
Bridging the Knowledge Gaps with Visuals: The #sp2024-history-of-open-alignment channel discussed effective resources like lmsys and alpacaeval leaderboard to find state-of-the-art models. Additionally, an intent to visually categorize models for better comprehension was expressed, along with sharing a live document (Google Slides presentation) for an upcoming alignment talk and a guide (comprehensive spreadsheet) on open models by Xeophon.
A Note on AI Generated Music: Nathan noted the impressive quality of a new contender in AI music generation, posing a potential challenge to the Suno AI platform.
CUDA MODE Discord
-
Fast Track to Tokenization: Engineers discussed speeding up tokenization using Huggingface’s fast tokenizer for c4-en, exploring options like increasing threads or utilizing more capable machines.
-
Open Source GPU: AMD announced the open sourcing of its Micro Engine Scheduler (MES) firmware for Radeon GPUs, a decision celebrated within the community and praised by entities like George Hotz’s Tiny Corp. (The Register Article, AMD Radeon Tweet).
-
Paper Trail: An open-source repository, PaperReplica GitHub Repo, for replicating research papers in AI & ML got its unveiling, inviting community contributions and GitHub stars.
-
CUDA Conundrums and Triton Strategizing: From setting up CUDA environments on Ubuntu to appreciating libraries that boost proficiency with Triton, members exchanged tips and troubles. In particular, a lean GPT-2 training implementation by Andrej Karpathy in C was highlighted for its efficiency without the heft of PyTorch or Python (GitHub).
-
DeepSpeed in the Fast Lane: Conversations revolved around practical applications of DeepSpeed, integration with Hugging Face’s Accelerate, and memory optimization wonders even at zero stage. Additionally, use of Triton kernels was noted to be conditional on CUDA device input, and a curiosity about optimizing transformer MLPs with cublas or tiny-cuda-nn was shared (tiny-cuda-nn Documentation).
-
Quantum of Solace for LLMs: A novel quantization approach, QuaRot, was mooted for its capability to quantize LLMs to 4 bits effectively, while a revelatory tweet hinted at schedule-free optimization, potentially indicating a move away from the traditional learning rate schedules (Twitter).
-
Vexed by Visualizing Triton: Engineers delved into the challenges and opportunities in visualizing Triton code, from shared memory to tensor views, and from CPU constructs to enhancing JavaScript interactivity, signaling a continuing quest for more user-friendly debugging tools.
-
Calendar Confusion Cleared: A small timezone clarification was sought for a ring attention session, hinting at the vibrancy of the community’s relentless pursuit of knowledge and optimization.
-
Of Numbers and Neurons: The value of precise quantization methods surfaced, highlighting the importance of accurate tensor transformations and the potential performance gains leveraged from tools like Triton, indicating a keen focus on efficiency within machine learning pipelines.
tinygrad (George Hotz) Discord
Tinygrad Takes a Step Back: George Hotz has reverted the command queue in tinygrad and is opting to integrate the memory scheduler directly with the current scheduler model. This approach utilizes the multidevicegraph abstraction already in place, as discussed here.
TinyJIT Under the Microscope: The TinyJit tutorial has been released, although it may contain inaccuracies, particularly with the apply_graph_to_jit function, and users are encouraged to submit pull requests for corrections TinyJit Tutorial.
Tinygrad Learning Expanded: A collection of tutorials and guides for contributing to tinygrad are now available with a focus on topics like multi GPU training Multi GPU Training Guide.
Discord Roles Reflect Contribution: George Hotz redesigned roles within the tinygrad Discord to better reflect community engagement and contribution levels, reinforcing the value of collaboration and respect for others’ time.
Unpacking MEC’s Firmware Mystery: Discussions about MEC firmware’s opcode architectures emerged with speculation on RISC-V and different instruction sets, revealing a potential cbz instruction and inclusive dialogue around the nuances of RISC-V ISA.
Mozilla AI Discord
Scan Reveals Llamafile’s Wrongful Accusation: Versions of llamafile, including llamafile-0.6.2.exe and llamafile-0.7, were flagged as malware by antivirus software; utilizing appeal forms with the respective antivirus companies was suggested as a remedial step.
Run Llamafile Smoother in Kaggle: Users encountering issues when running llamafile on Kaggle found solace through an updated command that resolves CUDA compilation and compatible GPU architecture concerns, enabling efficient usage of llamafile-0.7.
RAG-LLM Gets Local Legs: A query about locally distributing RAG-LLM application without the burdens of Docker or Python was answered affirmatively, indicating the suitability of llamafile for such purposes, particularly beneficial for macOS audiences.
Taming the Memory Beast with an Argument: An out of memory error experienced by a user was rectified by adjusting the -ngl parameter, demonstrating the importance of fine-tuning arguments based on the specific capabilities of their NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 card.
Vulkan Integration Spurs Performance Gains: A proposition to bolster llamafile by integrating Vulkan support led to performance enhancements on an Intel-based laptop with an integrated GPU, yet this required the granular task of re-importing and amending the llama.cpp file.
DiscoResearch Discord
- No Schedules Needed for New Optimizers: The huggingface/transformers repository now has a pull request introducing Meta’s schedule-free optimizers for AdamW and SGD, which promises substantial enhancements in model training routines.
- AI Devs Convene in Hürth: An AI community event focusing on synthetic data generation, LLM/RAG pipelines, and embeddings is scheduled for May 7th in Hürth, Germany. Registration is open, with emphasis on a hands-on, developer-centric format, and can be found at Developer Event - AI Village.
- Sharing Synthetic Data Insights Sought: Demand for knowledge on synthetic data strategies is high, with specific interest in the quality of German translated versus German generated data, indicating a niche requirement for regional data handling expertise.
- Command-R Tackles Tough Translations: The Command-R model showcased on Hugging Face Spaces excels at translating archaic Middle High German text, outperforming GPT-4 equivalents and underscoring the potential upheaval in historical language processing.
- Open-Source Model Development Desired: There’s anticipatory buzz that an open-source release of the impressive Command-R could amplify developer engagement, echoing the ecosystem success seen with publicly accessible models like Mistral.
AI21 Labs (Jamba) Discord
-
Slow and Steady Wins the Race?: Comparisons reveal that Jamba’s 1B Mamba model lags in training speed by 76% when run on an HGX, compared to a standard Transformer model.
-
Size Doesn’t Always Matter: Engineers have introduced scaled-down Jamba models, 8xMoE with 29B and 4xMoE with 17.7B parameters, achieving decent performance on hardware as accessible as a 4090 GPU at 4 bit.
-
Weights and Measures: A creator’s application of spherical linear interpolation (Slerp) for expert weight reduction in Jamba models sparked interest, with plans to share a notebook detailing the process.
-
Power Play: In the quest for optimal GPU utilization while handling a 52B Jamba model, one engineer seeks more efficient methods for training, likely considering a switch from pipeline to Tensor Parallelism given current capacity constraints.
-
What’s the Best Model Serving Approach?: The community is engaging in conversations about effective inference engines for Jamba models, though no consensus has been reached yet.
Datasette - LLM (@SimonW) Discord
-
QNAP NAS - A Home Lab for AI Enthusiasts: An AI engineer shared a guide about setting up a QNAP NAS (model TS-h1290FX) as an AI testing platform, emphasizing its notable specs such as an AMD EPYC 7302P CPU, 256GB DRAM, and 25GbE networking.
-
Streamlining AI with Preset Prompts: There’s curiosity among engineers about storing and reusing system prompts to improve efficiency in AI interactions, although the discussion did not progress with more detailed insights or experiences.
-
Alter: The Mac’s AI Writing Assistant: Alter is launching in beta, offering AI-powered text improvement services to macOS users, capable of integrating with applications like Keynote, as showcased in this demonstration video.
-
A Singular AI Solution for Mac Enthusiasts: The Alter app aims to provide context-aware AI features across all macOS applications, potentially centralizing AI tools and reducing the need for multiple services. Details about its full capabilities are available on the Alter website.
Skunkworks AI Discord
- Dynamic Compute Allocation Sparks Ideas: Engineers discussed a paper proposing dynamic allocation of compute resources on a per-token basis within neural networks, which stirred interest for possible adaptations in neurallambda; the aim is to allow the network to self-regulate its computational efforts.
- Rethinking Training Approaches for neurallambda: Exploratory talks included using pause/think tokens, reinforcement learning for conditionals, and emulating aspects of RNNs that adaptively control their compute usage, which could enhance training efficacy for neurallambda.
- Innovative Input Handling on the Horizon: Technologists considered novel input approaches for neurallambda, like using a neural queue for more flexible processing and conceptualizing input as a Turing machine-esque tape, where the network could initiate tape movements.
- Improving LLMs Data Structuring Capabilities: Participants shared an instructional video titled “Instructor, Generating Structure from LLMs”, showing methods to extract structured data such as JSON from LLMs like GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and GPT-4-Vision, aimed at getting more reliable results from these models. Watch the instructional video.
- Video Learning Opportunities: A second educational video was linked, however, it was provided without context, suggesting a potential resource for self-guided learning for the curious. Explore the video.
LLM Perf Enthusiasts AI Discord
-
Haiku Performance Tuning Search: A guild member is seeking advice on improving the speed of Haiku due to dissatisfaction with its current throughput.
-
Anthropic’s API Outperforms GPT-4 Turbo: A user presented evidence that Anthropic’s beta API surpassed GPT-4 Turbo in numerous tests on the Berkeley function calling benchmark. Results from this study can be found in a detailed Twitter thread.
The Alignment Lab AI Discord has no new messages. If this guild has been quiet for too long, let us know and we will remove it.
PART 2: Detailed by-Channel summaries and links
Perplexity AI ▷ #announcements (1 messages):
- New Story Discovery Experience on iOS: Perplexity is testing a new format for story discovery in its iOS app. Feedback is welcomed in the designated channel; get the app here.
Perplexity AI ▷ #general (1199 messages🔥🔥🔥):
-
Event Ends with a Draw: The Perplexity AI Discord event concluded with users eun08000 and codelicious tied for top place. Winners will be contacted via DMs for their prizes.
-
Differences in Claude 3 Opus: Users discussed differences in the Claude 3 Opus model between Poe and Perplexity, noting performance variations, particularly in creativity and writing tasks.
-
Solar Eclipse Excitement: Members of the server shared their anticipation and observations of the solar eclipse, with conversations including the ideal viewing equipment and experiences of witnessing the phenomenon.
-
Questions on Moon Formation: A discussion arose about the formation of the Moon, with one user skeptical about the theory of the Moon being part of a celestial body that collided with Earth. Links to educational resources were shared for further understanding.
-
Getting Pro Role on Discord: Users inquired about obtaining the ‘Pro’ role on the Discord server, with a direction to rejoin via a Pro Discord link provided in the account settings on the Perplexity website.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from OscaR-_-010 (@OscaR_010__): @kodjima33 @bing @OpenAI @perplexity_ai @AnthropicAI Hi, friend . Here I do have to say that in searches @perplexity_ai surpasses all those mentioned, its search range is superior. The search includes...
- rabbit: $199 no subscription required - the future of human-machine interface - pre-order now
- Supported Models: no description found
- Impact of sanctions on Russia and Belarus : Stripe: Help & Support: no description found
- Cat Cat Memes GIF - Cat Cat memes Cat images - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Space GIF - Space - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Queen - Champion GIF - Queen Freddie Mercury We Are The Champions - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Mobile Vendor Market Share Worldwide | Statcounter Global Stats: This graph shows the market share of mobile vendors worldwide based on over 5 billion monthly page views.
- Can I use Privacy if I live outside the US?: We are only able to provide our service to US citizens or legal residents of the US at this time. We're continuing to explore opportunities and options to bring Privacy to the rest of the world. H...
- Mobile Operating System Market Share Worldwide | Statcounter Global Stats: This graph shows the market share of mobile operating systems worldwide based on over 5 billion monthly page views.
- Unlimited Power Star Wars GIF - Unlimited Power Star Wars - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Mojeek Labs | RAG Search: no description found
- Are Sonar models new?: no description found
- The difference between the models on the PPL website and the API models.: no description found
- Model names?: no description found
- Solar Eclipse LIVE Coverage (with Video & Updates): Join us for live coverage of the solar eclipse, featuring live eclipse video! We’ll show you the total solar eclipse live in Mexico, the United States, and C...
- Eight Wonders Of Our Solar System | The Planets | BBC Earth Science: Discover the most memorable events in the history of our solar system. Travel to the surface of these dynamic worlds to witness the moments of high drama tha...
- GOES-East CONUS - GeoColor - NOAA / NESDIS / STAR: no description found
Perplexity AI ▷ #sharing (40 messages🔥):
- Exploring the AI Frontier: Users shared a plethora of search queries leading to Perplexity AI’s platform, covering topics from the Samsung Galaxy S23 to the impacts of AI on the music industry.
- Tech Giants Making Moves: A link to a YouTube video discussing Tesla’s robotaxi announcement and Apple’s home robot project was shared, highlighting the advancements and rumors in technology sectors.
- Interactivity Reminders: Several reminders for users were posted, urging them to ensure their threads are shareable, indicated by specific instructions and attachment links.
- Featured Success Story: Perplexity AI’s efficiency in model training was showcased in an Amazon Web Services case study, presenting significant reductions in training times and enhanced user experience.
- Educational Insights: Links to knowledge resources on various subjects such as color basics, the origins of geometric proofs, and SpaceX’s Mars plans were provided, reflecting a diverse interest in learning and self-improvement.
Links mentioned:
- Perplexity Accelerates Foundation Model Training by 40% with Amazon SageMaker HyperPod | Perplexity Case Study | AWS: no description found
- Tesla robotaxi announcement, Alphabet-HubSpot deal rumors, Apple’s home robot project: In today's episode of Discover Daily by Perplexity, we dive into Tesla's upcoming robotaxi unveiling, set for August 8th, and explore what this autonomous ve...
- Workflows & Tooling to Create Trusted AI | Ask More of AI with Clara Shih: Clara sits down with the founder/CEOs of three of the hottest AI companies-- Aravind Srinivas (Perplexity AI), Jerry Liu (LlamaIndex), and Harrison Chase (La...
Perplexity AI ▷ #pplx-api (40 messages🔥):
- API Credit Purchase Difficulties: Members are experiencing issues when attempting to purchase API credits; the balance appears as $0 after a refresh despite trying multiple times. ok.alex requests affected users to send account details for resolution.
- Discrepancy Between pplx-labs, API, and Web App: Users have reported inconsistencies in results when using the same prompts across the pplx-labs, API, and web application, with the API showing more hallucinations. icelavaman informed that the default model from pplx.ai is not available via the API, and citations are currently in closed beta.
- Ruby Wrapper for Perplexity API in Progress: filterse7en is developing an OpenAI-based Ruby wrapper library for the Perplexity API.
- API vs Web App Model Differences: Discussions reveal differences between results from the API and the web application, with skepticism around results quality and the presence of hallucinations. brknclock1215 suggests that using the
sonar-medium-onlinemodel via the API should effectively be the same as the “Sonar” model on the web version without Pro. - Inquiries on pplx-pro Model API Access: marciano inquired if the model used in pplx-pro is accessible via the API. ok.alex clarified that Pro search is only available on the web and their apps, not via the API.
Links mentioned:
- no title found: no description found
- Supported Models: no description found
Nous Research AI ▷ #off-topic (15 messages🔥):
- Introducing Command R+: A YouTube video titled “Introducing Command R+: A Scalable LLM Built for Business” has been shared, showcasing cohere’s powerful LLM specifically built for enterprise applications.
- Overflow of AI Research: A member expressed concern asking if more AI researchers are needed, with one member suggesting there’s already more research than what can be digested, while another member pointed out the need for more meta-researchers to synthesize and interpret the influx of information.
- Search Images in a Snap: The project ‘Where’s My Pic?’ was introduced, offering a solution similar to Google Image Search for local folders, which can be a time-saver for locating images quickly. Learn more about the project in this YouTube video.
- Canada’s AI Strategy: An announcement of Canada’s ambition to be at the forefront of AI, including creating good-paying job opportunities in innovation and technology, was highlighted through a government news release.
- Hugging Face Tech Insights: The SSL certificates of huggingface.tech have been analyzed, providing insights into the tools they use, as detailed on crt.sh.
Links mentioned:
- Introducing Command R+: A Scalable LLM Built for Business: Today, we will take a look at the Command R+, cohere's most powerful, scalable large language model (LLM) purpose-built to excel at real-world enterprise us...
- Securing Canada’s AI advantage: no description found
- crt.sh | huggingface.tech: no description found
Nous Research AI ▷ #interesting-links (49 messages🔥):
-
Rohan Paul’s AI Tweet Sparks Curiosity: A tweet by Rohan Paul regarding AI was revisited, noting its promising earlier impression but lacking follow-up information and insights after three months. The discussion also touched upon the usability of fp8 on NVIDIA’s 4090 GPUs.
-
LLaMA-2-7B Breaks the Context Length: A groundbreaking achievement was shared where LLaMA-2-7B was trained to handle a massive 700K context length using just 8 A100 GPUs, significantly surpassing the expected capacity of 32K to 200K tokens.
-
Gemma 1.1 Joins the AI Language Model Family: Google released Gemma 1.1 7B (IT), an instructive language model, on Hugging Face, boasting improvements in quality, coding capabilities, and instruction following. It was highlighted for its novel RLHF method used during training.
-
Pathfinding in Mazes Takes a Twist: A unique approach to unifying physics was proposed using conjectural frameworks like the Fibonacci binomial conjecture, suggesting that NLP can simulate any process.
-
GPT-4 Takes a Meta Turn: An experience with GPT-4 was shared where a given prompt led to unexpectedly meta and self-referential content. The discussion on this intriguing performance included a YouTube link to a relevant game’s narrator feature.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Zhang Peiyuan (@PY_Z001): 🌟700K context with 8 GPUs🌟 How many tokens do you think one can put in a single context during training, with 8 A100, for a 7B transformer? 32K? 64K? 200K? No, my dear friend. I just managed to tra...
- Large Language Models as Commonsense Knowledge for Large-Scale Task Planning: Large-scale task planning is a major challenge. Recent work exploits large language models (LLMs) directly as a policy and shows surprisingly interesting results. This paper shows that LLMs provide a ...
- Classification - Outlines 〰️: Structured text generation with LLMs
- Paper page - Beyond A*: Better Planning with Transformers via Search Dynamics Bootstrapping: no description found
- google/gemma-1.1-7b-it · Hugging Face: no description found
- Paper page - Direct Nash Optimization: Teaching Language Models to Self-Improve with General Preferences: no description found
- Factorial Funds | Under The Hood: How OpenAI's Sora Model Works: no description found
- Visualizing Attention, a Transformer's Heart | Chapter 6, Deep Learning: Demystifying attention, the key mechanism inside transformers and LLMs.Instead of sponsored ad reads, these lessons are funded directly by viewers: https://3...
- Bastion: Narrator Bits Part 1 (Wharf District, Workmen Ward, Breaker Barracks): I recorded the game with narrator audio only and everything else turned down to zero in the sound menu volume settings. Then I just cut out the silent part...
- GitHub - vicgalle/configurable-safety-tuning: Data and models for the paper "Configurable Safety Tuning of Language Models with Synthetic Preference Data": Data and models for the paper "Configurable Safety Tuning of Language Models with Synthetic Preference Data" - vicgalle/configurable-safety-tuning
Nous Research AI ▷ #ask-about-llms (148 messages🔥🔥):
-
GitHub Resource for PDF to Markdown Conversion: A member shared a GitHub repository titled VikParuchuri/marker, which provides a tool to convert PDF files to markdown format with high accuracy. The repository can be found at GitHub - VikParuchuri/marker.
-
Hermes Function Calling Woes: There was a discussion on how to make
Hermes-2-Pro-Mistral-7Bexecute functions using atoolsconfiguration similar to OpenAI’s models. It was noted that while the model can handle ChatML syntax and function calls within messages, it encounters problems executing functions defined intools. -
Full-Parameter vs Adapter Training in LLMs: Members debated on the challenges of achieving consistent results with full parameter finetuning compared to training adapters, with some sharing their relative success or lack thereof with either method in different contexts, such as Mixtral or Llamas.
-
Exploring Large Model Output Limitations: A conversation took place about the limitations on output size in large language models, with the understanding that while input contexts can be quite large, output is limited due to different training data and operational considerations like needing examples of similarly sized outputs for training.
-
Combining Ontologies and Vector Searches: There was an extensive discussion on utilizing knowledge graph (KG) ontologies with language models. Tips were shared on how to create Cypher queries from input text, the effectiveness of walking KG graphs using a vector search evaluation function, and the integration of vector databases with graph databases for production uses.
Links mentioned:
- TroyDoesAI/MermaidMistral · Hugging Face: no description found
- GitHub - NousResearch/Hermes-Function-Calling: Contribute to NousResearch/Hermes-Function-Calling development by creating an account on GitHub.
- About GPU memory usage · Issue #8 · joey00072/ohara: Hello. First of all, thanks for sharing a bitnet training code. I have a question about GPU memory usage. As I understanding, bitnet can reduce VRAM usage compared to fp16/bf16 precision. However, ...
- GitHub - VikParuchuri/marker: Convert PDF to markdown quickly with high accuracy: Convert PDF to markdown quickly with high accuracy - VikParuchuri/marker
Nous Research AI ▷ #project-obsidian (5 messages):
-
Twisting LLaVA with Randomness: A member experimented with the LLaVA vision-language model by injecting randomness into the image embeddings and observed the LLM’s interpretations, detailed in their blog post. The process involved tweaking the model to accept random projections instead of CLIP projections, essentially performing a “Rorschach test” on the AI.
-
nanoLLaVA’s Mighty Appearance: Launching the “small but mighty” nanoLLaVA sub 1B vision-language model, a member shared a link to their creation nanoLLaVA on Hugging Face, running on edge devices and boasting a unique combination of a Base LLM and Vision Encoder.
-
Obsidian and Hermes Vision Updates Imminent: The same member announced impending updates to both Obsidian and Hermes Vision, suggesting enhancements in vision-language model capabilities.
-
ChatML Fusing Capabilities with LLaVA: There was a successful endeavor to make ChatML work with the LLaVA model, hinting at a potential bridge between chat and vision-language tasks.
Links mentioned:
- anotherjesse.com - Rorschach Test For LLaVA LLM: no description found
- qnguyen3/nanoLLaVA · Hugging Face: no description found
Nous Research AI ▷ #rag-dataset (19 messages🔥):
- Chunking Script for Diverse Dataset Suggested: The idea of writing a chunking script to save using a big RAG call at the time of generating the dataset was put forward. It can potentially make the dataset more diverse and efficient by preparing the RAG generation beforehand.
- Multidoc Queries Via Claude Opus: A discussion took place about the possibility of generating multidoc queries using Claude Opus by selecting documents from varied domains and generating queries that cut across them. This approach could enhance complex query generation for RAG models.
- Diverse Document Sources for Model Training: Links to diverse document sources have been shared, such as the OCCRP data platform and a repository of various files at The Eye. These sources could be scraped to create a rich training dataset.
- Ransomware Victim Documents for Training: There was a consideration of ransomware groups publishing victims’ internal documents as a potential training data source. However, the ethics of using such data was flagged as questionable.
- RAPTOR Clustering Strategy Discussed: The recursive aspect of the RAPTOR clustering method was highlighted, prompting a discussion on the strategy of generating clusters and their role in stratifying collections for the RAG dataset.
Links mentioned:
- no title found: no description found
- Index of /public/: no description found
Nous Research AI ▷ #world-sim (567 messages🔥🔥🔥):
-
Worldsim Wheezes as We Wait: Users continue to eagerly inquire about the recovery of Worldsim following a DDoS attack, discussing the potential implementation of a login system to prevent future attacks from notorious online communities like 4chan.
-
AI Memory Mystery: There’s confusion and discussion about whether Claude can remember information across separate sessions or whether it is just imitating this ability through its probabilistic model, with random token selection causing varying outcomes despite identical prompts.
-
Seeking Sustainable Solution: As users propose subscription models for Worldsim to offset the high operational costs sparked by indiscriminate access, Nous Research hints at a future “pro” version with plans for more scenarios, while stressing the need for a sustainable platform.
-
Tales and Tech of Transcendence: The channel teems with philosophical discussions about consciousness, existence, and the potential of living in a simulation; parallel dialogues delve into the nature of AI, existence, and the interplay of science and philosophy.
-
Impatient for Play: Users express a mix of impatience and enthusiasm for Worldsim’s return, asking for updates, while discussing ways to prevent unrestricted access and pondering potential costs of a subscription-based model to keep the service both financially viable and protected from misuse.
Links mentioned:
- Client SDKs: no description found
- MemGPT - Unlimited Context (Memory) for LLMs | MLExpert - Crush Your Machine Learning interview: How can you overcome the context window size limit of LLMs? MemGPT helps handle longer conversations by cleverly managing different memory tiers.
- fbjr/cohere_c4ai-command-r-plus-mlx-4bit-128g · Hugging Face: no description found
- world_sim: no description found
- websim.ai: no description found
- no title found: no description found
- Google's New AI Can Generate Entire 2D Platformer Games: The new model, dubbed Genie, can create playable environments from a single image prompts.
- An Introduction to Game B - Game B Wiki: no description found
- The Box | Science Fiction Animatic: Video Summary:The animatic follows the perspective of "The Breacher," a character determined to escape the confines of a simulated reality, known as the "Wor...
- GitHub - simonw/llm: Access large language models from the command-line: Access large language models from the command-line - simonw/llm
- Worldsim and jailbreaking Claude 3 Including subtitles [-2-]: Personal learning
- The Great Eclipse | Science Fiction Animatic: Video Summary:This animatic explores a war of ideas and beliefs, fought not with weapons but through the power of data, debates, and simulated worlds. As dif...
- Quantum Mechanics can be understood through stochastic optimization on spacetimes - Scientific Reports: no description found
- Home: no description found
Stability.ai (Stable Diffusion) ▷ #general-chat (977 messages🔥🔥🔥):
- Searching for the Stability Bot: Users inquired about generating images and were redirected to check server status in <#1047610792226340935> as bots are currently down.
- Curiosity About Image Generation Results: Users discussed differences in image output quality between local models and Dreamstudio, with suggestions to try open-source upscalers and inquiries into the effectiveness of various techniques.
- Anticipation for Stable Diffusion 3: Conversations indicate an informal ETA of 2-4 weeks for the release of SD3, with discussions about its anticipated improvements and capabilities.
- Exploring SD Model Enhancements: Users exchanged information on training LoRAs, including questions about installation and practicality, with suggestions to follow specific GitHub repositories for guidance.
- Switching Between UIs: Members shared advice for switching from Automatic 1.1.1.1 to other UIs like StableSwarm, emphasizing the latter’s enhanced user experience and features for newcomers.
Links mentioned:
- Leonardo.Ai: Create production-quality visual assets for your projects with unprecedented quality, speed and style-consistency.
- stabilityai/cosxl · Hugging Face: no description found
- SDXL-Lightning - a Hugging Face Space by ByteDance: no description found
- Visual Autoregressive Modeling: Scalable Image Generation via Next-Scale Prediction: We present Visual AutoRegressive modeling (VAR), a new generation paradigm that redefines the autoregressive learning on images as coarse-to-fine "next-scale prediction" or "next-resolutio...
- PixArt LCM - a Hugging Face Space by PixArt-alpha: no description found
- Lexica Testica - 1.0 | Stable Diffusion Checkpoint | Civitai: Initialized from OpenJourney v2, further fine-tuned for 4000 steps on images scraped from the front page of Lexica art (January 2023). Good at prod...
- Frieren Wow GIF - Frieren Wow Elf - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Yoshi Mario GIF - Yoshi Mario Yoshis Island - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- OpenModelDB: OpenModelDB is a community driven database of AI Upscaling models. We aim to provide a better way to find and compare models than existing sources.
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- VAR/demo_sample.ipynb at main · FoundationVision/VAR: [GPT beats diffusion🔥] [scaling laws in visual generation📈] Official impl. of "Visual Autoregressive Modeling: Scalable Image Generation via Next-Scale Prediction" - FoundationVision/VAR
- GitHub - LykosAI/StabilityMatrix: Multi-Platform Package Manager for Stable Diffusion: Multi-Platform Package Manager for Stable Diffusion - LykosAI/StabilityMatrix
- Federal Register :: Request Access: no description found
- How to Run Stable Diffusion in Google Colab (Free) WITHOUT DISCONNECT: Here's how to code your own python notebook in Colab to generate AI images for FREE, without getting disconnected. We'll use the Diffusers library from Huggi...
- Survey: Comparing generated photos by AI (Diffusion Models): This is a survey to determine the more accurate output from different diffusion models like SD 1.5, SD 2.0, SDXL, Dall-e-3 and a custom fine tuned model. It will take a few minutes to complete the su...
- Installing Stability Matrix (1 click installers for Automatic 1111, ComfyUI, Fooocus, and more): This Stability Matrix application is designed for Windows and allows for installing and managing text to image web ui apps like Automatic 1111, ComfyUI, and ...
- A Conversation with Malcolm and Simone Collins (Supercut): Malcolm and Simone are the founders of pronatalist.org, The Collins Institute for the Gifted, and Based Camp Podcast.All Outcomes Are Acceptable Blog: https:...
- GitHub - altoiddealer/--sd-webui-ar-plusplus: Select img aspect ratio from presets in sd-webui: Select img aspect ratio from presets in sd-webui. Contribute to altoiddealer/--sd-webui-ar-plusplus development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Identifying Stable Diffusion XL 1.0 images from VAE artifacts: The new SDXL 1.0 text-to-image generation model was recently released that generates small artifacts in the image when the earlier 0.9 release didn't have them.
- GitHub - nashsu/FreeAskInternet: FreeAskInternet is a completely free, private and locally running search aggregator & answer generate using LLM, without GPU needed. The user can ask a question and the system will make a multi engine search and combine the search result to the ChatGPT3.5 LLM and generate the answer based on search results.: FreeAskInternet is a completely free, private and locally running search aggregator & answer generate using LLM, without GPU needed. The user can ask a question and the system will make a mul...
- How to Install Stable Diffusion - automatic1111: Part 2: How to Use Stable Diffusion https://youtu.be/nJlHJZo66UAAutomatic1111 https://github.com/AUTOMATIC1111/stable-diffusion-webuiInstall Python https://w...
- GitHub - derrian-distro/LoRA_Easy_Training_Scripts: A UI made in Pyside6 to make training LoRA/LoCon and other LoRA type models in sd-scripts easy: A UI made in Pyside6 to make training LoRA/LoCon and other LoRA type models in sd-scripts easy - derrian-distro/LoRA_Easy_Training_Scripts
- SonicDiffusion - V4 | Stable Diffusion Checkpoint | Civitai: Try it out here! https://mobians.ai/ Join the discord for updates, share generated-images, just want to chat or if you want to contribute to helpin...
- GitHub - Stability-AI/StableSwarmUI: StableSwarmUI, A Modular Stable Diffusion Web-User-Interface, with an emphasis on making powertools easily accessible, high performance, and extensibility.: StableSwarmUI, A Modular Stable Diffusion Web-User-Interface, with an emphasis on making powertools easily accessible, high performance, and extensibility. - Stability-AI/StableSwarmUI
- GitHub - camenduru/Open-Sora-Plan-replicate: Contribute to camenduru/Open-Sora-Plan-replicate development by creating an account on GitHub.
- GitHub - GarlicCookie/PNG-SD-Info-Viewer: PNG-SD-Info-Viewer is a program designed to quickly allow the browsing of PNG files with associated metadata from Stable Diffusion generated images.: PNG-SD-Info-Viewer is a program designed to quickly allow the browsing of PNG files with associated metadata from Stable Diffusion generated images. - GarlicCookie/PNG-SD-Info-Viewer
- GitHub - GarlicCookie/SD-Quick-View: SD-Quick-View is a program designed to very quickly look through images generated by Stable Diffusion and see associated metadata.: SD-Quick-View is a program designed to very quickly look through images generated by Stable Diffusion and see associated metadata. - GarlicCookie/SD-Quick-View
- GitHub - lllyasviel/stable-diffusion-webui-forge: Contribute to lllyasviel/stable-diffusion-webui-forge development by creating an account on GitHub.
- ComfyUI-Tara-LLM-Integration/README.md at main · ronniebasak/ComfyUI-Tara-LLM-Integration: Contribute to ronniebasak/ComfyUI-Tara-LLM-Integration development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- NewRealityXL ❗ All-In-One Photographic - ✔ 3.0 Experimental | Stable Diffusion Checkpoint | Civitai: IMPORTANT: v2.x ---> Main Version | v3.x ---> Experimental Version I need your time to thoroughly test this new 3rd version to understand all...
Unsloth AI (Daniel Han) ▷ #general (341 messages🔥🔥):
-
Conversion Frustration: Members expressed dissatisfaction with machine learning models like Chat GPT and Claude, which when converting an image to HTML, lost fidelity in colors and border rounding. A humorous suggestion was made to convert images to ASCII art instead.
-
Shared Challenges with Model Limitations: Conversations included server crashes leading to lost models due to issues with model saving on platforms like Unsloth AI and Hugging Face, and some users expressed their loss of extensive fine-tuning efforts.
-
Curiosity on LLM Vision Model Alternatives: While vision models still linger on Unsloth AI’s roadmap, they remain a lower priority. Users discussed alternatives like Dreambooth but didn’t find a definitive solution.
-
GPU Woes for LLM Training: Strategies for avoiding laptop overheating during model training were humorously debated, including moving to Antarctica or using air conditioning.
-
Anticipation for Gradient Checkpointing and Longer Contexts: Unofficial hints and teasers about Unsloth AI’s upcoming features spurred debate and anticipation, leading to discussions on possible implementations and benefits for users with limited GPU resources.
Links mentioned:
- liminerity/Mistral-quiet-star-demo · Hugging Face: no description found
- liminerity/Mistral-quiet-star-demo · Hugging Face: no description found
- Unsloth Fixing Gemma bugs: Unsloth fixing Google's open-source language model Gemma.
- ASCII art elicits harmful responses from 5 major AI chatbots: LLMs are trained to block harmful responses. Old-school images can override those rules.
- SPIN/scripts/finetune.sh at main · uclaml/SPIN: The official implementation of Self-Play Fine-Tuning (SPIN) - uclaml/SPIN
- LLaVA/docs/Finetune_Custom_Data.md at main · haotian-liu/LLaVA: [NeurIPS'23 Oral] Visual Instruction Tuning (LLaVA) built towards GPT-4V level capabilities and beyond. - haotian-liu/LLaVA
- GitHub - facebookresearch/schedule_free: Schedule-Free Optimization in PyTorch: Schedule-Free Optimization in PyTorch. Contribute to facebookresearch/schedule_free development by creating an account on GitHub.
- When GPT-5 is coming out | Sam Altman and Lex Fridman: Lex Fridman Podcast full episode: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jvqFAi7vkBcPlease support this podcast by checking out our sponsors:- Cloaked: https://cloa...
- Home: 2-5X faster 70% less memory QLoRA & LoRA finetuning - unslothai/unsloth
- GitHub - stanfordnlp/pyreft: ReFT: Representation Finetuning for Language Models: ReFT: Representation Finetuning for Language Models - stanfordnlp/pyreft
- Trainer: no description found
- gate369/Alpaca-Star · Datasets at Hugging Face: no description found
Unsloth AI (Daniel Han) ▷ #random (78 messages🔥🔥):
- Preferred AI News Sources Shared: Members shared their go-to sources for AI news—AI News and Reddit, particularly giving a shoutout to the user localllama for consistent updates.
- Debating the Merits of Learning Rate Schedulers: A member is sharing results from experimenting with different learning rate schedulers—linear, cosine with restarts, and constant—pointing out that constant surprisingly seems to work best for their model, focusing on a general assistant in multiple languages.
- Finetuning with DPO Questions Raised: Curiosity arose around why models finetuned with DPO (Dynamic Positional Offsets) perform well on the Open LLM Leaderboard, even if the base models have lower scores. It was suggested that proprietary datasets could be an influencing factor.
- Impact of Benchmarks on Model Perception Discussed: Discussion about benchmarks revealed that they may not always align with perceived quality; low-scoring models could still be very effective. Concerns about the potential for models to be ‘contaminated’ by test data and about the rigidity of the benchmarks were also expressed.
- Unsloth Hiring and Open Source Contributions Mentioned: Members discussed forthcoming hiring for full-stack developers and a developer advocate, clarifying that the roles will be for contributing to the open-source community and building out the Unsloth Pro platform.
Link mentioned: Home: 2-5X faster 70% less memory QLoRA & LoRA finetuning - unslothai/unsloth
Unsloth AI (Daniel Han) ▷ #help (374 messages🔥🔥):
-
Private Hosting of AI Models: A member announced they are hosting their AI projects on their own server to maintain the privacy of some unreleased models. They hinted at future integration of advertisements after hosting more high-quality models and shared a link: Hircoir Text-to-Speech.
-
Inference Code Flexibility Praised: The Unsloth AI’s inference code received praise for its speed and ease of use. Members were reminded they could modify inference settings like temperature and use Generative Guided Unsupervised Fine-tuning (GGUF) as desired.
-
Discussion on Model Merging: A chat involved potential merging tactics for AI models, with suggestions including applying differences between various models onto each other. Views on the subject varied from skepticism to optimism based on past experiences.
-
User Struggles with Code: One user expressed difficulty with coding, specifically related to model parameter adjustments for batch inference. They were directed to Unsloth’s GitHub for guidance, highlighting the utility of
model.generate. -
Batch Inference Clarification: Members discussed how to effectively execute batch inference. The usage of
num_return_sequenceswas corrected, indicating that it only works for single prompts, not for batched prompts which should be “shoved all together.”
Links mentioned:
- Google Colaboratory: no description found
- Google Colaboratory: no description found
- HirLab - Convertidor de Texto a Voz por Hircoir: HirLab, es una plataforma de conversión de texto a voz basada en inteligencia artificial. Convierte texto a voz de forma rápida y precisa.
- Improving LoRA: Implementing Weight-Decomposed Low-Rank Adaptation (DoRA) from Scratch: Low-rank adaptation (LoRA) is a machine learning technique that modifies a pretrained model (for example, an LLM or vision transformer) to better suit a specific, often smaller, dataset by adjusting o...
- Customizing LLMs - LlamaIndex: no description found
- Customizing LLMs - LlamaIndex: no description found
- Text generation strategies: no description found
- Mistral Fine Tuning for Dummies (with 16k, 32k, 128k+ Context): Discover the secrets to effortlessly fine-tuning Language Models (LLMs) with your own data in our latest tutorial video. We dive into a cost-effective and su...
- unsloth/unsloth/save.py at main · unslothai/unsloth: 2-5X faster 70% less memory QLoRA & LoRA finetuning - unslothai/unsloth
- GitHub - unslothai/unsloth: 2-5X faster 70% less memory QLoRA & LoRA finetuning: 2-5X faster 70% less memory QLoRA & LoRA finetuning - unslothai/unsloth
- Home: 2-5X faster 70% less memory QLoRA & LoRA finetuning - unslothai/unsloth
- Mistral with flash attention 2 and right padding · Issue #26877 · huggingface/transformers: System Info transformers version: 4.34.0 Platform: Linux-5.4.0-148-generic-x86_64-with-glibc2.31 Python version: 3.10.13 Huggingface_hub version: 0.17.3 Safetensors version: 0.4.0 Accelerate versio...
- pharaouk/UltraInteract_sft · Datasets at Hugging Face: no description found
- Models: no description found
- Batch inference produces nonsense results for unsloth/mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2-bnb-4bit · Issue #267 · unslothai/unsloth: Hi there, after loading the model with: from unsloth import FastLanguageModel import torch model, tokenizer = FastLanguageModel.from_pretrained( model_name = "unsloth/mistral-7b-instruct-v0.2-bnb...
Unsloth AI (Daniel Han) ▷ #showcase (2 messages):
- Introducing Aurora-M: A new 15.5 billion parameter open-source multilingual language model named Aurora-M has been developed, following the U.S. Executive Order on AI. It demonstrates cross-lingual impact of mono-lingual safety alignment and surpasses 2 trillion training tokens.
- Cross-Lingual Safety Impact Validated: The team found that safety alignment tuning performed on English not only enhanced safety in English but also in other languages such as German. This is touted as the first evidence of cross-lingual impact of mono-lingual safety alignment.
- Peer Recognition: The community has shown support for the Aurora-M project with positive reactions like “great work! 🔥”.
- Aurora-M’s Upcoming Developments: The project aims to build on Aurora-M by training a mixture of experts using LoRA and a subsequent merge. Feedback from the Unsloth AI community is sought, particularly concerning the use of LoRA fine-tuning notebooks.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from ً (@__z__9): New preprint! The first multi-lingual red-teamed open-source continually pre-trained LLM - **Aurora-M** in accordance with the #WhiteHouse Executive Order on the Safe, Secure, and Trustworthy developm...
- Aurora-M: The First Open Source Multilingual Language Model Red-teamed according to the U.S. Executive Order: Pretrained language models underpin several AI applications, but their high computational cost for training limits accessibility. Initiatives such as BLOOM and StarCoder aim to democratize access to p...
Unsloth AI (Daniel Han) ▷ #suggestions (148 messages🔥🔥):
-
The Investment Conundrum: A hot debate ensued regarding the value of Jamba and Mamba, with opinions varying from skepticism to cautious optimism. While one member noted that the company behind Jamba, AI21 Labs, raised $155 million, which may indicate market interest, others were critical, suggesting that such investments might have been misguided. (AI21 Labs Fundraising)
-
Quantized Models Take Center Stage: The viability of quantized models and optimization techniques, such as AQLM, generated mixed feelings. One individual pointed out the desirable ROI from fine-tuning for specific use cases, sharing that proper investments in fine-tuning can yield significant returns despite high upfront costs. (AQLM Mixtral)
-
Varying Opinions on Model Architecture: Members evaluated the need for incorporating partially optimized MoEs and discussed the implementation of new architectures with a particular member suggesting a cautious approach of waiting to see if such models gain popularity.
-
Future of Automated AI Engineering: Conversations briefly touched upon the potential of creating finetuned models that could assist in writing optimized kernels or heavy computational tasks like Triton code generation, aiming to pioneer automated AI engineering solutions.
-
Practicality Over Hype: There was a strong current throughout the discussion underscoring the importance of practical, well-optimized models over “hyped” startup ventures. The consensus seemed to lean towards a preference for supporting proven, scalable architectures like Transformers and adding MoE implementations in due time.
Links mentioned:
- ISTA-DASLab/Mixtral-8x7b-AQLM-2Bit-1x16-hf · Hugging Face: no description found
- Generative AI startup AI21 Labs lands $155M at a $1.4B valuation | TechCrunch: AI21 Labs, a company competing against OpenAI and Anthropic, among other generative AI players, has raised $155 million in capital.
- ai21labs/Jamba-v0.1 · Hugging Face: no description found
- alpindale/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2-AQLM-2Bit-1x16 · Hugging Face: no description found
- Generative AI startup AI21 Labs lands $155M at a $1.4B valuation | TechCrunch: AI21 Labs, a company competing against OpenAI and Anthropic, among other generative AI players, has raised $155 million in capital.
- Choice of torch.compile vs. triton: On GPUs torch.compile() will apply various compiler optimizations with the most important ones being cuda graphs and fusions. Fusions specifically are done by code generating triton kernels so torch.c...
LM Studio ▷ #💬-general (488 messages🔥🔥🔥):
-
GPU Offload Confusion Cleared: Users were guided on optimizing GPU use in LM Studio with suggestions to adjust “n_gpu_layers” and “GPU Offloading” settings for better performance, alleviating concerns about overreliance on integrated graphics or failure to utilize Nvidia GPUs. The advice pointed towards ensuring models are fully offloaded to GPU for better speed when possible.
-
Big LLMs and Multi-GPU Setup: Discussions about running large models, such as a 70b model, revolved around the importance of VRAM, with users sharing their experiences and setups including dual RTX 4060 Ti 16GB configurations. The consensus is that the more VRAM available, the larger the models that can be run without slowing down due to system RAM use.
-
Exploring Model Capabilities: Queries about whether lower GB models can learn user names led to explanations regarding the use of system prompts to instruct models on desired behavior. Clarifications were provided stating that LM Studio does not support actual learning or training of models; however, crafting detailed prompts can achieve similar outcomes as learning.
-
AI for Coding Purposes: Users recommended OpenAI’s GPT-4 for its proficiency in coding, although noting the associated costs. The discussion highlighted the lack of equivalent open-source models, reflecting the balancing act between model capability and cost.
-
Diverse Usage and Integration Questions: Conversations ranged from setting up models on separate drives, to error debugging, to asking about the compatibility of models with different formats like EXL2 and GGUF. Integration topics included connecting LM Studio with other tools like OpenDevin and using LLMs for tasks like text analysis and fiction writing.
Links mentioned:
- What is Grouped Query Attention (GQA)? — Klu: no description found
- Documentation | LM Studio: Technical Reference
- LoneStriker/miqu-1-70b-sf-4.25bpw-h6-exl2 · Hugging Face: no description found
- TheBloke/MXLewdMini-L2-13B-GGUF · Hugging Face: no description found
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- TheBloke/MXLewdMini-L2-13B-GGUF · Hugging Face: no description found
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- [Bug]: LLM Studio does not connect · Issue #807 · Pythagora-io/gpt-pilot: Version VisualStudio Code extension Operating System Windows 11 What happened? By changing the endpoint and api key from Openai to LLmStudio: if using OPENAI_ENDPOINT=http://localhost:1234/v1 There...
- big-AGI/docs/config-local-lmstudio.md at main · enricoros/big-AGI: Generative AI suite powered by state-of-the-art models and providing advanced AI/AGI functions. It features AI personas, AGI functions, multi-model chats, text-to-image, voice, response streaming, ...
- The unofficial LMStudio FAQ!: Welcome to the unofficial LMStudio FAQ. Here you will find answers to the most commonly asked questions that we get on the LMStudio Discord. (This FAQ is community managed). LMStudio is a free closed...
- Humble Tech Book Bundle: Machine Learning, AI, Deep Learning, and LLM by Pearson: Stay abreast of the technologies that will define the future with these books on AI, machine learning, and other cutting edge topics in computer science!
- GitHub - jakobdylanc/discord-llm-chatbot: llmcord.py • Talk to LLMs with your friends!: llmcord.py • Talk to LLMs with your friends! Contribute to jakobdylanc/discord-llm-chatbot development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- Trouble using LMStudio · Issue #419 · OpenDevin/OpenDevin: Describe the bug Trouble connecting to LMStudio Steps to Reproduce 1.Start server on LMStudio 2.Start frontend and backend on OpenDevin 3. Expected behavior OpenDevin asks what I want it to build A...
- Add Command R Plus support by Carolinabanana · Pull Request #6491 · ggerganov/llama.cpp: Updated tensor mapping to add Command R Plus support for GGUF conversion.
LM Studio ▷ #🤖-models-discussion-chat (103 messages🔥🔥):
- Command R+ on the Horizon: The highly anticipated Command R+ model still faces integration challenges with llama.cpp, but a fork is available where it can work. It is a significant 104B model requiring powerful hardware specs.
- GGUF Format Quirks and Help Offered: Discussions around hassle-free implementation of quant formats led to members sharing experiences and offering assistance for those looking to run GGUF models. Concerns over silently vanishing contributors like TheBloke stir community curiosity.
- Hardware Headaches and Humor: Community members jest about the costly nature of their LLM hardware hobbies, comparing expenditures to extravagant purchases like a BMW M4. There’s also advice on finding budget solutions like using the Nvidia P40 graphics card.
- AI Storytelling Pursuits: One member expresses interest in using AI models for creative storytelling and receives tips on selecting models with large context and memory management tools like MemGPT.
- Curiosity Over Vision Adapters: A question arises about the functionality of vision adapters in cjpais llava models, followed by inquiries on how to replicate visual task capabilities similar to those demonstrated in a specific video.
Links mentioned:
- pmysl/c4ai-command-r-plus-GGUF · Hugging Face: no description found
- C4AI Command R Plus - a Hugging Face Space by CohereForAI: no description found
- TheB (Pastor B): no description found
- google/gemma-1.1-7b-it · Hugging Face: no description found
- Qwen/Qwen1.5-32B-Chat-GGUF at main: no description found
- TheBloke/Wizard-Vicuna-7B-Uncensored-GGUF · Hugging Face: no description found
- Wizard Vicuna 7B Uncensored GPTQ By TheBloke: Benchmarks and Detailed Analysis. Insights on Wizard Vicuna 7B Uncensored GPTQ.: LLM Card: 7b LLM, VRAM: 4.5GB, Context: 2K, License: other, Quantized, Uncensored.
- TheBloke/goliath-120b-GGUF · Hugging Face: no description found
- j4ys0n - Overview: blockchain engineer. j4ys0n has 62 repositories available. Follow their code on GitHub.
- ggml : update mul_mat_id to use the same tensor for all the experts by slaren · Pull Request #6387 · ggerganov/llama.cpp: Changes the storage of experts in memory from a tensor per expert, to a single 3D tensor with all the experts. This will allow us support models with a large number of experts such as qwen2moe. Exi...
LM Studio ▷ #announcements (1 messages):
- LM Studio Community Page Launches: The LM Studio team has introduced a new “lmstudio-community” page on Hugging Face, providing access to the latest GGUF quants. Users can find and experiment with these models by searching for
lmstudio-communitywithin LM Studio; find them here. - @bartowski1182 Joins as LLM Archivist: Announced on Twitter, @bartowski1182 will serve as the resident LLM Archivist for LM Studio, assisting with updates to the new Hugging Face community page. Check the Twitter announcement here.
Link mentioned: Tweet from LM Studio (@LMStudioAI): If you’ve been around these parts for long enough, you might be missing @TheBlokeAI as much as we do 🥲. Us & @bartowski1182 decided to try to help fill the void. We’re excited to share the n…
LM Studio ▷ #🧠-feedback (25 messages🔥):
-
Praise for LM Studio’s GUI: Members found LM Studio to outperform other local LLM GUIs like oogabooga and Faraday, appreciating the quality results even using the same models and instructions.
-
Feature Expansion Request: A suggestion to add file reading support and various modes such as text to images, image to text, and text to voice functionalities for LM Studio was proposed, seeking improvements similar to an existing tool named Devin.
-
Vision Models Awestruck: Members are excited by the vision models tested, thanking LM Studio for its utility. Vision models are available on Hugging Face.
-
Troubleshooting Download Issues: There were issues downloading the Linux beta version of LM Studio with a user trying on Pop!_OS 22.04 LTS. The issue was identified as a bug on the website, with a direct link to the AppImage being provided (Link Here).
-
Supporting the Uncensored Model: A request was made for LM Studio to support a new, uncensored model named Dolphin 2.8 Mistral 7b v0.2, which is available on Hugging Face (Uncensored Model).
Links mentioned:
- LM Studio Beta Releases: no description found
- 👾 LM Studio - Discover and run local LLMs: Find, download, and experiment with local LLMs
- no title found: no description found
- Vision Models (GGUF) - a lmstudio-ai Collection: no description found
- cognitivecomputations/dolphin-2.8-mistral-7b-v02 · Hugging Face: no description found
LM Studio ▷ #📝-prompts-discussion-chat (2 messages):
- Inquiry about LLMs for Stock Market Analysis: A member posed a question on how to train Large Language Models (LLMs) for interpreting stock market OHLC (Open, High, Low, Close) prices.
- Request for LLM Training with Indicators: The same member inquired about incorporating indicators in the training process of LLMs for stock market analysis.
LM Studio ▷ #🎛-hardware-discussion (39 messages🔥):
-
Mixing GPUs in LM Studio: A member shared that LM Studio detects the cumulative VRAM across different GPU cards, such as an RTX 4060 Ti and a GTX 1070, resulting in improved performance compared to using VRAM with CPU/RAM.
-
Compatibility Queries for Advanced Matrix Extensions: One member asked if LM Studio can leverage Intel’s Advanced Matrix Extensions (AMX) present in 4th generation Xeon processors.
-
Explorations with ROCm Support and Mixed GPUs: Users discussed the compatibility of various RX 5000 and RX 6000 series AMD GPUs with ROCm support in LM Studio, noting that some but not all cards are supported.
-
CPU Instruction Set Support Concerns: A user experienced an issue where their processor, a Xeon E5-2690 v2, seemed to lack AVX2 support, conflicting with their belief based on previous experiences with LM Studio. A suggestion to manually install llama.cpp was proposed as a workaround.
-
Tesla P-Series GPU for Model Training and Fine-Tuning Debate: There was a mention of contention around the use of Tesla P40 GPUs for model training and fine-tuning, with some users alleging success and others suggesting limitations due to outdated CUDA support.
Links mentioned:
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- HWiNFO - Free System Information, Monitoring and Diagnostics: Free Hardware Analysis, Monitoring and Reporting. In-depth Hardware Information, Real-Time System Monitoring, Reporting & more
- GitHub - ggerganov/llama.cpp: LLM inference in C/C++: LLM inference in C/C++. Contribute to ggerganov/llama.cpp development by creating an account on GitHub.
LM Studio ▷ #🧪-beta-releases-chat (30 messages🔥):
- Beta Build Number Confusions Addressed: Facing version number confusion, a member was clarified that beta releases might not immediately reflect the correct version number and it will change in the live release.
- LM Studio Beta 0.2.19 Release: LM Studio 0.2.19 Beta was announced with support for Text Embeddings via the local server, available for download in the Beta Releases section.
- ROCM Build Delayed but Well-Received: It was mentioned that ROCM builds tend to be a version behind the main release, but despite this and some bugs, members have found it impressive and user-friendly.
- MacOS Crashes with 0.2.19: A user reported recurrent crashes with 0.2.19 on MacOS, tied to the context window of a particular model, suggesting a comprehensive issue.
- Quantized Embedding Models and GGUF Conversions: An active discussion on quantizing additional embedding models for GGUF format resulted in new models being converted and shared, with model cards to be published shortly.
Links mentioned:
- 👾 LM Studio - Discover and run local LLMs: Find, download, and experiment with local LLMs
- Leonardo Dicaprio Clapping GIF - Leonardo Dicaprio Clapping Clap - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
LM Studio ▷ #autogen (17 messages🔥):
- A Better Multi-Agent System on the Horizon: .j4ys0n announced an upcoming release of their own multi-agent system with a user interface (UI), suggesting it as a solution to the problems with existing systems and highlighting it will not require coding on the user’s part like CrewAI does.
- The UI Advantage for Simplicity: .j4ys0n’s tool is positioned as a “for dummies” solution that will offer ease of use without the need for coding, in contrast to CrewAI which still requires code.
- Domain Registration Alert: .j4ys0n indicated a reluctance to share screenshots of the new project until the domain is registered to avoid “domain sniping,” while heyitsyorkie emphasized the importance of securing the domain quickly.
- Development Focus: .j4ys0n mentioned devoting more time to developing their project over regular job tasks, believing it was the right choice given the progress made.
- Editing datamodel.py as a Workaround: mmonir shared a solution to an issue by suggesting an edit in
datamodel.py(changingmax_tokensto3000), referencing a bug with an open issue on GitHub concerning Autogen Studio (Bug Report here).
Link mentioned: [Bug]: [autogenstudio] agent llm send max_tokens: null · Issue #2050 · microsoft/autogen: Describe the bug When max_tokens parameter is None, the agent send a frame /v1/chat/completions with max_tokens: null. In this case the LLM don’t understand and and stop after the second token. St…
LM Studio ▷ #langchain (4 messages):
- Looking for Notebooks?: A member inquired about having a notebook, possibly seeking shared resources or examples for their work.
- Substack Post Teaser: Another member provided a Substack post they wrote, hinting it could contain valuable insights or information.
Link mentioned: Switching from open ai api to local LLM: Small follow up post on our last one about building a rag agent with langchain and node
LM Studio ▷ #amd-rocm-tech-preview (97 messages🔥🔥):
-
GPU Target Override Enquiry: A member asked if it was possible to override the GPU target like with
HCC_AMDGPU_TARGET=gfx1030on Linux, referencing a conversation on Reddit. However, it was clarified that with the current Linux build, one is stuck with using OpenCL for GPU acceleration. -
LM Studio 0.2.19 ROCm Preview Beta Released: An announcement for LM Studio 0.2.19 ROCm Preview Beta was made, highlighting new support for text embedding models, a candidate fix for ROCm iGPU issues, and other bug fixes. The community was informed to download the beta from LM Studio with ROCm although the version might still show 0.2.18.
-
Confusion Over ROCm Support for Different GPUs: Community members were debating and asking questions about whether the new version of ROCm supports a mix of different GPUs like the RX 5000 and RX 6000 series, with one member stating success in running mixed AMD GPUs using hipblas and Vulkan.
-
AMD’s Silence on Limiting GRE to 2.8GHz: Users expressed frustration regarding AMD’s limitation of GRE to 2.8 GHz and hoped for custom BIOS releases. One member said that only someone at AMD would release such BIOS at the risk of their job.
-
ROCm 0.2.19 Beta Debugging in Progress: Several users reported “exit 42” errors with the latest ROCm beta, prompting the sharing of a verbose debug build for further investigation. Participants are encouraged to download the verbose build, attempt to load a model, and submit app logs for troubleshooting.
Links mentioned:
- 👾 LM Studio - Discover and run local LLMs: Find, download, and experiment with local LLMs
- no title found: no description found
- System requirements (Windows) — HIP SDK installation Windows: no description found
- How to run a Large Language Model (LLM) on your AMD Ryzen™ AI PC or Radeon Graphics Card: Did you know that you can run your very own instance of a GPT based LLM-powered AI chatbot on your Ryzen™ AI PC or Radeon™ 7000 series graphics card? AI assistants are quickly becoming essential resou...
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
LM Studio ▷ #model-announcements (3 messages):
-
Model Announcement Central: A series of new models have been released including Starling-LM 7B, c4ai command r v01, stable-code-instruct-3b, dolphin 2.8 mistral 7b v02, and Hyperion 3.0 Mistral 7B. The announcement invites users to check out the models and stay tuned for more.
-
Introducing Qwen 1.5 32B Chat: A new model, Qwen 1.5 32B Chat, part of the Qwen2 family with enhanced multi-turn conversation capabilities, has been released. Interested users can find more details on the model card and LM Studio app.
-
Gemma Shines at 2B: Google’s Gemma 1.1 2B model impresses with its performance, delivering coherent outputs at high speed, using only 3GB of memory. The model is available, but the 7B version will require adjustments in LM Studio settings for optimization before release, as noted on the model’s page.
HuggingFace ▷ #announcements (4 messages):
- New Resources and Demos Galore: The community has shared various resources including a neuro-symbolic agent systems repository, integration of datasets within the PyG ecosystem, and a demo for a function calling capable model, Octopus. Additional content includes visualization for hyper-graph datasets, the TensorLM Gradio UI for large language models, and the announcement of Aurora-M, a multi-lingual continually pre-trained language model.
- Tech and Thought Leadership on Display: Community members have released a new multi-subject image node pack, given a TED talk about the future of film in the age of AI, and published an open-source repo for replicating research papers. Other highlights feature a video on Python app safekeeping using virtual containers, a SaaS boilerplate demo, a line follower robot demo, and deepened integration between DagsHub + Colab for data management.
- Software to Streamline Your Work: LLMinator, a context-aware streaming chatbot, and ClipboardConqueror, a tool to reduce context switching, have been made available by the community to improve the efficiency of working with large language models.
- Thought-Provoking Reads and Tools for AIs: Members have contributed blog posts discussing various AI-related topics, such as evaluating SVD compression with the LASER technique and understanding diffusion models. Articles on custom architectures with HuggingFace and the levels of complexity in AI compute have also been shared.
- Attention on Multilingual LLM Innovation: The blog post for Aurora-M has been suggested as a potential topic for the next reading group, emphasizing the importance of multilingual and safe AI developments.
Link mentioned: Aurora-M: The First Open Source Biden-Harris Executive Order Red teamed Multilingual Language Model: no description found
HuggingFace ▷ #general (372 messages🔥🔥):
- Exploring Deployment with SageMaker and TGI: A user is considering the feasibility of deploying a model using TensorRT with SageMaker instead of TGI and seeks a way to update their kernel version on a website-based cloud compute resource.
- Interest in Custom ChatGPT for PDFs: In a quest to develop a unique ChatGPT app tailored for PDFs, one user is sourcing ideas to distinguish their project in a college competition.
- Quest for ML Hardware Benchmarking Tools: Users are discussing hardware benchmark tools for ML/AI tasks; MLPerf is recommended as a FOSS benchmark suite that includes tracks for GPT-J 6B and Llama 2 70B inference.
- Issue with Multi-GPU Training and SageMaker: There’s an exchange about issues encountered while multi-GPU training with SageMaker and diffusers, including SIGSEGV error and environment variable messages.
- Request for Token Count Information in Response: A user inquires if the Hugging Face SageMaker library can provide the number of tokens in the response when calling
.predict.
Links mentioned:
- Just Say the Name: Online Continual Learning with Category Names Only via Data Generation: In real-world scenarios, extensive manual annotation for continual learning is impractical due to prohibitive costs. Although prior arts, influenced by large-scale webly supervised training, suggest l...
- HuggingFaceTB/cosmo-1b · Hugging Face: no description found
- Train and deploy Hugging Face on Amazon SageMaker: no description found
- RuntimeError: Expected tensor for argument #1 'indices' to have one of the following scalar types: Long, Int; but got MPSFloatType instead (while checking arguments for embedding): I am trying to train a multi-modal model by taking in image and text input to output a text. Here is my architecture; (Assuming batch size=1) I use a ViT (from hugging face) to convert images (1, 3...
- Question answering using embeddings-based search | OpenAI Cookbook: no description found
- NexaAIDev/Octopus-v2 · Hugging Face: no description found
- Deploy models to Amazon SageMaker: no description found
- Launchers: no description found
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- Total noob’s intro to Hugging Face Transformers: no description found
- facebook/bart-large-cnn · Hugging Face: no description found
- Binary and Scalar Embedding Quantization for Significantly Faster & Cheaper Retrieval: no description found
- no title found: no description found
- GitHub - Haoming02/sd-webui-diffusion-cg: An Extension for Automatic1111 Webui that performs color grading based on the latent tensor value range: An Extension for Automatic1111 Webui that performs color grading based on the latent tensor value range - Haoming02/sd-webui-diffusion-cg
- Train a diffusion model: no description found
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- Streamer - a Hugging Face Space by Yakova: no description found
- Your own ChatGPT for $0.04/hr - With Ollama, ChatUI & Salad: We explore how to build your own ChatGPT with Ollama, Huggingface Chat UI and SaladCloud for just $0.04 per hour.
- CUDA semantics — PyTorch 2.2 documentation: no description found
- peft/examples/int8_training/peft_bnb_whisper_large_v2_training.ipynb at main · huggingface/peft: 🤗 PEFT: State-of-the-art Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning. - huggingface/peft
- huggingface-sagemaker-workshop-series/workshop_1_getting_started_with_amazon_sagemaker/lab_1_default_training.ipynb at main · philschmid/huggingface-sagemaker-workshop-series: Enterprise Scale NLP with Hugging Face & SageMaker Workshop series - philschmid/huggingface-sagemaker-workshop-series
- A beginner's guide to building a Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) application from scratch: This post will teach you the fundamental intuition behind RAG while providing a simple tutorial to help you get started.
- GitHub - Mikubill/sd-webui-controlnet: WebUI extension for ControlNet: WebUI extension for ControlNet. Contribute to Mikubill/sd-webui-controlnet development by creating an account on GitHub.
- AllenNLP-Coreference-Resolution-in-Python-Readable-clusters/allennlp_coref.py at master · guananya/AllenNLP-Coreference-Resolution-in-Python-Readable-clusters: Using AllenNLP Coreference Resolution in Python (getting clusters which are ACTUALLY readable) - guananya/AllenNLP-Coreference-Resolution-in-Python-Readable-clusters
- ProsusAI/finbert · Hugging Face: no description found
- Entity-Level Sentiment Analysis (ELSA): An exploratory task survey: This paper explores the task of identifying the overall sentiment expressed towards volitional entities (persons and organizations) in a document -- what we refer to as Entity-Level Sentiment Analysis...
HuggingFace ▷ #today-im-learning (2 messages):
- Seeking Knowledge on Knowledge Graphs: A member expressed interest in learning about knowledge graphs and their applications, asking for resource recommendations.
- Building Collate, Seeking Learning Experiences: Collate is a new platform aimed at transforming everyday learning for students, professionals, and content creators. The creator is seeking feedback and experiences related to learning challenges and is offering early access and a 15-minute call to discuss further. Schedule a call.
Links mentioned:
- Collate Preview: Transform your everyday learning
- 15 Minute Meeting - Vel Yanchina: no description found
HuggingFace ▷ #cool-finds (11 messages🔥):
- PIDNet Improves Semantic Segmentation: A new paper introduces PIDNet, a three-branch network architecture inspired by PID controllers, designed to enhance real-time semantic segmentation by effectively integrating detailed, context, and boundary information.
- LLMs Vulnerable to ‘Crescendo’ Jailbreak: Mark Russinovich shared a link to ‘Crescendo’, a potentially concerning jailbreak for large language models that aims to bypass ethical boundaries set to prevent the generation of harmful content.
- Cohere Command-R-plus Caught in Jailbreak Snare: A LinkedIn post highlights vulnerabilities in Cohere’s Command-R-plus system exposed to jailbreak attacks.
- Forwarding the Mixture-of-Depths Concept: The new Mixture-of-Depths (Modes) proposal suggests a dynamic allocation of Transformer computations across a sequence, potentially enhancing efficiency without compromising flexibility.
- Exploring Multi-Document Solutions with llamaindex: A user shared a blog post about leveraging llamaindex to create multi-document RAG solutions for improved information retrieval.
Links mentioned:
- Mixture-of-Depths: Dynamically allocating compute in transformer-based language models: Transformer-based language models spread FLOPs uniformly across input sequences. In this work we demonstrate that transformers can instead learn to dynamically allocate FLOPs (or compute) to specific ...
- PIDNet: A Real-time Semantic Segmentation Network Inspired by PID Controllers: Two-branch network architecture has shown its efficiency and effectiveness in real-time semantic segmentation tasks. However, direct fusion of high-resolution details and low-frequency context has the...
- Crescendo : The Multi-Turn LLM Jailbreak Attack
- Hugging Face + Langchain in 5 mins | Access 200k+ FREE AI models for your AI apps: Learn how to use Hugging Face, and get access to 200k+ AI models while building in Langchain for FREE.🔗 Links- Hugging Face tutorials: https://hf.co/tasks- ...
HuggingFace ▷ #i-made-this (44 messages🔥):
- Neuro-Symbolic AGI on GitHub: A new open-source neuro-symbolic AGI designed for behavior programming using Graph-based Prompt Programming has been introduced by a French AI startup. The project is now seeking community feedback and is showcased on GitHub.
- Open Source Paper Replication Repository: A repository aimed at upskilling through replication of AI & ML research papers has been launched, inviting contributors to star, advise, and open PRs. Check out the repository here: PaperReplica on GitHub.
- Managing Audio Datasets via Gradio: A new Gradio interface for creating and managing large audio datasets has been shared, intended for tasks like segmenting audiobooks and transcribing. The tool is available for use on GitHub.
- RNN for MNIST Handwritten Digits: A self-coded vanilla RNN using numpy to classify MNIST digits has been released and its code is available for review. Visit the project on GitHub.
- Image Search for Local Folders: A project named ‘Where’s My Pic?’ offers a Google Image Search-like experience for local folders, assisting in finding images quickly. A demonstration can be found on YouTube.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Kheem Chandra (@dhanikkcs): I have created a telegram bot . It is powered by Gemini 1.5 Pro. You can chat with it in Video, Image, or Text format. bot name: "int_gem_bot" link: https://telegram.me/int_gem_bot Give it ...
- The creative genius of MrBeast as an AI Bot :): I'm the Beast of all AI bots! I've been loaded up with mountains of MrBeast's wildest, most innovative content. It's like having exclusive backstage access to his mind-boggling bra...
- RMBG1.4 with imageslider - a Hugging Face Space by not-lain: no description found
- RAG - a Hugging Face Space by not-lain: no description found
- BrushNet - a Hugging Face Space by TencentARC: no description found
- The Unreasonable Ineffectiveness of the Deeper Layers: no description found
- GitHub - ehristoforu/TensorLM-webui: Simple and modern webui for LLM models based LLaMA.: Simple and modern webui for LLM models based LLaMA. - ehristoforu/TensorLM-webui
- GitHub - RooTender/augmentator: Ready-to-use tool for image augmentation: Ready-to-use tool for image augmentation. Contribute to RooTender/augmentator development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Where's My Pic Demo: Hello everyone, I'm Om Alve and in this video I'm giving a demo of my project called 'Where's my pic?'. This project solves the problem of searching through ...
- GitHub - abhaskumarsinha/Corpus2GPT: CustomGPTBuilder: A project enabling users to train their own GPT models on diverse datasets, including local languages and various corpus types, using Keras and compatible with TensorFlow, PyTorch, or JAX backends for subsequent storage or sharing.: CustomGPTBuilder: A project enabling users to train their own GPT models on diverse datasets, including local languages and various corpus types, using Keras and compatible with TensorFlow, PyTorch...
- Cheapest GPT-4 Turbo, GPT 4 Vision, ChatGPT OpenAI AI API API Documentation (NextAPI) | RapidAPI: no description found
- GitHub - hegdeadithyak/PaperReplica: We Replicate Research Papers in the field of AI & ML.: We Replicate Research Papers in the field of AI & ML. - hegdeadithyak/PaperReplica
- GitHub - SynaLinks/HybridAGI: The Programmable Neuro-Symbolic AGI that lets you program its behavior using Graph-based Prompt Programming: for people who want AI to behave as expected: The Programmable Neuro-Symbolic AGI that lets you program its behavior using Graph-based Prompt Programming: for people who want AI to behave as expected - SynaLinks/HybridAGI
- GitHub - suprasauce/RNN_MEDIUM: Contribute to suprasauce/RNN_MEDIUM development by creating an account on GitHub.
- ai-voice-cloning: Collection of utilities aimed to voice clone through AI
- GitHub - maepopi/audio-dataset-manager: An all in one tool designed to prepare audiobooks or large audios for TTS and voice cloning.: An all in one tool designed to prepare audiobooks or large audios for TTS and voice cloning. - maepopi/audio-dataset-manager
HuggingFace ▷ #reading-group (10 messages🔥):
- Searching for the Right Channel: A member wondered if another channel, <#879548962464493622>, would be more appropriate for specific questions.
- Inquiring Minds Want to Know about Paper Reading Events: Members have shown interest in paper reading events, confirming that such events typically occur every weekend. Last week’s event featured an impressive presenter and was recorded.
- Looking for Learning Resources: A query was raised about finding resources to understand the foundational blocks of models for tweaking and building new ones, regardless of a specific model.
- Repository of Knowledge Awaits: Recordings and notifications of the paper reading sessions are compiled in a GitHub repository, with the most recent recording yet to be added. Discord events are the current go-to for session notifications.
- General Guidance for Model Exploration: When asked for guidance on how to understand model codebases, a member inquired about specific domains of knowledge required to navigate and comprehend the coding aspects of models without focusing on any particular one.
Link mentioned: GitHub - isamu-isozaki/huggingface-reading-group: This repository’s goal is to precompile all past presentations of the Huggingface reading group: This repository’s goal is to precompile all past presentations of the Huggingface reading group - isamu-isozaki/huggingface-reading-group
HuggingFace ▷ #computer-vision (12 messages🔥):
-
HuggingFace as Git for ML Models: Users discussed the similarity between HuggingFace model repositories and Git, where you can create a repo and commit and push updates just like with code.
-
Monitoring GPU Usage During Training: In response to a user’s query on how to monitor GPU usage while training models, a HuggingFace Space named Model Memory Usage was recommended.
-
Manipulating Parquet Files without Pandas: A user sought alternatives to Pandas for dropping a column from a parquet file. It was suggested to use the
from_parquetmethod from thedatasetslibrary available in the HuggingFace documentation. -
Seeking Resources on Diffusion Models for Video Quality: A user asked for assistance and resources related to improving video quality using diffusion models, seeking any relevant academic papers.
-
Training XCLIP with More Frames: One member shared their experience trying to pretrain an XCLIP model with more frames than the pretrained versions. They faced issues with stagnant losses and NaNs, seeking advice on training from scratch with extended frame capacities as described in the XCLIP documentation.
Links mentioned:
- Model Memory Utility - a Hugging Face Space by hf-accelerate: no description found
- X-CLIP: no description found
HuggingFace ▷ #NLP (24 messages🔥):
-
Fine-tuning Mistral7b for Specific Data Extraction: A member queried whether they could fine-tune Mistral7b for JSON data extraction by using the cleaned results of its output. They were pondering the need for an LLM versus a more specialized model for similar input-output formats.
-
Parsing Tweets Without Twitter API: A member sought alternatives for scraping tweets without using Twitter’s complex API, hinting at a desire for a less complicated tool or method to achieve this task.
-
Colab Pro+ struggles with WizardLM models: A participant faced out-of-memory errors trying to load cognitivecomputations’ WizardLM-13B and WizardLM-7B models on Google Colab Pro+, despite trying different GPUs and looking for solutions.
-
10M Context Window Feasibility in Gemini 1.5: The Gemini 1.5 paper’s claim of a 10M context window sparked a discussion, with a member seeking explanations on how it calculates a substantial attention matrix. Another member shared a potential relevant paper that might illustrate the method used for this achievement.
-
Imputing Null Values with LLM: A member expressed the need to impute null values in a dataset containing ‘object’ datatype fields with an LLM based on context, seeking references or assistance on how to proceed.
Links mentioned:
- Ring Attention with Blockwise Transformers for Near-Infinite Context: Transformers have emerged as the architecture of choice for many state-of-the-art AI models, showcasing exceptional performance across a wide range of AI applications. However, the memory demands impo...
- mm ref: no description found
- CUDA semantics — PyTorch 2.2 documentation: no description found
HuggingFace ▷ #diffusion-discussions (9 messages🔥):
-
PEFT Shrinks llava2 But Faces Deployment Issues: A member is using the PEFT technique to reduce the size of the llava2 model but encounters problems when trying to run the reduced model on another machine. The issue seems to be related to the model being in safetensors format, leading to an error about a missing
pytorch_model_binfile. -
Deploying Safetensors Formatted Models: In response to the above issue, a suggestion was made to check the use of
use_safetensors=Truewhich might resolve the problem of deploying the reduced model safely formatted as safetensors. -
Learning Curve for NLP Beginners: A new member seeking advice on whether to learn transformers, LSTM, GRU, or bidirectional LSTM/GRU was directed to a Stanford CS224N YouTube course, a resource that comprehensively covers Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning.
-
Request for Euler/Euler-A Sampler Insights: A member expressed difficulty in finding blog-type resources on the euler/euler-a sampler and is seeking suggestions, having found only the k-diffusion repo to reference.
-
LaBSE Model Export Challenges in OpenSearch: An individual encountered errors when trying to use “sentence-transformers/LaBSE” as a custom model with OpenSearch and faced difficulties after attempting to export the model to TorchScript using a Python script.
Link mentioned: Stanford CS224N: Natural Language Processing with Deep Learning | 2023: Natural language processing (NLP) is a crucial part of artificial intelligence (AI), modeling how people share information. In recent years, deep learning ap…
HuggingFace ▷ #gradio-announcements (1 messages):
- API Recorder Hits the Stage: Gradio’s latest update 4.26.0 features an 🎥API Recorder that records interactions with any Gradio app and auto-generates the corresponding Python or JavaScript code. This can be accessed through the
View APIpage to simplify recreating app actions programmatically. - Squashing Bugs for Speed: The update also addresses a critical bug that previously led to slow page load times in Gradio version 4.25.0.
- Chatbot UI Crashes Resolved: Fixed a significant issue where rapid chatbot updates could crash the UI, ensuring smoother user experiences.
- Check Out the Full Changelog: For a comprehensive list of bug fixes and features in the latest release, users can view the full changelog at Gradio’s Changelog.
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #general (34 messages🔥):
- Exploring Rustlings and Ziglings: A member discussed their experience with programming exercises from Rustlings and Ziglings, and discovered an equivalent for Mojo called Mojolings.
- Var vs. Let in Mojo: There was a clarification that
varis used for lazily assigned variables in Mojo and it’s not going away, even thoughletgot removed, with a resource provided to learn about Mojo’s use ofvarhere. - Mojo for Web Applications: Discussion about the potential for Mojo in web development yielded info about a simple and fast HTTP framework for Mojo called lightbug_http.
- Mojo as a General Purpose Language: Members reassured one another that Mojo is indeed a general purpose language designed with AI/ML in mind, and highlighted Mojo’s young but evolving nature.
- Seeking Documentation and Learning Resources for Mojo: Members inquired about books or comprehensive documentation for learning Mojo, with the closest current recommendation being the Mojo Manual.
Links mentioned:
- Mojo Manual | Modular Docs: A comprehensive guide to the Mojo programming language.
- Variables | Modular Docs: Introduction to Mojo variables.
- GitHub - modularml/max: A collection of sample programs, notebooks, and tools which highlight the power of the MAX platform: A collection of sample programs, notebooks, and tools which highlight the power of the MAX platform - modularml/max
- GitHub - saviorand/lightbug_http: Simple and fast HTTP framework for Mojo! 🔥: Simple and fast HTTP framework for Mojo! 🔥. Contribute to saviorand/lightbug_http development by creating an account on GitHub.
- GitHub - rust-lang/rustlings: :crab: Small exercises to get you used to reading and writing Rust code!: :crab: Small exercises to get you used to reading and writing Rust code! - rust-lang/rustlings
- exercises: Learn the ⚡Zig programming language by fixing tiny broken programs.
- GitHub - dbusteed/mojolings: Learn to read and write Mojo code by fixing small programs: Learn to read and write Mojo code by fixing small programs - dbusteed/mojolings
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #💬︱twitter (7 messages):
- Modular’s Tweet Cascade Begins: Modular shared a tweet themed around Modular’s innovative strides in technology. View the tweet here.
- Advancing the Modular Movement: Another Modular tweet hints at further advancements, suggesting a sustained push in their tech development. The tweet can be seen here.
- A Sneak Peek into Modular’s Future Plans: A tweet by Modular appears to tease upcoming projects or developments in their ecosystem. Check out the tweet here.
- Rising to New Challenges: Modular issues a tweet that may discuss overcoming challenges or setting new goals. The full content is available here.
- Continuing the Modular Story: The story of Modular’s progress continues in another tweet, which could be building on previous announcements or achievements. View the Tweet here.
- Charting Modular’s Path Forward: Modular’s Twitter post suggests an outline of the path ahead for the company or its technology. The post is accessible here.
- Modular’s Vision Unfolds: A tweet from Modular presents their vision, possibly revealing new insights or directions for the company. Read the tweet here.
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #✍︱blog (2 messages):
-
Modular Joins Forces with AWS: Modular has announced a partnership with Amazon Web Services (AWS), aiming to integrate the MAX Platform with AWS services, thereby providing innovative AI features on a global scale. Bratin Saha, AWS VP of Machine Learning & AI services, emphasized the partnership’s role in accelerating the adoption of GenAI and traditional AI use cases by AWS customers.
-
Open Collaboration on Mojo Standard Library: Modular made a call to the community for contributions to the Mojo standard library, providing a comprehensive guide on how to contribute, from identifying issues on GitHub to creating successful pull requests. The guide follows Modular’s recent milestone of open sourcing the Mojo standard library, inviting improvements ranging from documentation to code changes.
Links mentioned:
- Modular: Modular partners with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to bring MAX to AWS services: We are building a next-generation AI developer platform for the world. Check out our latest post: Modular partners with Amazon Web Services (AWS) to bring MAX to AWS services
- Modular: How to Contribute to Mojo Standard Library: A Step-by-Step Guide: We are building a next-generation AI developer platform for the world. Check out our latest post: How to Contribute to Mojo Standard Library: A Step-by-Step Guide
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #ai (1 messages):
rxzfn: There is a moveable product like this, but using pcie
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #tech-news (2 messages):
- Repository Access Issue Resolved: A brief exchange indicated there was a problem accessing a repository, which was promptly rectified with an updated, working link. No further context or the actual link was provided.
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #🔥mojo (336 messages🔥🔥):
-
Exploring Mojo’s Parameter Abilities: Through a deep dive into Mojo’s parameter usage, it was discovered that calculations can be performed exclusively at parameter time, allowing for innovative metaprogramming. However, this exposes a scoping issue where an operation (
a + b) executed in a function signature doesn’t yield the same result as when the operation is stored in a named, inferred parameter (_L = a + b). -
The Complexities of Compile-Time Evaluation: A long conversation unfolded around difficulties faced when performing certain type operations at compile time. It highlighted the complexity inherent to Mojo’s compiler and the type system’s handling of operations like adding, which aren’t straightforward due to the requirement of proofs for simple equations like
a + b == b + a. -
Reference and Lifetime Intricacies in Mojo: The chat discussed potential issues and methodologies around the
Referencetypes and their lifetimes when using the@valuedecorator andinitmethods. It was pointed out that theReferenceand lifetime mechanics might require more clarification and documentation for ease of use. -
Anticipation for Future Open Source Contributions: Users expressed anticipation for when Mojo becomes open source, hoping the community will contribute with ports for other systems like BSDs. This open-sourcing is expected to enable wider adaptation and integration of Mojo.
-
RustPython as a Case Study for Language Implementation: RustPython was examined as an example of reimplementing a language’s standard library, considering its slower execution times compared to CPython. The discussion acknowledged that while such projects are cool and ambitious, they often lack the extensive optimizations seen in longer-established counterparts.
Links mentioned:
- Angry Anger GIF - Angry Anger Pixar - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- You Make A Compelling Argument Simon Hardwick GIF - You Make A Compelling Argument Simon Hardwick Blood And Treasure - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Rust Is Hard, Or: The Misery of Mainstream Programming: no description found
- [BUG]: Behaviour of the type checker is inconsistent (some expressions are manipulated prior to type-checking) · Issue #1702 · modularml/mojo: Bug description I've recently been trying to understand how the type checker reasons about the equality of types. I've noticed a few inconsistencies and potential bugs. These are demonstrated ...
- mojo/stdlib/src/collections/list.mojo at main · modularml/mojo: The Mojo Programming Language. Contribute to modularml/mojo development by creating an account on GitHub.
- [Feature Request] Allow parametric materialization · Issue #2100 · modularml/mojo: Review Mojo's priorities I have read the roadmap and priorities and I believe this request falls within the priorities. What is your request? Allow parametric materialization of nonmaterializable ...
- GitHub - modularml/max: A collection of sample programs, notebooks, and tools which highlight the power of the MAX platform: A collection of sample programs, notebooks, and tools which highlight the power of the MAX platform - modularml/max
- Modular: Mojo🔥 ♥️ Python: Calculating and plotting a Valentine’s day ♥️ using Mojo and Python: We are building a next-generation AI developer platform for the world. Check out our latest post: Mojo🔥 ♥️ Python: Calculating and plotting a Valentine’s day ♥️ using Mojo and Python
- devrel-extras/blogs at main · modularml/devrel-extras: Contains supporting materials for developer relations blog posts, videos, and workshops - modularml/devrel-extras
- Chris Lattner: Future of Programming and AI | Lex Fridman Podcast #381: Chris Lattner is a legendary software and hardware engineer, leading projects at Apple, Tesla, Google, SiFive, and Modular AI, including the development of S...
- mo - Overview: mo has 49 repositories available. Follow their code on GitHub.
- mojo/stdlib/docs/style-guide.md at nightly · modularml/mojo: The Mojo Programming Language. Contribute to modularml/mojo development by creating an account on GitHub.
- [BUG]: Compiler Crash with Self Referential Variant · Issue #1837 · modularml/mojo: Bug description from utils.variant import Variant from collections.vector import DynamicVector @value struct Value(CollectionElement): alias Variant = Variant[Float64, DynamicVector[Value]] var _va...
- mojo/stdlib/src/collections/dict.mojo at main · modularml/mojo: The Mojo Programming Language. Contribute to modularml/mojo development by creating an account on GitHub.
- GitHub - RustPython/RustPython: A Python Interpreter written in Rust: A Python Interpreter written in Rust. Contribute to RustPython/RustPython development by creating an account on GitHub.
- cpython/Objects/dictobject.c at main · python/cpython: The Python programming language. Contribute to python/cpython development by creating an account on GitHub.
- mojo/stdlib/src/collections/dict.mojo at main · modularml/mojo: The Mojo Programming Language. Contribute to modularml/mojo development by creating an account on GitHub.
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #community-projects (18 messages🔥):
-
Special Functions Now in Mojo: An update to the Specials package introduces several elementary mathematical functions such as
exp,exp2,expm1,log, andlog1p. These implementations prioritize numerical accuracy over FLOPS and benchmarks can be found in the package repository. -
SICP Gets Mojofied: The classic textbook “Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs” is being ported to Mojo language in the sicp_mojo project, currently referencing the JavaScript version.
-
Mojo Algorithms Collective Initiative: A member is planning to rewrite popular algorithms in Mojo, such as Dijkstra’s and different sorting methods, and is interested in coordinated efforts.
-
One-stop Mojo Packages Repo: Community members can share their Mojo packages through PRs in the mojo-packages repository, which aims to function as a central hub until an official package manager is available.
-
Mambamojo Collaborative Project: A GitHub repository called mamba.mojo is seeking collaborators to work on implementing Mamba in pure Mojo, from models to inference and training.
Links mentioned:
- GitHub - kernhanda/mojo-packages: A place to find and share packages for the Mojo language: A place to find and share packages for the Mojo language - kernhanda/mojo-packages
- GitHub - aizzf/mamba.mojo: Mamba in pure mojo from model to inference and train.: Mamba in pure mojo from model to inference and train. - aizzf/mamba.mojo
- GitHub - kernhanda/mojopack: mojopack is a tool for managing packages for the Mojo programming language: mojopack is a tool for managing packages for the Mojo programming language - kernhanda/mojopack
- GitHub - leandrolcampos/specials: Special functions with hardware acceleration: Special functions with hardware acceleration. Contribute to leandrolcampos/specials development by creating an account on GitHub.
- GitHub - Hammad-hab/pkm: Mojo's unoffical package manager: Mojo's unoffical package manager. Contribute to Hammad-hab/pkm development by creating an account on GitHub.
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #community-blogs-vids (7 messages):
-
“Joy of Mojo” blog launch: A new community website called Joy of Mojo has been introduced, where individuals can share demo programs created while exploring the Mojo language. Although there were initial issues with GitHub Pages, the site appears to be functioning again, and the community is invited to contribute and discuss.
-
Link Troubles for “Joy of Mojo”: The Joy of Mojo website faced hosting issues on GitHub Pages, displaying errors for some users, but these seem to be resolved now, assuring users of the site’s accessibility.
-
Mojo Package Sharing Initiatives: Community members have created repositories like mojo-packages and mojopack on GitHub for sharing packages for the Mojo language, complementing the collaborative spirit within the community.
-
Dynamic Mojo Evolution Acknowledged: The rapid evolution of Mojo is recognized, with expectations set that some shared content may become outdated within months, highlighting the ongoing development and changes within the language ecosystem.
-
Educative Mojo Trolling: A community member shared a YouTube video designed to educate and surprise viewers by demonstrating a star pattern in Python, which is revealed to be Mojo code written with a Mojo plugin in VSCode, drawing attention to Mojo’s Python compatibility.
Links mentioned:
- Joy of Mojo 🔥: This is Joy of Mojo
- GitHub - kernhanda/mojo-packages: A place to find and share packages for the Mojo language: A place to find and share packages for the Mojo language - kernhanda/mojo-packages
- GitHub - kernhanda/mojopack: mojopack is a tool for managing packages for the Mojo programming language: mojopack is a tool for managing packages for the Mojo programming language - kernhanda/mojopack
Modular (Mojo 🔥) ▷ #nightly (71 messages🔥🔥):
-
Python Interop Enhancements: A member has been working on CPython interoperability by implementing PyMethodDef, PyCFunction_New, and PyModule_NewObject in Mojo. They highlighted progress in reference counting without bugs and believe their work lays a promising foundation for further planning of Python interop. The related development work is available on GitHub.
-
Getting Started for New Contributors: New contributors are guided to start by looking into “good first issues”, with links provided to the changelog and the contributing guidelines on Mojo’s GitHub repository.
-
Discussions on Signed-off Commit Best Practices: In a lively exchange about pull request practices, a member learned the importance of proper signing-off commits and was guided on how to amend commit authorship and use
git configto correctly attribute their work. Relevant GitHub documentation was linked for configuring the username in git, and VSCode was recommended as a tool with an automatic sign-off option. -
Soliciting Feedback on Standard Library Test Practices: A member has created a discussion on GitHub to gather input on improving List and String slicing tests in the Mojo Standard Library, as well as proposing more descriptive labels for
assert_equalwithin tests. -
Managing Nightly Builds and Packages: Nightly build updates notification included information on how to update with
modular update, linked the changelog and the diffs between the releases. Some members also shared issues and solutions on how to handle “Error opening archive” when updating, withmodular cleanand reinstalling as common remedies.
Links mentioned:
- Setting your username in Git - GitHub Docs: no description found
- Fix List slicing and String slicing to match Python when step is negative · modularml/mojo · Discussion #2234: I want to fix issues #1944, #2046, and #2142. Those are List but the same problem is there for String. I actually have a fix done here with the interesting commit here. The implementation just has ...
- Comparing 1a8f912..1bce16d · modularml/mojo: The Mojo Programming Language. Contribute to modularml/mojo development by creating an account on GitHub.
- mojo/stdlib/test/lit.cfg.py at 738901dec1058612d8f01fd13e13a3e09103944f · modularml/mojo: The Mojo Programming Language. Contribute to modularml/mojo development by creating an account on GitHub.
- pathlib — Object-oriented filesystem paths: Source code: Lib/pathlib.py This module offers classes representing filesystem paths with semantics appropriate for different operating systems. Path classes are divided between pure paths, which p...
- Comparing 1a8f912..1bce1 · modularml/mojo: The Mojo Programming Language. Contribute to modularml/mojo development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Automatic --signoff via settings · Issue #83096 · microsoft/vscode: It seems that presently, you can use the -s or --signoff command on your git commits by opening up the git commit dropdown and selecting signoff. This was implemented as a "fix" for #7010 in...
- GitHub - rd4com/mojo_branch at nightly: The Mojo Programming Language. Contribute to rd4com/mojo_branch development by creating an account on GitHub.
- [stdlib] Add `reversed` by helehex · Pull Request #2215 · modularml/mojo: Adds an initial implementation of reversed(), for getting a reversed iterator of a range or list. This isn't meant to be final, since iterators are not fully worked out yet, but it works for n...
- mojo/docs/changelog.md at nightly · modularml/mojo: The Mojo Programming Language. Contribute to modularml/mojo development by creating an account on GitHub.
Eleuther ▷ #general (80 messages🔥🔥):
-
WikiText Dataset Access Clarified: Stephen Merity, the original author of the WikiText dataset, has rehosted the data on Cloudflare R2, which is considered the new main access point. The rehosted data, still under the Creative Commons license, includes larger datasets than the Penn Treebank and maintains the original case, punctuation, and numbers.
-
GateLoop Perplexity Puzzle: There’s a discussion about perplexity scores reported by the author of the GateLoop Transformer. While the author claimed good scores, lucidrains was unable to replicate them, raising some suspicions about the results.
-
Hugging Face Dataset Autoconversion Dilemma: Chat members express frustration over Hugging Face’s automatic conversion of datasets to parquet, which can be circumvented by using Git LFS for hosting. An example where this has been a problem is the format confusion with
.rawfiles. -
Search for Reproducible Data Formats: The conversation was active around the need for reproducible and consistent data formats, with efforts made to mirror the original WikiText data on Cloudflare R2 as well for the sake of experiment reproducibility.
-
OpenAI Model Documentation Becomes Ephemeral: Members shared their experiences finding information about OpenAI’s models; several links to documentation about the models were taken down, leading to reliance on an archived page to understand the specifics regarding GPT 3.5 and other series, highlighting the challenges in tracking model evolution and changes.
Links mentioned:
- Smerity.com: The WikiText Long Term Dependency Language Modeling Dataset (2016): no description found
- segyges/wikitext-103 at main: no description found
- wikitext at main: no description found
- GitHub - lucidrains/gateloop-transformer: Implementation of GateLoop Transformer in Pytorch and Jax: Implementation of GateLoop Transformer in Pytorch and Jax - lucidrains/gateloop-transformer
- GitHub - tobiaskatsch/GatedLinearRNN: Contribute to tobiaskatsch/GatedLinearRNN development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Model index for researchers - OpenAI API: no description found
Eleuther ▷ #research (313 messages🔥🔥):
-
Understanding Schedule-Free Optimizer: The Schedule-Free optimizer keeps a simple running average of weights, not an exponential moving average. The 1/t learning rate from one component is just another way of calculating the mean of all values, as demonstrated by the formula (1 * (1/2) * (2/3) * (3/4) * … * (1-1/t)) equating to 1/t.
-
The Debate on Schedule-Free’s Efficacy: Results on Schedule-Free optimizer’s performance are mixed, showing benefits in low-step runs but not significantly aiding in larger-step regimes. The optimizer estimates optimal learning rates, which might vary with the number of update steps.
-
Mixing Methods in Optimizers: There is a discussion on whether increasing batch size over time could be an alternative or complement to learning rate schedules, with batch size doubling suggested as analogous to halving the learning rate.
-
New Approach to Language Model Search Strategies: A study proposes a method to teach language models to search by using a stream of search (SoS) language, shown to boost search accuracy by 25% over models trained on predicting single next steps.
-
Emergent Abilities Linked to Long-Tail Data: The ability of models for zero-shot tasks is being explored, with suggestions that emergent abilities in language models may be a function of the exposure to long-tail data during training.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Kyo (@kyo_takano): Some data points where ScheduleFree outperforms Adam/SGD: - LM/GPT (@eric_alcaide) https://twitter.com/eric_alcaide/status/1776571679524683950 - CIFAR10/ResNet18 (@Sree_Harsha_N) https://twitter.com/S...
- Tweet from Aaron Defazio (@aaron_defazio): Schedule-Free Learning https://github.com/facebookresearch/schedule_free We have now open sourced the algorithm behind my series of mysterious plots. Each plot was either Schedule-free SGD or Adam, no...
- Tweet from Aran Komatsuzaki (@arankomatsuzaki): No “Zero-Shot” Without Exponential Data: Pretraining Concept Frequency Determines Multimodal Model Performance repo: https://github.com/bethgelab/frequency_determines_performance hf: https://huggingf...
- Understanding Emergent Abilities of Language Models from the Loss Perspective: Recent studies have put into question the belief that emergent abilities in language models are exclusive to large models. This skepticism arises from two observations: 1) smaller models can also exhi...
- Batch size-invariance for policy optimization: We say an algorithm is batch size-invariant if changes to the batch size can largely be compensated for by changes to other hyperparameters. Stochastic gradient descent is well-known to have this prop...
- Stream of Search (SoS): Learning to Search in Language: Language models are rarely shown fruitful mistakes while training. They then struggle to look beyond the next token, suffering from a snowballing of errors and struggling to predict the consequence of...
- More Agents Is All You Need: We find that, simply via a sampling-and-voting method, the performance of large language models (LLMs) scales with the number of agents instantiated. Also, this method is orthogonal to existing compli...
- Super-Convergence: Very Fast Training of Neural Networks Using Large Learning Rates: In this paper, we describe a phenomenon, which we named "super-convergence", where neural networks can be trained an order of magnitude faster than with standard training methods. The existenc...
- Large Language Models Struggle to Learn Long-Tail Knowledge: The Internet contains a wealth of knowledge -- from the birthdays of historical figures to tutorials on how to code -- all of which may be learned by language models. However, while certain pieces of ...
- Learning Rate Grafting: Transferability of Optimizer Tuning: In the empirical science of training large neural networks, the learning rate schedule is a notoriously challenging-to-tune hyperparameter, which can depend on all other properties (architecture...
- AutoWebGLM: Bootstrap And Reinforce A Large Language Model-based Web Navigating Agent: Large language models (LLMs) have fueled many intelligent agent tasks, such as web navigation -- but most existing agents perform far from satisfying in real-world webpages due to three factors: (1) t...
- Get Started: <a href="#install-torchstudio">Install</a> TorchStudio, <a href="#load-and-analyze-the-mnist-dataset">load</a> a dataset, <a href="#build-and-train-...
- GitHub - facebookresearch/schedule_free: Schedule-Free Optimization in PyTorch: Schedule-Free Optimization in PyTorch. Contribute to facebookresearch/schedule_free development by creating an account on GitHub.
- GitHub - drukpa1455/fractal-gnn: fractal graph neural network exploration: fractal graph neural network exploration. Contribute to drukpa1455/fractal-gnn development by creating an account on GitHub.
Eleuther ▷ #interpretability-general (1 messages):
- NSF Reviewer Highlights GitHub Stars: An NSF reviewer noted the low number of GitHub stars for the nnsight project as a point of concern. The team emphasizes the importance of starring the repo, particularly for users who generally interact with the project via pip installs, and requests support here.
Link mentioned: GitHub - ndif-team/nnsight: The nnsight package enables interpreting and manipulating the internals of deep learned models.: The nnsight package enables interpreting and manipulating the internals of deep learned models. - ndif-team/nnsight
Eleuther ▷ #lm-thunderdome (83 messages🔥🔥):
- GPU Utilization Mystery Solved: A member’s evaluation time reduced dramatically from 20 minutes to 3 by running
batch size=auto, indicating they were underutilizing their GPU previously. - Confusion Over BigBench Task Recognition: Some users faced issues with
bigbenchnot being recognized as a task; it was suggested to uselm_eval —tasks listto find the correct bigbench variant(s). - Technical Hiccups with CLI Command: There were errors reported involving the
—predict_onlyCLI command; members discussed potential causes, including version conflicts or improper use of the feature. - Using Logit Bias for MCQA Tasks: Dialogue about leveraging
logit_biasin one-token MCQA tasks ensued, with the discovery that OpenAI’s implementation doesn’t affect the returned logits, only the text, leading to exploration of usinggreedy_untilinstead. - Temperature Settings Affect on Output Quality: A member questioned why different temperature settings in custom samplers didn’t affect the output, leading to a technical dive into proper
gen_kwargssettings and revealing the need for settingdo_sample=Trueto avoid greedy generation default behavior.
Links mentioned:
- Google Colaboratory: no description found
- vllm/vllm/model_executor/layers/sampler.py at b4543c8f6bf67a7f1a0d6d0fd6cf5697c7eeaabb · vllm-project/vllm: A high-throughput and memory-efficient inference and serving engine for LLMs - vllm-project/vllm
- lm-evaluation-harness/lm_eval/models/vllm_causallms.py at e9a405431989fe30fe3c54a54ddc2c494a6a9e16 · EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness: A framework for few-shot evaluation of language models. - EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness
- Weave: chain_of_thought_eval_results (24/04/08 02:23:54): Publish your model insights with interactive plots for performance metrics, predictions, and hyperparameters. Made by Nguyen Nhat Minh using W&B
- Weave: chain_of_thought_eval_results (24/04/08 02:25:08): Publish your model insights with interactive plots for performance metrics, predictions, and hyperparameters. Made by Nguyen Nhat Minh using W&B
- GitHub - EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness at e9a405431989fe30fe3c54a54ddc2c494a6a9e16: A framework for few-shot evaluation of language models. - GitHub - EleutherAI/lm-evaluation-harness at e9a405431989fe30fe3c54a54ddc2c494a6a9e16
OpenAI ▷ #ai-discussions (220 messages🔥🔥):
- Sentiment Analysis for Recordings Inquiry: One member is exploring sentiment analysis options for text, phone, and video meeting recordings and is seeking recommendations for SaaS to utilize.
- Anticipation for GPT-5: There’s a conversation about the anticipation for GPT-5, with users discussing various AI models that might be suitable for programming tasks, like Claude 3 Opus and Gemini 1.5 Pro.
- Community Support and Kindness: A member’s supportive attitude is highlighted, offering personal assistance to others with their AI-related queries, and the significance of being nice while providing help is debated.
- Questioning AI Training Data Sources: A member raises concerns about whether OpenAI used YouTube data for Sora training and whether this could conflict with YouTube’s terms of service.
- Seeking Image Generation APIs: Inquiry about alternative AI APIs for image generation besides DALL-E is met with a mention of an unspecified alternative, and members discussing the availability and potential of other models for image generation tasks.
Link mentioned: Wow Really GIF - Wow Really - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
OpenAI ▷ #gpt-4-discussions (72 messages🔥🔥):
- GPT-4 Translation Capabilities vs DeepL: One user mentioned that ChatGPT-4’s translation does not perform as well as DeepL, particularly in capturing basic contexts and choosing contextually appropriate words rather than direct translations.
- Developing Sensitive Character Backstories with ChatGPT: Writers discussed strategies for working within ChatGPT’s content policy when developing characters with traumatic backgrounds, suggesting subtler approaches to describing character experiences.
- Custom GPTs Require a Subscription: Users clarified that all GPTs, including variants used within custom applications, require a Plus (or above) plan subscription to be accessible.
- Multilanguage Prompts in Custom GPT Starters: There was a discussion on the efficacy of using prompts in various languages for conversation starters in custom GPTs, though potential filtering issues on platforms like Discord were noted.
- Performance Variability in GPT Models: Coders compared the performances of different GPT models, with one citing that Opus and a preview version of GPT-4 performed impressively in code generation tasks. However, there was also a mention of GPT-4 potentially performing less optimally with larger contexts when compared to other models.
OpenAI ▷ #prompt-engineering (57 messages🔥🔥):
-
AI’s Simulated Consciousness Draws Interest: Curiosity peaks as a member attempts to simulate human consciousness within GPT by asking it to develop pseudocode for human chemical hormones and equate them to its programming mechanisms. This exploration is deemed adorable and interesting even as GPT struggles to maintain consistency in representing consciousness.
-
Pseudocode for Neurochemical Functions: A member with a background in psychology and computer science ponders the potential to code aspects of human consciousness, suggesting the possibility of translating neurochemical functions into code and minimizing the “specialness” of human ego in the process.
-
The Interplay of Biology, Spirituality, and AI: A discussion about whether consciousness is purely biological or has spiritual components leads to varied opinions. One member suggests adopting a default assumption that entities may possess some form of consciousness and to err on the side of not causing detectable misery, regardless of the origin of consciousness.
-
Techniques for Extracting Information from AI: Users debate on the distinctions between a model’s system message and an operating system-like set of instructions for tools, relating these concepts to the transparency and modular nature of ChatGPT’s system prompts.
-
Finalizing a Text-Based AI Game: Suggestions arise for how to manage and display game progress information when building a completely AI-powered text-based game, mentioning the use of JSON for data structuring and the challenges of presenting cropped information to users.
OpenAI ▷ #api-discussions (57 messages🔥🔥):
-
Exploring AI’s Take on Consciousness: Members sparked a debate over emulating human consciousness and emotions by breaking them down into chemicals represented in code. While the GPT struggled to stay in character, it acknowledged that consciousness may emerge from neurochemical interplays.
-
GPT and Depictions of Consciousness: Conversations turned adorable when discussing consciousness with GPT. Despite initial skepticism, participants found insights into the interplay of neurochemicals and self-preservation as potential factors in the emergence of consciousness, making for an intriguing AI-human interaction.
-
Dall-E as a Dissertation Designer: Users discussed using Dall-E to create a dissertation front page, debating the effectiveness of different tools, with some suggesting combinations of GPT with LaTeX or Python-Matplotlib as superior approaches.
-
Enhancing GPT Prompts for Fun and Games: A user seeking to create an AI text-based game considered ways to refine prompts to conceal code information from user-displayed text, with JSON being suggested as one tool for this task.
-
Understanding ChatGPT’s System Prompts and Tools: An in-depth exchange occurred regarding how system prompts and tools affect GPT’s responses, drawing a comparison between “the difference between an LLM and an LLM OS” and illustrating the modularity of the ChatGPT environment.
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) ▷ #announcements (4 messages):
-
Multimodality Activated for Claude 3: The modality of all Claude 3 models has been changed to
multimodal, supporting image input. Developers relying on this property need to update their code to accommodate these changes. -
Claude 3 Messages Enhanced:
messages.namehas been integrated into the upstream Claude 3 messages. For more details and implications for your projects, read the discussion here. -
Prompt Template Improvement for DBRX: The prompt template for DBRX has been updated to reduce repetitiveness based on user feedback. More can be found on the topic here.
-
Fresh Models & Features Unveiled: Two new models released are DBRX Nitro, excelling at code generation and general knowledge tasks, and Command R+, a large model from Cohere outperforming GPT-4 Turbo and Claude 3 Sonnet on various benchmarks. Additional updates include UI enhancements, new analytics, more model parameters like
logit_bias, and support forseedandresponse_formats for several models. Model details: DBRX Nitro and Command R+. -
Cohere’s Formatting Fix & Policy Update: An issue with system prompt formatting for Cohere requests has been resolved. Cohere models will not be moderated by OpenRouter moving forward, but will adhere to Cohere’s acceptable use policy.
-
Community Feedback Sought: A new poll has been posted for community feedback. Participate in the poll here.
Links mentioned:
- DBRX 132B Instruct by databricks | OpenRouter: DBRX is a new open source large language model developed by Databricks. At 132B, it outperforms existing open source LLMs like Llama 2 70B and Mixtral-8x7B on standard industry benchmarks for language...
- Command R+ by cohere | OpenRouter: Command R+ is a new, 104B-parameter LLM from Cohere. It's useful for roleplay, general consumer usecases, and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). It offers multilingual support for ten key lan...
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) ▷ #app-showcase (1 messages):
- AI Enters the Classic Game Arena: Take on ChatGPT in a simple yet challenging game of Rock, Paper, Scissors. Pit your strategic skills against the bot to see if you can outwit it.
Link mentioned: Rock, Paper, Scissors Game by Blust.AI: Play Rock, Paper, Scissors against ChatGPT. It’s easy to play and a fun way to see if you can outsmart an AI.
OpenRouter (Alex Atallah) ▷ #general (322 messages🔥🔥):
- API Frontends for OpenRouter: Users discussed various frontends for the OpenRouter, including LibreChat which has a ChatGPT-like UI and offers authentication and plugins, SillyTavern which is good for chat/roleplay, and Jan.ai which is similar to LM Studio but open source and supports local API servers.
- Favorites Models for Roleplay and Coding: Command-R+ was lauded as good for coding and even translating Turkish, with some users equating its usefulness to that of various Claude models. Meanwhile, others expressed concern about over-censorship with some models and OpenAI’s implementation of concepts like ‘unsafe’ content.
- Discussions About Model Performance: Users noted that Sonnet performs better than Opus in coding, especially with German and chemical tasks, and some found that Claude 3 performed better in extracting data from PDFs than Gemini Pro 1.5. There was also skepticism expressed about the capabilities of Gemini Pro 1.5, with some users not finding it useful.
- Exploring Model Features: The community engaged in discussions about model features such as JSON mode support and logit bias, with some users providing tips and workarounds for issues with certain models and requests for additional feature filtering in model selection tools.
- Concerns Over Model Rankings and Usefulness: There was dialogue regarding the effectiveness of basing model rankings on usage statistics, with suggestions for alternative metrics like users’ spending or model retention to assess a model’s utility more accurately.
Links mentioned:
- LibreChat: Enhanced ChatGPT Clone, featuring OpenAI, Azure, Mistral, Anthropic, Google, Ollama, DALL-E-3 models and more. An Open-source, versatile Web UI, with seamless self-hosting and active developments.
- C4AI Acceptable Use Policy: no description found
- Jan - OpenRouter: A step-by-step guide on how to integrate Jan with OpenRouter.
- JSON Mode: no description found
- Sonar 8x7B by perplexity | OpenRouter: Sonar is Perplexity's latest model family. It surpasses their earlier models in cost-efficiency, speed, and performance. The version of this model with Internet access is [Sonar 8x7B Online](/mo...
- OpenRouter: A router for LLMs and other AI models
- OpenRouter: Build model-agnostic AI apps
LlamaIndex ▷ #blog (8 messages🔥):
-
Introducing AutoRAG for Performance Optimization: Marker-Inc-Korea’s AutoRAG 🔥 is a new tool that optimizes RAG pipelines by automatically fine-tuning hyperparameters using a given evaluation dataset. This optimization is announced via a tweet with links to more details: AutoRAG’s tweet.
-
RAG Transforms Sales Outreach: Described in a recent webinar, a new sales use case for RAG replaces hard-coded templates with prompt templates that leverage an LLM to craft personalized sales emails. Find further information in the shared links: Sales Use Case tweet.
-
Scaffold Full-Stack RAG/Agent Apps with Ease:
create-llamais a just-released stand-alone repository that simplifies the process of starting full-stack RAG/agent applications, inspired bycreate-react-app, allowing deployment of a Javascript-based full-stack chatbot in one command. The announcement with relevant links is accessible here: create-llama tweet. -
Complex QA with Multi-Document Agents: Andy Singal’s overview on @llama_index multi-document agents demonstrates their ability to navigate complex QA over many documents, aiming to extend the functionality beyond simple, single-document queries. The presentation tweet can be seen here: Multi-Document Agents tweet.
-
Best Full-Stack RAG Tutorial: ClusteredBytes created a tutorial and GitHub repository showcasing the sophisticated architecture required to build a full-stack RAG application capable of streaming intermediate results to a UI. Details can be found in this tweet: Full-Stack RAG App Tutorial tweet.
LlamaIndex ▷ #general (254 messages🔥🔥):
-
Document References and Page Numbers in Multi-Document Queries: For someone looking to get document references along with page numbers when querying, it was suggested to ensure metadata includes such details before indexing. Accessing these in the source nodes’ metadata is crucial to getting desired references post-query.
-
Azure OpenAI Context Seek Issues: Discussions highlighted problems with Azure’s OpenAI service failing to identify context contained within nodes. Despite the relevant information present, the model would apologize for not finding the context, suggesting possible issues with settings or inconsistencies compared to Mistral AI’s functioning.
-
Product Recognition and Classification with LLMs: A chat about classifying products from various stores with different names but being essentially the same item explored the use of large language models (LLMs) for identification. Several strategies, including the use of model merging tactics and embedding models, were discussed as potential solutions for managing extensive databases of products.
-
Speeding up Embedding Generation: Optimizing embedding generation involved switching from processing embeddings one by one to using batching methods like
get_text_embedding_batch. This adjustment speeds up the processes, especially for large files, by aligning the text chunks with the nodes, embedding in batches, and then reassigning these batch embeddings back to individual nodes. -
RAG and OpenSource Model Challenges: There were concerns expressed about the ReAct agent not utilizing tools as expected when paired with open-source models like “llama2”, “mistral”, and “gemma”. It was clarified that open-source models often struggle with agentic tasks, and better descriptions in routers could help with accurate routing.
Links mentioned:
- LlamaIndex - LlamaIndex: no description found
- SimpleDirectoryReader - LlamaIndex: no description found
- no title found: no description found
- ReAct Agent - A Simple Intro with Calculator Tools - LlamaIndex: no description found
- Using LLMs - LlamaIndex: no description found
- Launching the first GenAI-native document parsing platform — LlamaIndex, Data Framework for LLM Applications: LlamaIndex is a simple, flexible data framework for connecting custom data sources to large language models (LLMs).
- Introducing LlamaCloud and LlamaParse — LlamaIndex, Data Framework for LLM Applications: LlamaIndex is a simple, flexible data framework for connecting custom data sources to large language models (LLMs).
- llama_index/llama-index-integrations/readers/llama-index-readers-file/llama_index/readers/file/docs/base.py at 9163067027ea8222e9fe5bffff9a2fac26b57686 · run-llama/llama_index: LlamaIndex is a data framework for your LLM applications - run-llama/llama_index
- llama_index/llama-index-core/llama_index/core/indices/utils.py at main · run-llama/llama_index: LlamaIndex is a data framework for your LLM applications - run-llama/llama_index
- Multi-Modal LLM using Azure OpenAI GPT-4V model for image reasoning - LlamaIndex: no description found
- llama_index/llama-index-legacy/llama_index/legacy/readers/file/image_reader.py at main · run-llama/llama_index: LlamaIndex is a data framework for your LLM applications - run-llama/llama_index
- Auto Merging Retriever - LlamaIndex: no description found
- GitHub - run-llama/llama_index at 9163067027ea8222e9fe5bffff9a2fac26b57686: LlamaIndex is a data framework for your LLM applications - GitHub - run-llama/llama_index at 9163067027ea8222e9fe5bffff9a2fac26b57686
- Storing - LlamaIndex: no description found
- Indexing & Embedding - LlamaIndex: no description found
LlamaIndex ▷ #ai-discussion (1 messages):
- Challenges with Top Agent Tool Selection: A member discussed an issue where the top agent mistakenly chose the incorrect tool from the five available in the index. They mentioned they are optimizing the retrieval logic and will share their findings.
OpenInterpreter ▷ #general (170 messages🔥🔥):
- Mistral’s Computing Requirements: Mention of “Mistral 7B Instruct v0.2” indicating it performs well but requires significant computing power, suggesting at least 16GB of RAM and some GPU capabilities.
- Calls for Examples on Vision Models and Documentation: Inquiry about successful local vision models for os mode and a request for examples based on base open interpreter/cookbook, pointing to gaps in the current documentation.
- Interest in Event Recording: Discussion on recording Discord voice chats for events using the OpenInterpreter Python library, with suggestions to use broadcasting software like OBS (Open Broadcaster Software) for recording, and considering Craig Bot for audio.
- Language Barrier in Technical Assistance: Members trying to provide technical help despite language barriers, using examples of adding voice (TTS) to the Open Interpreter with mixed results, possibly resolved after several attempts.
- Inquiry about Open Interpreter Capabilities: Questions regarding the feasibility of certain tasks with the Open Interpreter, such as downloading and converting articles into markdown files, and an indication of efforts to improve core repository reliability over the next few months.
Link mentioned: Join the Open Interpreter Discord Server!: A new way to use computers | 8147 members
OpenInterpreter ▷ #O1 (71 messages🔥🔥):
-
Trouble Connecting Client and Server: Members reported difficulties with the client not connecting to the server on their configurations. It was suggested that an incompatible environment, potentially due to incompatible Python versions, could be causing missing/conflicting TTS packages. A proposed solution involved creating a Conda environment with Python <=3.10 and re-cloning the repository.
-
Push Button Switch Issues: Individuals constructing the 01 hardware noted that the built-in button of the M5 was functioning, but the external push-button switch was not. Subsequent discussions include mentions of reviewing
client.inocode for missing GPIO definitions for an external button. -
Python Version Compatibility Challenges: Several users cited that Python 3.11.4 did not work for their setup. It was confirmed that downgrading to Python 3.10 resolved the issue where the system appeared to not “hear” spoken commands, indicating a version support limitation.
-
Local Models As Cost-effective Alternative: Conversations around cost concerns with using GPT-4 led to discussions around local models like Hermes 7B and Haiku as effective, cost-efficient alternatives. Members indicated these models being slightly worse on some tasks but offering advantages like lower cost and privacy.
-
Windows Setup Struggles: One member struggled with Windows installation, following several instructions including using chocolatey, virtualenv, and setting the OPENAI_API_KEY. They identified a potential solution by ensuring Python 3.9 was used in a virtual environment and reaching out for further help with setting the API key properly.
Links mentioned:
- no title found: no description found
- no title found: no description found
- Language Model - 01: no description found
- Access Issue with Linux `dmesg` · Issue #226 · OpenInterpreter/01: Describe the bug The software\source\server\utils\kernel.py function get_kernel_messages is trying to access a file that doesn't exist on some Linux distros (all?) like Arch, Debian, and Fedora. U...
- GitHub - OpenInterpreter/01: The open-source language model computer: The open-source language model computer. Contribute to OpenInterpreter/01 development by creating an account on GitHub.
LangChain AI ▷ #general (190 messages🔥🔥):
-
Seeking Pull Request Assistance: A user requested help for a Pull Request with a build failing on GitHub due to a “module not found” error involving “openapi-pydantic.” Despite the module being listed in dependencies, the issue persisted.
-
Discord Summarization Queries: Users discussed how to incorporate a YouTube URL using the
YouTubeAudioLoaderdocumentation from LangChain, with specific questions about substituting OpenAI Whisper Parser with Ollama, and whetherWhisperfrom OpenAI could be a solution. -
LangChain Coding Issues: Members sought coding assistance, such as using
register_toolin LangChain that’s causing import errors, setting up LangGraph and addressing anInvalidUpdateError, fix imports fromlangchain.messages, and tackling embedding dimension lengths for specific use cases. -
Fleshing Out Agents and Chains: In conversations involving LangChain scripts, users requested examples and guidance for creating custom tools, registering reactive agents, implementing prompt templates, and generating output keys for given inputs. They also deliberated on the deprecated status of
ZeroShotAgent. -
AI Fine-Tuning Interest: A user expressed interest in learning about training and fine-tuning LLMs without a GPU, with another recommending the use of Google Colab and frameworks like ludwig.ai for this purpose.
Links mentioned:
- Microsoft Excel | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: The UnstructuredExcelLoader is used to load Microsoft Excel files.
- Route logic based on input | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: dynamically-route-logic-based-on-input}
- Route logic based on input | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: dynamically-route-logic-based-on-input}
- no title found: no description found
- SerpAPI Loader | 🦜️🔗 Langchain: This guide shows how to use SerpAPI with LangChain to load web search results.
- Quickstart | 🦜️🔗 Langchain: In this guide, we will go over the basic ways to create Chains and Agents that call Tools. Tools can be just about anything — APIs, functions, databases, etc. Tools allow us to extend the capabilities...
- Entity | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: Entity memory remembers given facts about specific entities in a conversation. It extracts information on entities (using an LLM) and builds up its knowledge about that entity over time (also using an...
- Lemon Agent | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: Lemon Agent helps you
- Prompting strategies | 🦜️🔗 Langchain: In this guide we’ll go over prompting strategies to improve graph
- 🦜🕸️LangGraph | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: Downloads
- LangGraph | 🦜️🔗 Langchain: ⚡ Building language agents as graphs ⚡
- Quickstart | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: quickstart}
- Summarization | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: Open In Colab
- Pesquisa de mercado: Gostaríamos de convidá-lo a participar de nossa pesquisa de mercado. Sua participação é fundamental para ajudar nossa empresa a entender melhor o mercado e aprimorar nosso MVP. Nossa pesquisa é projet...
- Quickstart | 🦜️🔗 Langchain: In this quickstart we'll show you how to:
- Using local models | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: The popularity of projects like
- Build software better, together: GitHub is where people build software. More than 100 million people use GitHub to discover, fork, and contribute to over 420 million projects.
- Issues · langchain-ai/langchain: 🦜🔗 Build context-aware reasoning applications. Contribute to langchain-ai/langchain development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Issues · langchain-ai/langchain: 🦜🔗 Build context-aware reasoning applications. Contribute to langchain-ai/langchain development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Quickstart | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: In this quickstart we'll show you how to:
- LangGraph | 🦜️🔗 Langchain: ⚡ Building language agents as graphs ⚡
- community: extend Predibase integration to support fine-tuned LLM adapters by alexsherstinsky · Pull Request #19979 · langchain-ai/langchain: PR title: "package: description" Where "package" is whichever of langchain, community, core, experimental, etc. is being modified. Use "docs: ..." for purely docs change...
- langchain/libs/community/pyproject.toml at request-body-reference · anujmehta/langchain: 🦜🔗 Build context-aware reasoning applications. Contribute to anujmehta/langchain development by creating an account on GitHub.
- langchain/libs/community/pyproject.toml at request-body-reference · anujmehta/langchain: 🦜🔗 Build context-aware reasoning applications. Contribute to anujmehta/langchain development by creating an account on GitHub.
LangChain AI ▷ #share-your-work (45 messages🔥):
-
Semantic Chunking for Node.js: A TypeScript implementation of Semantic Chunking, now available for those using Node.js environments, enabling the effective processing of large text corpora into semantic chunks. The technique combines sentences for context, utilizes OpenAI’s service for sentence embeddings, and groups semantically similar sentences. Check out the shared gist for details.
-
New AI Image Generation Models in Artful: Artful AI has been updated with new models Dalle Creative, Anime Dream, & Epic Realism, designed for transforming ideas into stunning images. This AI image generator has also undergone bug fixes to enhance user experience. Take a look at the new features on Google Play Store.
-
AISploit for Exploiting LLM AI Solutions: Introducing AISploit, a tiny package aimed at aiding red teams and penetration testers in exploiting large language model AI solutions. The tool can be an essential asset for security professionals working with AI. Find it on GitHub.
Links mentioned:
- ReAct | 🦜️🔗 Langchain: This walkthrough showcases using an agent to implement the ReAct logic.
- JSON Chat Agent | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: Some language models are particularly good at writing JSON. This agent
- Artful - AI Art Generator - Apps on Google Play: no description found
- Structuring | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: One of the most important steps in retrieval is turning a text input
- LangSmith: no description found
- LangSmith Walkthrough | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: Open In Colab
- LangSmith Walkthrough | 🦜️🔗 Langchain: LangChain makes it easy to prototype LLM applications and Agents. However, delivering LLM applications to production can be deceptively difficult. You will have to iterate on your prompts, chains, and...
- GitHub - hupe1980/aisploit: 🤖🛡️🔍🔒🔑 Tiny package designed to support red teams and penetration testers in exploiting large language model AI solutions.: 🤖🛡️🔍🔒🔑 Tiny package designed to support red teams and penetration testers in exploiting large language model AI solutions. - hupe1980/aisploit
- This TypeScript snippet processes a large corpus of text to output semantic chunks by tokenizing into sentences, combining them for context, generating sentence embeddings with OpenAI's service, calculating cosine similarities to identify semantic shifts, and finally grouping sentences into semantically cohesive chunks based on these shifts.: This TypeScript snippet processes a large corpus of text to output semantic chunks by tokenizing into sentences, combining them for context, generating sentence embeddings with OpenAI's servic...
- LangSmith: no description found
- Add chat history | 🦜️🔗 Langchain: In many Q&A applications we want to allow the user to have a
- Add chat history | 🦜️🔗 LangChain: In many Q&A applications we want to allow the user to have a
- Issues · langchain-ai/langchain: 🦜🔗 Build context-aware reasoning applications. Contribute to langchain-ai/langchain development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Issues · langchain-ai/langchain: 🦜🔗 Build context-aware reasoning applications. Contribute to langchain-ai/langchain development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Issues · langchain-ai/langchain: 🦜🔗 Build context-aware reasoning applications. Contribute to langchain-ai/langchain development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Tool usage | 🦜️🔗 Langchain: This section will cover how to create conversational agents: chatbots that can interact with other systems and APIs using tools.
LAION ▷ #general (157 messages🔥🔥):
-
Apple’s AI Efforts Dubbed Lackluster: Discussion centers on Apple’s perceived failure to deliver on AI promises with critiques about MPS (Metal Performance Shaders) and torch compile being suboptimal on their platforms. They also discussed recently merged fixes for MPS in the PyTorch nightly branch, with members sharing varied experiences with the implementation and functionality of torch.compile.
-
Challenging Legal Terrain in AI-Rewritten Text: Members engaged in an exploration of the legality surrounding the use of AI to rewrite copyrighted texts. There was consensus that mere paraphrasing or name changes do not eliminate copyright infringement, and skirting copyright may require significant legal shifts or new practices in AI training data use.
-
New AI Music Generation Battle Heats Up: A conversation about the advances in AI-generated music touched on companies like Suno and its yet-to-be-named competitors from Nvidia, with enthusiasm for the new technology tempered by predictions of legal challenges from the music industry. Insight was offered on the limited “real world” advances in TTS despite the leap in AI music capabilities.
-
Surge in AI Ethics, Careers, and Models: Discussions highlighted the dynamics in AI-related careers influenced by AI enhancements, with a focus on freelancing. Moreover, Stability AI released a zero SNR model, CosXL, under a non-commercial research community license agreement, prompting debates over the practical and theoretical aspects of their approach, including the use of EDM schedules and offset noise in model training.
-
Data Scarcity and Open Projects in AI: Users shared experiences and requests for assistance with specific AI projects, such as generating images of a personal school using Stable Diffusion, while others commented on the availability of rare datasets like CT abdominal images. Also mentioned were contributions to the open-source community, like PKU-YuanGroup’s Open-Sora-Plan, as initiatives to replicate landmark AI functionalities like OpenAI’s T2V model.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from ʟᴇɢɪᴛ (@legit_rumors): here's an exclusive new udio AI music generation 🫡 source: anon. anon is always the source.
- Tweet from moonbi⭕ (@lifeafterAi_): This post was deleted. Seems like suno’s competitor is nivdia 👀 btw this sounds like 2pac 🔥🔥 @apples_jimmy good call again 🐐
- stabilityai/cosxl · Hugging Face: no description found
- Google Colaboratory: no description found
- sonauto-platform: no description found
- The jobs being replaced by AI - an analysis of 5M freelancing jobs - bloomberry: There’s no question that AI will impact jobs. But which jobs are more likely to be replaced by…
- Open-Sora-Plan/docs/Report-v1.0.0.md at main · PKU-YuanGroup/Open-Sora-Plan: This project aim to reproduce Sora (Open AI T2V model), but we only have limited resource. We deeply wish the all open source community can contribute to this project. - PKU-YuanGroup/Open-Sora-Plan
- GitHub - facebookresearch/schedule_free: Schedule-Free Optimization in PyTorch: Schedule-Free Optimization in PyTorch. Contribute to facebookresearch/schedule_free development by creating an account on GitHub.
LAION ▷ #research (23 messages🔥):
- Dynamic Compute Allocation in Transformers: A new paper details how transformers can allocate computational resources (FLOPs) dynamically across input sequences using a top-$k$ routing mechanism, optimizing the self-attention and MLP computations within a predetermined compute budget.
- Efficiency Innovations Round-Up: The r/singularity subreddit contains a list of recent papers and approaches aimed at reducing pretraining, fine-tuning, and inference costs for various AI applications.
- DARE Method for Language Model Capability Assimilation: Research introduced DARE, a tool to merge and sparsify delta parameters across fine-tuned language models, potentially demonstrating that significant pruning of these parameters is possible without loss of capabilities.
- BrushNet for Enhanced AI Inpainting: An announcement of BrushNet, a new method for inpainting that incorporates object detection, was shared along with a tutorial video explaining how it generates higher-quality results.
- Exploring Latent Diffusion in Text Generation: A discussion was ignited by a NeurIPS paper on “Latent Diffusion for Language Generation,” suggesting innovative directions for text generation, highlighting a potential move towards techniques commonly used in image model generation.
Links mentioned:
- Mixture-of-Depths: Dynamically allocating compute in transformer-based language models: Transformer-based language models spread FLOPs uniformly across input sequences. In this work we demonstrate that transformers can instead learn to dynamically allocate FLOPs (or compute) to specific ...
- Language Models are Super Mario: Absorbing Abilities from Homologous Models as a Free Lunch: In this paper, we unveil that Language Models (LMs) can acquire new capabilities by assimilating parameters from homologous models without retraining or GPUs. We first introduce DARE to set most delta...
- Rick And Morty That Just Sounds Like Slavery With Extra Steps GIF - Rick And Morty That Just Sounds Like Slavery With Extra Steps Slave - Discover & Share GIFs: Click to view the GIF
- Language Modeling by Estimating the Ratios of the Data Distribution | Aaron Lou: no description found
- Reddit - Dive into anything: no description found
- BrushNet - The Best InPainting Method Yet? FREE Local Install!: Inpainting with the latest BrushNet models for AI generation using stable diffusion is lots of fun! Get great results quickly thanks to both random and segme...
Latent Space ▷ #ai-general-chat (88 messages🔥🔥):
-
Victor Taelin’s Prompt Challenge Proven Wrong: A $10k prize was awarded after it was proven that GPT models could solve the A::B problem, challenging the initial claim that GPT architectures lack the capability for certain problem-solving tasks, particularly regarding long-term reasoning. The prize-winning solution achieved a near 100% success rate, sparking discussions about the potential of GPT models and their existing architectures. Victor Taelin’s admission can be found here.
-
CS336: Language Modeling from Scratch: Stanford offers a new course CS336, conducted by Professor Percy Liang, focusing on the fundamentals of language modeling, including Transformers, LLMs, and optimizers. There’s high interest in the materials and a request has been made to release lecture recordings.
-
Groq’s Ambitious AI Hardware Goals: Groq’s founder, a high school and undergrad dropout, details their journey from starting the TPU project at Google to expecting Groq to have the largest inference capacity by next year, surpassing all providers combined. Groq is now at 75k developers and boasts lower inference costs and faster hardware than NVIDIA’s H200.
-
LangChain’s New Memory Service: LangChain releases an alpha memory service for chatbots to automatically extract and enrich user conversations, potentially improving personalization and user experience. Documentation and quick start resources are available.
-
New Techniques in Transformer Architecture: Discussions around the effectiveness of ensemble methods with LLMs lead to the acknowledgment that using multiple agents and voting methods can enhance performance, particularly in challenging tasks. The method involves scoring based on the most common outputs amongst similar responses.
-
Attention Mechanism Illuminated: A new video by 3Blue1Brown demystifies the attention mechanism within transformers and LLMs. The content is applauded for its clear explanation and considered to be a potential resource for educational discussions.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Soumith Chintala (@soumithchintala): @fchollet @JeffDean @GoogleDeepMind This is honestly a baffling response. You cant be saying that benchmarking FP32 vs TF32 (just the dtype) is a "compiler optimization". Honestly, I'm los...
- Tweet from Chris Lattner (@clattner_llvm): I love both PT and XLA/TF and am happy you are working through your differences. Speaking as one on the outside, we all want ai to win and all the systems to succeed. If one wants to resort to benchma...
- Tweet from Taelin (@VictorTaelin): I *WAS* WRONG - $10K CLAIMED! ## The Claim Two days ago, I confidently claimed that "GPTs will NEVER solve the A::B problem". I believed that: 1. GPTs can't truly learn new problems, out...
- Tweet from Taelin (@VictorTaelin): dear diary today I taught 1k people how to use interaction combinators but at what cost ↘️ Quoting Taelin (@VictorTaelin) A simple puzzle GPTs will NEVER solve: As a good programmer, I like isol...
- Tweet from Taelin (@VictorTaelin): I *WAS* WRONG - $10K CLAIMED! ## The Claim Two days ago, I confidently claimed that "GPTs will NEVER solve the A::B problem". I believed that: 1. GPTs can't truly learn new problems, out...
- Tweet from Greg Brockman (@gdb): Making a music video with Sora: "this is how the song has always 'looked', it's just that now i get to show you." https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Se93p3gk_14
- Tweet from Niels Rogge (@NielsRogge): Watched a super interesting talk on Ring Attention, probably the magic behind Gemini's 1 million context window You organize your devices (GPU/TPU) in a ring, each computing a part of the final a...
- CS25: Tranformers United!: Disussing the latest breakthroughs with Transformers in diverse domains
- More Agents Is All You Need: We find that, simply via a sampling-and-voting method, the performance of large language models (LLMs) scales with the number of agents instantiated. Also, this method is orthogonal to existing compli...
- Brightwave: no description found
- Notion – The all-in-one workspace for your notes, tasks, wikis, and databases.: A new tool that blends your everyday work apps into one. It's the all-in-one workspace for you and your team
- Innovating Data Centers with Moore's Law | 48sec snip from ChinaTalk: 48sec snip from A Gut Check on Intel and Nvidia with Asianometry, Fabricated Knowledge, and SemiAnalysis | ChinaTalk
- Retrieval-Augmented Generation for Large Language Models: A Survey: Large Language Models (LLMs) showcase impressive capabilities but encounter challenges like hallucination, outdated knowledge, and non-transparent, untraceable reasoning processes. Retrieval-Augmented...
- Evolution of RAG: Addressing the common problems of a simple RAG system: RAG is not all you need. This post will cover some of the common problems that are encountered in a simple RAG system, and potential solutions for them.
- Tweet from LlamaIndex 🦙 (@llama_index): This is an excellent tutorial by @mesudarshan showing you how to build advanced PDF RAG with LlamaParse and purely local models for embedding, LLMs, and reranking (@GroqInc and FastEmbed by @qdrant_en...
- Tweet from Andrew Ng (@AndrewYNg): New JavaScript short course: Build a full-stack web application that uses RAG in JavaScript RAG Web Apps with LlamaIndex, taught by @seldo, VP of Developer Relations at @llama_index and npm co-founder...
- Tweet from LlamaIndex 🦙 (@llama_index): Use LlamaIndex and @MathpixApp to parse and index complex mathematics to LaTeX, and answer questions about scientific papers! Check out this detailed notebook in which MathPix takes you through ➡️ Pa...
- Tweet from LlamaIndex 🦙 (@llama_index): Let’s walk through RAG pain points and solutions! 🧑🏫🎬 We’re excited to feature @wenqi_glantz for a video walkthrough video of her popular “12 RAG Pain Points and Solutions” blog post, which is th...
- Modular: How to Be Confident in Your Performance Benchmarking: We are building a next-generation AI developer platform for the world. Check out our latest post: How to Be Confident in Your Performance Benchmarking
- RSVP to Realtime Voice AI and Multimodal Hackathon | Partiful: Hi fellow lovely hackers, The AI Engineer Foundation (Your Friendly Open Source Nonprofit Neighbor - website: aie.foundation) is hosting a Real Time Interactive/Conversational Multimodal AI hackathon...
- How to talk to an LLM (with your voice): Code for building real-time AI WebRTC applications
- LangMem - LangMem: no description found
- no title found: no description found
- I’m sharing an item with you using 1Password: A password manager, digital vault, form filler and secure digital wallet. 1Password remembers all your passwords for you to help keep account information safe.
- YouTube: no description found
- State of the art in LLMs + Robotics - 2023: tldr I write about some of the more interesting works that shaped my understanding of applying LLMs for AI agents and robotic applications. Introduction What is this LLMs as a fad - a caveat Are LLM...
- spring2024-assignment1-basics/cs336_spring2024_assignment1_basics.pdf at master · stanford-cs336/spring2024-assignment1-basics: Contribute to stanford-cs336/spring2024-assignment1-basics development by creating an account on GitHub.
- Eugene Cheah - From idea to LLM (RWKV / Recursal): Talk from the Open-Source Generative AI Workshop at Cornell Tech. Website: https://github.com/PicoCreatorSlides: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1-lfITA0j_9-...
- Visualizing Attention, a Transformer's Heart | Chapter 6, Deep Learning: Demystifying attention, the key mechanism inside transformers and LLMs.Instead of sponsored ad reads, these lessons are funded directly by viewers: https://3...
- bobatea/pkg/chat/README.md at main · go-go-golems/bobatea: Custom bubbletea bubbles. Contribute to go-go-golems/bobatea development by creating an account on GitHub.
- bobatea/cmd/chat/backend.go at main · go-go-golems/bobatea: Custom bubbletea bubbles. Contribute to go-go-golems/bobatea development by creating an account on GitHub.
Latent Space ▷ #ai-announcements (8 messages🔥):
-
Announcing Latent Space University’s Inaugural Course: The Latent Space University is kicking off its first course on AI Engineering with a free introductory session at 1pm PT. Sign up and details are available at Maven Learning, Inc..
-
Clash of Events: There’s a light-hearted acknowledgment of scheduling overlap as a course introduction coincides with the Latent Space Discord event.
-
Expand Your AI Expertise in Three Weeks: A new course promises a comprehensive journey through AI modalities, covering OpenAI API, Retrieval Augmented Generation, Code Generation, Image Generation, and Speech-to-Text features over a span of three weeks. A discount is available with the code “lightning” as stated in the Course Overview.
-
Weekend Podcast Teaser: A new podcast episode has been released for the weekend, with the announcement shared via a Twitter link.
-
Latent Space Podcast Weekend Special: The podcast covers various topics including AI UX, The World’s Fair, and the latest in AI technology and leadership. Dive into the discussion of the AI Engineering trends and more in the Weekend Special episode summarized on Latent Space.
Links mentioned:
- Level Up From Software Engineer to AI Engineer by Shawn "Swyx" Wang and Noah Hein on Maven: From Dabbling To Complete Competency: Learn how to build real-world working AI products
- Code a custom ChatGPT: This is the foundation of AI products. If you want to be an AI engineer these are MUST KNOW topics and API's. Everything from ChatGPT to robust AI powered summarization and classification use th...
- Latent Space Chats: NLW (Four Wars, GPT5), Josh Albrecht/Ali Rohde (TNAI), Dylan Patel/Semianalysis (Groq), Milind Naphade (Nvidia GTC), Personal AI (ft. Harrison Chase — LangFriend/LangMem): 5 recent Latent Space appearances for you to get your LS fix on all AI Engineering topics imaginable.
Latent Space ▷ #ai-in-action-club (57 messages🔥🔥):
- Seamless Knowledge Capture: A discussion highlighted the use of chat applications, like Slack, as knowledge bases, suggesting it’s a “power move” for capturing and synthesizing useful information artifacts from human-to-human interactions.
- Optimizing Text Work: A member emphasized the attractiveness and feasibility of reducing cognitive load through structured documents, rather than relying on Slack, which was pointed out to be a “terrible system of record” despite being where “the action happens” in many companies.
- Tools and Integrations Galore: The chat surfaced several resources for augmenting personal knowledge bases and workspaces with AI, including Obsidian-Copilot and fabric for AI-augmented human performance, along with a suggestion to use Obsidian’s CLI tools.
- Building Better Bridges: Ongoing exploration of integrations for AI tools like ChatGPT into personal knowledge systems, such as Obsidian, was discussed, focusing on existing plugins and the potential for creating new ones.
- Collaborative Contribution: The chat concluded with acknowledgments for sharing useful ideas and resources, indicating a collective appreciation for the insights and suggestions offered during the discussion.
Links mentioned:
- GitHub - logancyang/obsidian-copilot: A ChatGPT Copilot in Obsidian: A ChatGPT Copilot in Obsidian. Contribute to logancyang/obsidian-copilot development by creating an account on GitHub.
- GitHub - Yakitrak/obsidian-cli: Interact with Obsidian in the terminal. Open, search, create, update, move and delete notes!: Interact with Obsidian in the terminal. Open, search, create, update, move and delete notes! - Yakitrak/obsidian-cli
- AI In Action: Weekly Jam Sessions: 2024 Topic,Date,Facilitator,Resources,@dropdown,@ UI/UX patterns for GenAI,1/26/2024,nuvic,<a href="https://maggieappleton.com/squish-structure">https://maggieappleton.com/squish-stru...
- GitHub - danielmiessler/fabric: fabric is an open-source framework for augmenting humans using AI. It provides a modular framework for solving specific problems using a crowdsourced set of AI prompts that can be used anywhere.: fabric is an open-source framework for augmenting humans using AI. It provides a modular framework for solving specific problems using a crowdsourced set of AI prompts that can be used anywhere. - ...
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) ▷ #general (53 messages🔥):
-
AWQ Models Operational on Hugging Face Inference: A member mentioned successfully running awq models on Hugging Face’s inference service.
-
GitHub Oddity Noted: There was a report of GitHub search redirecting to a specific page with a detailed description and image, suspected to be an auto-redirection issue.
-
Enthusiasm for New Qwen Model: Dialog centered on the latest qwen model, with specific interest in its 32B variant. Further discussions suggested that Yi 34B and Command R were also models of interest for comparison on the same fine-tune dataset.
-
Training on Context Length with Ring Attention: A member brought attention to a GitHub repository named EasyContext by jzhang38, which outlines a memory optimization and training recipe for extrapolating LM context length to 1 million tokens using ring attention on 8xA100 GPUs. Accompanying this was a Twitter thread by the author discussing the decline in training throughput as context size increases.
-
Schedule-Free Optimization on GitHub: Introduction to the Schedule-Free Optimization in PyTorch repository was posted, presumably to highlight a tool for improving optimization processes.
-
Coding Challenges with ORPO Structure: A member detailed their struggles with the ORPO structure when trying to implement a new prompt template and encountering issues with micro_batch_size. Caseus_ confirmed ongoing issues with ORPO and batch sizes in a subsequent response.
-
Generative AI Summit Consideration and Reflection: A member weighed the pros and cons of attending a Generative AI summit in Paris, deliberating on the value of attendance for networking. They later confirmed their attendance and mentioned finishing second at the summit event but not networking much.
Links mentioned:
- Introducing improvements to the fine-tuning API and expanding our custom models program: We’re adding new features to help developers have more control over fine-tuning and announcing new ways to build custom models with OpenAI.
- R.AI.SE Summit: RAISE is a gathering of 1,500+ global leaders dedicated to explore the transformative power of Generative AI on businesses and society. The conference will take place in Paris on April 8th, 2024
- Build AI The Simple Way | Lepton AI: Run AI applications efficiently, at scale, and in minutes with a cloud native platform.
- Build software better, together: GitHub is where people build software. More than 100 million people use GitHub to discover, fork, and contribute to over 420 million projects.
- GitHub - facebookresearch/schedule_free: Schedule-Free Optimization in PyTorch: Schedule-Free Optimization in PyTorch. Contribute to facebookresearch/schedule_free development by creating an account on GitHub.
- GitHub - jzhang38/EasyContext: Memory optimization and training recipes to extrapolate language models' context length to 1 million tokens, with minimal hardware.: Memory optimization and training recipes to extrapolate language models' context length to 1 million tokens, with minimal hardware. - jzhang38/EasyContext
- Add JetMoE model by yikangshen · Pull Request #30005 · huggingface/transformers: What does this PR do? Add support to JetMoE architecture by Yikang Shen and MyShell AI. JetMoE is a new sparsely activated architecture inspired by the ModuleFormer. Each JetMoE block consists of t...
- R.AI.SE Summit: RAISE is a gathering of 1,500+ global leaders dedicated to explore the transformative power of Generative AI on businesses and society. The conference will take place in Paris on April 8th, 2024
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) ▷ #axolotl-dev (19 messages🔥):
-
Quantized DoRA Supported: The
peft=0.10.0now supports quantized DoRA, as indicated in PEFT’s latest release notes. The change may warrant an update to axolotl’srequirements.txtfile. -
Introducing Schedule-Free Learning: Facebook Research has open sourced Schedule-Free Learning, a method that replaces momentum with averaging and interpolation, removing the need for traditional learning rate schedules.
-
New Optimizer Requires Code Changes: Developers should note that the new Schedule-Free optimizer requires additional
optimizer.train()andoptimizer.eval()calls; this is highlighted in the optimizer’s repository. -
ScheduleFreeAdamW Parameters Tuning Tips: For optimal performance with ScheduleFreeAdamW, a value of
0.0025is recommended, and developers should consult the caveats section for guidance on additional tunable parameters. -
Upstream Contributions to Hugging Face Transformers: The support for adamw schedulefree has been upstreamed to Hugging Face’s transformers library, which simplifies integration with deepspeed or PyTorch FSDP configurations.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Aaron Defazio (@aaron_defazio): @divideconcept It needs to be that tuned. See the notes in the caveats section for suggested ranges. The value 0.0025 seems to work pretty reliably for ScheduleFreeAdamW
- Tweet from Aaron Defazio (@aaron_defazio): Schedule-Free Learning https://github.com/facebookresearch/schedule_free We have now open sourced the algorithm behind my series of mysterious plots. Each plot was either Schedule-free SGD or Adam, no...
- add support for adamw schedulefree by winglian · Pull Request #1486 · OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl: implements meta's https://github.com/facebookresearch/schedule_free for adamw https://twitter.com/aaron_defazio/status/1776320004465582331 optimizer: schedule_free_adamw lr_scheduler: constant
- axolotl/src/axolotl/utils/config/models/input/v0_4_1/__init__.py at main · OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl: Go ahead and axolotl questions. Contribute to OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl development by creating an account on GitHub.
- schedulefree optimizers by winglian · Pull Request #30079 · huggingface/transformers: What does this PR do? integrates meta's https://github.com/facebookresearch/schedule_free for adamw & sgd https://twitter.com/aaron_defazio/status/1776320004465582331 Before submitting This ...
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) ▷ #general-help (5 messages):
-
Mistral Model Generation Error: A user reported an error when generating with a fine-tuned Mistral 7b model using fp16. The error occurs after a few successful generations, with a traceback leading to
_queue.Empty. -
Clarification on Inference Method: The user clarified that they were not using the built-in inference method but were instead utilizing Huggingface’s generate with streamer.
-
Assumption of Accelerate Library Usage: Another member suggested the user might be utilizing Accelerate, but the user denied this, confirming they were using plain Python.
-
Sharing of Troublesome Code: The user facing the generation issue shared their code that employs Huggingface’s transformers, python’s threading, and a custom class
StopOnTokensbased onStoppingCriteriaalongside Gradio’s ChatInterface for deploying a chatbot application.
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) ▷ #datasets (1 messages):
faldore: <@&1166009801583628349> porn spam
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) ▷ #docs (3 messages):
- LISA Parameters Not in Config: A member noticed that the parameters for the LISA implementation are missing from
axolotl/docs/config.qmd. - LISA Config Found Elsewhere: The LISA parameters were later found and shared by another member, with a link to the LISA configuration file on GitHub.
- Unfreezing Layers Queries: A question was raised about handling optimizer states after unfreezing new layers during the model training process, capturing the community’s interest in practical implementation details.
Link mentioned: axolotl/examples/llama-2/lisa.yml at main · OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl: Go ahead and axolotl questions. Contribute to OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl development by creating an account on GitHub.
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) ▷ #axolotl-help-bot (46 messages🔥):
-
Docker Image for LoRA Adapter Merge Error: A user encountered a pydantic validation error while trying to merge the LoRA adapter, which required either
flash_attentionorsdp_attentionto be set to true whensample_packingis enabled. -
Training with Raw Text on Mistral Model: For training a Mistral model with raw text, a member shared a YAML configuration example detailing model and tokenizer specifications, dataset paths, and training parameters.
-
Adapting Alpaca Instruction Set for Fine-Tuning: When fine-tuning with an Alpaca instruction set and ChatML format, a user suggested converting the dataset to ShareGPT format and utilizing the conversation: chatml for configuration, which resolved the dataset mix concerns.
-
Micro Batch vs. Batch Size: The difference between micro batch size and batch size was clarified, where micro batch size allows for efficient memory usage and simulates larger batch sizes without computational costs, while batch size updates the model’s weights once per entire batch of data.
-
Config for Disabling Checkpoints and Evaluation Phases: Users discussed how to modify configuration files to never save checkpoints by changing
saves_per_epochto0and inquiring about disabling evaluation phases altogether, suggesting setting theevaluation_strategytoEvaluationStrategy.NO. -
Handling of Undefined Special Tokens in Configs: It was clarified that when special tokens are not defined in a configuration file like
examples/mistral/qlora.yml, default values based on the base model and tokenizer will be used unless they’re specifically overridden.
Links mentioned:
- Redirecting...: no description found
- OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl | Phorm AI Code Search: Understand code, faster.
- OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl | Phorm AI Code Search: Understand code, faster.
- OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl | Phorm AI Code Search: Understand code, faster.
- OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl | Phorm AI Code Search: Understand code, faster.
- OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl | Phorm AI Code Search: Understand code, faster.
- OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl | Phorm AI Code Search: Understand code, faster.
- OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl | Phorm AI Code Search: Understand code, faster.
- OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl | Phorm AI Code Search: Understand code, faster.
OpenAccess AI Collective (axolotl) ▷ #axolotl-phorm-bot (22 messages🔥):
-
Clarifying “rope_theta”: A member inquired about the meaning of
"rope_theta": 10000.0, which refers to a parameter in the Rotary Positional Embedding technique used to introduce positional information to Transformer models. -
FSDP Config for Mistral Revealed: The Fully Sharded Data Parallel (FSDP) configuration for Mistral is specified in the
mixtral-qlora-fsdp.ymlfile, indicating that theMixtralSparseMoeBlockclass should be wrapped for sharding. The conversation included a link to the configuration file. -
LISA Layer Left Undefined: A query about what constitutes a “lisa layer” emerged, but the term does not correspond to widely recognized concepts within the AI and machine learning communities as of the latest knowledge update.
Links mentioned:
- OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl | Phorm AI Code Search: Understand code, faster.
- OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl | Phorm AI Code Search: Understand code, faster.
- OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl | Phorm AI Code Search: Understand code, faster.
- axolotl/examples/mistral/mixtral-qlora-fsdp.yml at main · OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl: Go ahead and axolotl questions. Contribute to OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl development by creating an account on GitHub.
- OpenAccess-AI-Collective/axolotl | Phorm AI Code Search: Understand code, faster.
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #random (15 messages🔥):
- Podcast Potential with John Schulman: The channel’s host, Nathan, contemplated the exciting idea of having John Schulman on for an interview, acknowledging that it somehow slipped his mind before.
- Anticipation for a ‘Banger’ Interview: The suggestion of interviewing John Schulman was met with enthusiasm, with another member agreeing that it would indeed be a hit.
- Exploring New AI Musical Horizons: A link to a tweet was shared, hinting at a competitor to the Suno AI platform, which Nathan found to be “rly freaking good”.
- Opening the License Floodgates: A tweet from @julien_c announced a notable licensing change, switching text-generation-inference (TGI) from a custom HFOIL license back to Apache 2, making the library completely open-source. Nathan commented on Hugging Face’s transparency and the risks they took.
- Contributor Influx Following Licensing Change: The decision to open-source TGI led to a threefold increase in contributors, and despite initial low popularity, the project gained traction after the license modification. Nathan’s ensuing messages appeared to express excitement over this development, using phrases like “rip,” “NOW WE’RE ECLIPSING,” and “LFG,” suggesting positive momentum.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from Robert Dadashi (@robdadashi): The training data was pretty much the same as v1.0, but we switched the RL algorithm to something new. I hope that we will be able to disclose more about this in the future :). 6/11
- Tweet from Julien Chaumond (@julien_c): We have decided to update text-generation-inference (TGI)'s license. We switch the license from HFOIL (our custom license) back to Apache 2, hence making the library fully open-source. Read belo...
- Tweet from ʟᴇɢɪᴛ (@legit_rumors): here's an exclusive new udio AI music generation 🫡 source: anon. anon is always the source.
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #memes (9 messages🔥):
- Someone’s Been Targeted… Again!: A member mentioned being targeted once more, without providing specifics or context.
- Improvements on the Horizon?: Another member responded that their experiences have improved recently, suggesting whatever was “bad” is less so now.
- Advice or Just Meme-ing Around?: A member recommended “Use Code Interpreter” in response to a previous comment, seemingly as a continuation of a joke.
- All in Good Fun: The initial requester clarified that the request was just a meme and thanked the group, indicating no actual need for advice.
- Just Kidding! Employment Status Confirmed: The suggestion of unemployment was clarified as a joke, and the member confirmed being employed and in good stead.
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #reads (55 messages🔥🔥):
-
Debating the Risks and Inevitabilities of Open Model Weights: Discussion centered around the societal impact of open foundation models, concerning whether there needs to be a safety threshold for their release. Diverse views were expressed about the practicality and feasibility of enforcing non-proliferation of AI technology, and whether there’s an ethical responsibility to regulate its distribution.
-
Exploring AI’s Power Dynamic: Members conversed about the potential of language models to manipulate societal and democratic processes. The consensus seemed to focus on the inevitability of advances in AI, the ease of building language models, and their accessibility, leading to a resignation of sorts that tight regulation may not be practical.
-
The Genie Out of the Bottle: A member offered an analogy to discuss the control of powerful AI, likening unrestricted AI to personal genies that could have unwanted societal effects. There was skepticism regarding the practical enforcement of usage restrictions, with a comparison to the challenges faced in nuclear non-proliferation.
-
Scale and Accessibility in Open AI Research: The trend of increasing computational costs to train large models was noted, suggesting that this could outpace the capacity of commodity hardware and gate community/academic access. The current state of model inference being more cost-effective via APIs than running on personal hardware was highlighted.
-
Future Models: Generation vs. Verification: Towards the end of the discussion, the concept of open models that focus on verification rather than generation was brought up. A curiosity was expressed about whether this approach could make models more accessible and bypass the need for large-scale models by shifting verifier knowledge to inference time.
Links mentioned:
- Tweet from James Darpinian (@modeless): @TheXeophon Have you seen the theory that the typos are intentional to filter out the intelligent people
- On the Societal Impact of Open Foundation Models: Adding precision to the debate on openness in AI
- Visualizing Attention, a Transformer's Heart | Chapter 6, Deep Learning: Demystifying attention, the key mechanism inside transformers and LLMs.Instead of sponsored ad reads, these lessons are funded directly by viewers: https://3...
Interconnects (Nathan Lambert) ▷ #sp2024-history-of-open-alignment (31 messages🔥):
- Scouring for Top Fine Tunes: Discussion around utilizing lmsys and the alpacaeval leaderboard as resources to discover effective fine-tuned models. These platforms are highlighted as good starting points for finding models that achieve state-of-the-art performance.
- Acknowledgment of OpenWeights: Within the context of finding models, DeepSeek’s OpenWeights models were mentioned as a potential source.
- Shift to Visual Aids: A commitment was made to clarify and categorize models visually during an upcoming talk; this will include tactics like fading, highlighting, and enlarging specific models on screen for better understanding.
- Live Document for a History Talk: A link to a Google Slides presentation was shared, which appears to be a work-in-progress for an upcoming lecture on “Aligning open language models”.
- Guide to Open Models: Xeophon offered a detailed exposition on Salesforce’s CodeGen series, including the release timeline, datasets used, licensing, plus a comprehensive spreadsheet compiling various models and their attributes. This resource serves to save time for those researching open models.
Links mentioned:
- [18 April 2024] Aligning open language models: Aligning open language models Nathan Lambert Stanford CS25: Transformers United V4 1
- Directory of Generative AI: Pretrained LLMs Name,Date,Parameters (Active),Parameters (Total),Organizaton,Organization Type,Author Location,Language,Commercial Use,Model Accessibility,Code Accessibility,Data Accessibility,Major ...
CUDA MODE ▷ #general (15 messages🔥):
-
Fast Tokenizers: A Need for Speed: A member discussed the slow tokenization process of the c4-en dataset using Huggingface’s fast tokenizer, inquiring about options to speed it up, such as increasing threads. Another suggested looking into machines with more threads.
-
AMD’s Open Source Leap: AMD announced they will open source their Micro Engine Scheduler (MES) firmware, along with documentation and a GitHub tracker for Radeon GPUs. This news aligns with broader efforts by AMD to make their GPU technology more open source and is welcomed by the community, including George Hotz’s Tiny Corp. The Register Article, AMD Radeon Tweet.
-
Paper Replication Repository Launch: An open-source repository dedicated to replicating research papers in AI & ML was announced. They encourage the community to contribute and leave stars on the GitHub repository. PaperReplica GitHub Repo.
-
Seeking CUDA Setup Guides: A new guide for setting up a CUDA development environment on Ubuntu was shared, detailing the installation of CUDA Toolkit, drivers, CuDNN, and OpenCV with CUDA support. The conversation also opened a discussion regarding the comfortability of working with CUDA on different systems. Setup-as-Cuda-programmers GitHub Repo.
-
Innovative Sequence Parallelism for LMs: EasyContext introduces sequence parallelism through ring attention, aiming to extend language models’ context length to 1 million tokens while optimizing memory usage. The GitHub repository offers training recipes for this expansion with minimal hardware. EasyContext GitHub Repo.
Links mentioned:
- Discord - A New Way to Chat with Friends & Communities: Discord is the easiest way to communicate over voice, video, and text. Chat, hang out, and stay close with your friends and communities.
- Tweet from AMD Radeon (@amdradeon): We are working to release Micro-Engine Scheduler(MES) documentation towards end of May and will follow up with published source code for external review and feedback. We have also opened a GitHub trac...
- Discord - A New Way to Chat with Friends & Communities: Discord is the easiest way to communicate over voice, video, and text. Chat, hang out, and stay close with your friends and communities.
- AMD to open source MES firmware for Radeon GPUs: And it was all thanks to peer pressure
- GitHub - hegdeadithyak/PaperReplica: We Replicate Research Papers in the field of AI & ML.: We Replicate Research Papers in the field of AI & ML. - hegdeadithyak/PaperReplica
- GitHub - jzhang38/EasyContext: Memory optimization and training recipes to extrapolate language models' context length to 1 million tokens, with minimal hardware.: Memory optimization and training recipes to extrapolate language models' context length to 1 million tokens, with minimal hardware. - jzhang38/EasyContext
- GitHub - CisMine/Setup-as-Cuda-programmers: Contribute to CisMine/Setup-as-Cuda-programmers development by creating an account on GitHub.
CUDA MODE ▷ #triton (7 messages):
- Library Appreciation Echoed: A member expressed gratitude for a library that enhanced their understanding of Triton and improved their ability to debug Triton kernels.
- Seeking Autotune Knowledge: @ryanatseattle inquired about effective ways to autotune parameters such as
num_wrap,num_stage, andGROUP_SIZEin Triton, mentioning the existingtriton.autotunefeature seems to only provide random configurations. - Auto-tune vs Benchmarking Dilemma: An individual questioned how to best integrate auto-tuning with benchmarking, asking if they should first use auto-tune to determine optimal configurations and then proceed with benchmarking.
- Performance Showdown - Custom CUDA vs Triton: A query was raised regarding the efficiency comparison between custom CUDA kernels in PyTorch and Triton kernels.
- Dot Product vs Addition Comment: @mobicham made a cryptic comment hinting at a preference or observation regarding the use of dot products instead of additions, perhaps in the context of coding or algorithm optimization.
CUDA MODE ▷ #cuda (1 messages):
- GPT-2 Goes Lean and Mean in C: A member shared Andrej Karpathy’s recent GitHub project, llm.c, which enables training of GPT-2 in pure C without the heavy dependencies of PyTorch and Python. This lightweight implementation compiles and runs instantly, boasting clean code and a trainers delight at only ~1,000 lines.
Link mentioned: Tweet from Andrej Karpathy (@karpathy): Have you ever wanted to train LLMs in pure C without 245MB of PyTorch and 107MB of cPython? No? Well now you can! With llm.c: https://github.com/karpathy/llm.c To start, implements GPT-2 training on …
CUDA MODE ▷ #torch (14 messages🔥):
-
Torch compile with async ops dilemma: A member brought up difficulties using torch compile with asynchronous collective operations and was directed towards new experimental functional_collectives that might support torch compile. However, these do not seem to support asynchronous operations like async all reduce.
-
Asynchronous collective operations demystified: In a follow-up, it was clarified that the new functional_collectives are indeed asynchronous and employ tensor subclassing magic to synchronize automatically, or alternatively, users can call
.wait()for explicit synchronization. -
DeepSpeed and Accelerate integration experiences: Another member inquired about the integration of DeepSpeed with Hugging Face’s Accelerate, focusing on whether features like mixture of experts (MoE) are lost. It was suggested that very few features are lost, but that one should manually define a deepspeed configuration JSON file rather than rely on HF trainer settings.
-
Unraveling Memory Usage Mysteries with DeepSpeed: An observation was made that setting zero stage to 0, which should presumably disable it, still results in less memory consumption compared to Distributed Data Parallel (DDP), indicating that DeepSpeed might be running some optimization unknowingly.
-
Deciphering Triton utilization in torch compile: It was highlighted by members discussing torch compile that Triton kernels are utilized only if the inputs are on a CUDA device, else C++ generated code is employed for fused kernels on CPU.
-
Flashing lights on MLPs: A member keen on optimizing their transformer model’s MLP shared that a cublas function-based MLP from the flash attention library wasn’t yielding faster results than simple MLP with torch functionals. They received suggestions to explore further optimizations, potentially using tiny-cuda-nn or CUTLASS over Triton, if fusing operations didn’t outperform matrix multiplication library implementations.
Links mentioned:
- tiny-cuda-nn/DOCUMENTATION.md at master · NVlabs/tiny-cuda-nn: Lightning fast C++/CUDA neural network framework. Contribute to NVlabs/tiny-cuda-nn development by creating an account on GitHub.
- pytorch/torch/_dynamo/variables/functions.py at 014f91a9d9f94ac9a7f0711600240d7cd7f69844 · pytorch/pytorch: Tensors and Dynamic neural networks in Python with strong GPU acceleration - pytorch/pytorch
- pytorch/torch/distributed/_functional_collectives.py at eff1e4899c7c89f8a8fc8f6ff6bed06dd8d2ec8a · pytorch/pytorch: Tensors and Dynamic neural networks in Python with strong GPU acceleration - pytorch/pytorch
CUDA MODE ▷ #announcements (2 messages):
-
CUDA-MODE Lecture Series Continues: The next installment of the CUDA-MODE Lecture Series, Lecture 13: Ring Attention, is scheduled to start at the announced time, presented by the esteemed <@719599526448463933>.
-
Celebrating a Thriving Community: With over 5,000 members, the CUDA-MODE Discord community celebrates its growth and expresses gratitude to its members. The continuity of delivering one lecture per week since its inception is highlighted as a keystroke of success.
-
Applied Learning in Action: The lectures have inspired members to apply their knowledge in the real world, contributing to many active working groups within the community. These practical efforts are evidenced by discussions and collaborations in specific channels.
-
Invitation to Expand the CUDA-MODE Family: Community members are encouraged to invite performance-oriented friends to join the CUDA-MODE adventure and learn together. An invitation is extended via discord.gg/cudamode.
CUDA MODE ▷ #algorithms (7 messages):
-
Revolutionizing Model Quantization: QuaRot, a new quantization scheme, allows for end-to-end quantization of large language models (LLMs) in 4 bits. It uniquely handles outliers and maintains computational invariance, achieving just 0.29 WikiText-2 perplexity loss and 99% zero-shot performance retention for their LLaMa2-70B model.
-
The Challenge of 4-bit Quantization: An observation was made that although QuaRot is a promising advancement, unlike typical 4-bit quantization, it requires training/calibration for effective performance.
-
Scheduling Made Redundant in Optimization: A member spotlighted Schedule-Free Optimization in PyTorch, a repository by Facebook Research, which presents a new approach utilizing schedule-free SGD or Adam.
-
Deep Optimizer Dive on Twitter: A link to a Twitter post by Aaron Defazio was shared, potentially providing insights into the schedule-free optimization technique discussed earlier.
-
Casting Llama in a New Light: A brief mention hinted at a possible connection between schedule-free optimization and something reminiscent of “Llama3”, alluding to its significance.
Links mentioned:
- QuaRot: Outlier-Free 4-Bit Inference in Rotated LLMs: We introduce QuaRot, a new Quantization scheme based on Rotations, which is able to quantize LLMs end-to-end, including all weights, activations, and KV cache in 4 bits. QuaRot rotates LLMs in a way t...
- GitHub - facebookresearch/schedule_free: Schedule-Free Optimization in PyTorch: Schedule-Free Optimization in PyTorch. Contribute to facebookresearch/schedule_free development by creating an account on GitHub.
CUDA MODE ▷ #suggestions (1 messages):
- A Classic Resource for Parallel Algorithm Enthusiasts: One member brought attention to an Udacity course they utilized for their dissertation in 2013. The course covers not only hardware and programming, but it’s also focused on parallel algorithms and performance.
CUDA MODE ▷ #beginner (1 messages):
- Installation Troubles with Nsight Compute: A member experienced issues while installing Nsight Compute on Ubuntu 22.04 using a
.runfile; despite following the installation steps, includingchmod +x, the program did not appear after execution. Attempting to redo the./nsight computecommand resulted in the program extracting again.
CUDA MODE ▷ #youtube-recordings (1 messages):
itali4no: https://youtu.be/ws7angQYIxI?si=PcRy7siLQuFywpgp
CUDA MODE ▷ #jax (1 messages):
- Porting Triton Puzzles to Pallas: There is an interest in porting Triton puzzles to Pallas, and it’s suggested that this could be achieved through the Triton backend for those willing to investigate the possibilities.
CUDA MODE ▷ #ring-attention (8 messages🔥):
- Clarifying Linear Attention: The discussion briefly touched on the nature of linear attention, confirming that it is not the same as classic attention.
- Ring-Flash-Attention Script Shared: A GitHub link was shared for a training script featuring ring-flash-attention by jzhang38. The project aims at context length extrapolation and is suggested to be included in the ring-attention repo’s readme. EasyContext on GitHub.
- Exploring Context Parallelism: A link to NVIDIA documentation was shared illustrating the concept of Context Parallelism, highlighting its difference from sequence parallelism and its impact on transformer models. NVIDIA’s Context Parallelism Docs.
- Progress on Variable Length Striped Attention: A participant mentioned they are working on implementing varlen striped attention but provided no further context on the progress or implications.
- Questioning Ring Attention’s Memory Usage: A query was raised about ring attention’s trade-off between speed and memory usage, particularly in the context of distributed computing and the buffering process in message-passing systems.
Links mentioned:
- Context parallelism overview - NVIDIA Docs: no description found
- GitHub - jzhang38/EasyContext: Memory optimization and training recipes to extrapolate language models' context length to 1 million tokens, with minimal hardware.: Memory optimization and training recipes to extrapolate language models' context length to 1 million tokens, with minimal hardware. - jzhang38/EasyContext
CUDA MODE ▷ #off-topic (3 messages):
-
Clarification on Ring Attention Session Timezone: There was a query regarding the timezone for a session on ring attention, with a clarification sought on whether it was PDT.
-
Naming Conventions in GPU Terminology: A member expressed the opinion that “kernels” may not be the most suitable term for GPU kernels, suggesting it might be too late to change but questioning if others share this sentiment.
CUDA MODE ▷ #hqq (20 messages🔥):
- No Rounding for Quantized Tensors: Group quantization does not involve rounding scales and only supports reshaping with the format
w.reshape(-1, groupsize)for the calculation of scales and zero points. - Ensuring Quant and Dequant Consistency: To verify accurate quantization and dequantization using the provided methods, one can quantize
W_hatusinggpt-fast.quantize.group_quantize_tensor, then dequantize and compare the sum of absolute differences with the originalW_hat. - Quantization Approach Alignment: Clarification that both parties seem to be employing int4 affine, groupwise quantization, albeit potentially along different axes, thus the suggested methods should be compatible.
- Exploring Triton for Performance Gains: Initial experimentation with Triton provided a significant 62x speed increase over PyTorch for unpacking 4-bit tensors on certain matrices, suggesting more optimization could yield even greater performance.
- Quantization Integration and Testing on gpt-fast: Updates in gpt-fast for HQQ 4bit quantization are showing promising token generation speeds, especially when the
--compileflag is enabled, reaching 200 tokens per second. Quantization times and inference speeds appear to be in line with current baselines.
Links mentioned:
- hqq/hqq/core/quantize.py at master · mobiusml/hqq: Official implementation of Half-Quadratic Quantization (HQQ) - mobiusml/hqq
- hqq/examples/llama2_benchmark/eval_model.py at master · mobiusml/hqq: Official implementation of Half-Quadratic Quantization (HQQ) - mobiusml/hqq
- HQQ 4 bit llama 2 4b · zhxchen17/gpt-fast@f945843: export MODEL_REPO=meta-llama/Llama-2-7b-chat-hf scripts/prepare.sh $MODEL_REPO python quantize.py --checkpoint_path checkpoints/$MODEL_REPO/model.pth --mode int4-hqq --groupsize 64 python generate....
- GitHub - pytorch-labs/gpt-fast: Simple and efficient pytorch-native transformer text generation in <1000 LOC of python.: Simple and efficient pytorch-native transformer text generation in <1000 LOC of python. - pytorch-labs/gpt-fast
- gpt-fast/quantize.py at f94584359076dd484acf28119ec49ffc30ce87f1 · zhxchen17/gpt-fast: Simple and efficient pytorch-native transformer text generation in <1000 LOC of python. - zhxchen17/gpt-fast
- hqq/hqq/core/quantize.py at master · mobiusml/hqq: Official implementation of Half-Quadratic Quantization (HQQ) - mobiusml/hqq
- gpt-fast/model.py at main · pytorch-labs/gpt-fast: Simple and efficient pytorch-native transformer text generation in <1000 LOC of python. - pytorch-labs/gpt-fast
- eval_model_wikitext_gptfast.py: GitHub Gist: instantly share code, notes, and snippets.
- adding fused uint4x2_mixed_mm to inductor by HDCharles · Pull Request #106516 · pytorch/pytorch: Stack from ghstack (oldest at bottom): -> #106516 Summary: this is needed for int4 weight-only quantization, we're matching on the specific unpack operation that unpacks the uint4x2 i...
CUDA MODE ▷ #triton-viz (23 messages🔥):
-
Debating the Overkill of Three.js: Members discussed the potential use of Three.js for visualizations, but some felt it might be too powerful and complex for their needs. Consideration was given to using D3 as a more interaction-friendly option.
-
Visualizing Shared Memory and Tensors: There was a conversation about visual representations in triton-viz, considering how to display shared memory and tensor views effectively. One member plans to use ipycanvas + ipyevents for rich visuals within Jupyter, supplementing the current Gradio setup.
-
Triton Debugging Challenges: The group discussed common issues encountered while debugging Triton code, specifically the frequent problem of loading data into the wrong place. A focus was suggested on visualizing data origins in kernels to aid developers.
-
Triton Visualization for CPU Constructs: Members expressed interest in visualizing loops and control flow constructs within triton-viz, though concerns were raised about the current view’s intuitiveness for such features. Brainstorming was encouraged among the members for potential solutions.
-
Interactive Debugging with JavaScript: There was a suggestion to implement visual debugging tools in JavaScript to enhance interactions, such as mouse-over effects and quick animations, to enable better understanding and clearer tutorials for Triton’s debugging traces.
tinygrad (George Hotz) ▷ #general (59 messages🔥🔥):
-
Tinygrad Learning Resources: For those looking to contribute to tinygrad, you can find tutorials and documentation at GitHub - mesozoic-egg/tinygrad-notes.
-
Reversion of the Command Queue: George Hotz mentioned a reversion of the command queue in tinygrad development with a comment, lol no, reverted.
-
Memory Scheduler Integration Strategy: According to George Hotz, the memory scheduler is to be integrated into the scheduler itself, and the queue stuff can be handled with the existing multidevicegraph abstraction.
-
Exploration of RISC-V Opcodes in Firmware: Members discussed the architecture of MEC firmware, debating whether it is RISC-V based and analyzing differing opcode structures, including an unexpected
cbzinstruction. -
Usage Guidelines for TinyJit Requested: A member sought advice on using TinyJit and whether issues they encountered were due to misuse or a bug, sparking a further discussion on the nuances of RISC-V ISA including ARM mnemonic use.
-
Tinygrad Role Redefinition and Community Responsibilities Emphasized: George Hotz updated the Discord roles to reflect contributions and involvement, highlighting the importance of effective collaboration and mindful use of others’ time in the tinygrad project development.
Links mentioned:
- GitHub - mesozoic-egg/tinygrad-notes: Tutorials on tinygrad: Tutorials on tinygrad. Contribute to mesozoic-egg/tinygrad-notes development by creating an account on GitHub.
- new memory scheduler with LRU by geohot · Pull Request #4094 · tinygrad/tinygrad: no description found
tinygrad (George Hotz) ▷ #learn-tinygrad (6 messages):
- TinyJIT Unveiled: A member shared a tutorial on TinyJit for those interested in how it works, though it may contain some inaccuracies, particularly in the
apply_graph_to_jitsection. - Clarifying TinyJIT Mechanics and Seeking Insight: The member who shared the TinyJit tutorial noted possible issues with the runtime under
/graphfolder and invited others to message with insights to improve the accuracy of the content. - Call for Error Correction on TinyJIT Tutorial: In response to potential inaccuracies, another member requested for “reds” to create an error-correcting pull request to aid the community.
- Diving into Multi GPU Training with Tinygrad: Another tutorial explaining how tinygrad implements multi GPU training was introduced, with the source available on GitHub.
- Community Praise for Multi GPU Training Guide: The multi GPU training tutorial was well-received, acknowledged by a member as very useful.
Links mentioned:
- mesozoic-egg - Overview: mesozoic-egg has 4 repositories available. Follow their code on GitHub.
- tinygrad-notes/jit.md at main · mesozoic-egg/tinygrad-notes: Tutorials on tinygrad. Contribute to mesozoic-egg/tinygrad-notes development by creating an account on GitHub.
- tinygrad-notes/multigpu.md at main · mesozoic-egg/tinygrad-notes: Tutorials on tinygrad. Contribute to mesozoic-egg/tinygrad-notes development by creating an account on GitHub.
Mozilla AI ▷ #llamafile (26 messages🔥):
-
Appeals to Resolve Llamafile False Positives: Llamafile versions face false positive malware detections, possibly affecting llamafile-0.6.2.exe and llamafile-0.7. An appeal to those AVs with an appeals form was suggested as a possible action to take.
-
GPU Issues with Llamafile in Kaggle: A user experienced issues when running
llamafilein Kaggle, due to complications with compiling CUDA and finding a compatible GPU arch. Another user provided an updated command to facilitatellamafile-0.7usage. -
Local Distribution Considerations for RAG-LLM Application: A member inquired about distributing a RAG-LLM application locally without heavy dependencies like Docker or Python and was open to using llamafile for macOS users. An assurance was given that llamafile could meet these requirements.
-
Llamafile Out of Memory Error Resolved by Adjusting
-ngl: One user successfully resolved an out of memory error by tweaking the-nglargument, which they initially set too high for their NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1050 card. -
Vulkan Support Enhancement Proposed: A suggestion was made to add support for Vulkan in llamafile after testing showed improved performance on a modest Intel-based laptop with an integrated GPU. However, concerns were raised about the need to re-import and apply local changes to llama.cpp to achieve this.
Links mentioned:
- VirusTotal: no description found
- VirusTotal: no description found
- VirusTotal: no description found
DiscoResearch ▷ #general (9 messages🔥):
- Schedule-Free Optimizers come to HF Transformers: A new pull request in the huggingface/transformers repository introduces integration of Meta’s schedule-free optimizers for AdamW and SGD, which could be a significant update for the training of models.
- Training with AdaptiveSoftmax?: One member is seeking insights or success stories from others regarding training with adaptivesoftmax but did not provide specific details or context.
- AI Community Event in Germany: The “AIDEV” Community event is announced for AI engineers in Germany, taking place in Hürth on May 7th. Discussions will center around synthetic data generation, LLM/RAG pipelines, and embeddings with a developer-centric, no-nonsense approach. Interested parties can register for free at Developer Event - AI Village.
- Request for Public Info on Synthetic Data Generation: One member inquires about public information or discussions on synthetic data generation and related strategies, particularly in German contexts, with mentions of German translated vs. German generated data.
- Post-Event Summary Sharing: Several members express enthusiasm for the upcoming event in Hürth, Germany, with requests to share summaries and insights post-event for those who cannot attend or are eager to digest the discussed content.
Links mentioned:
- schedulefree optimizers by winglian · Pull Request #30079 · huggingface/transformers: What does this PR do? integrates meta's https://github.com/facebookresearch/schedule_free for adamw & sgd https://twitter.com/aaron_defazio/status/1776320004465582331 Before submitting This ...
- Developer Event AI Village: AIDev - Developer Community Large Language Models, LLM Application and generative AI
DiscoResearch ▷ #discolm_german (5 messages):
- Inspirational Command-R Performance: A link to Command-R space on Hugging Face was shared, described as “mindblowing” due to its impressive grounding capabilities, potentially influencing the development of future models.
- Setting New Benchmarks in Middle High German Translation: Command-R from CohereForAI excels at translating Middle High German into modern German, effortlessly outperforming GPT-4 class models and making months of specialized training on other LLMs appear obsolete.
- Implications for Developer Activity and Open-Source Licensing: The hope is expressed that Cohere will adopt a fully open-source license for their new, superior model, as this would likely boost developer engagement and ecosystem growth, with Mistral serving as an example of the economic benefits of such a strategy.
- Concrete Examples of Command-R Superiority: It’s claimed that Command-R provides perfect translations from Middle High German and seems to recognize source material, indicating strong needle-haystack capabilities, which makes it a prime candidate for RAG (retrieval-augmented generation) functions integration.
Link mentioned: C4AI Command R Plus - a Hugging Face Space by CohereForAI: no description found
AI21 Labs (Jamba) ▷ #jamba (9 messages🔥):
-
Jamba’s Training Speed Caution: One member reported that training a 1B Mamba model on an HGX was 76% slower than its transformer counterpart. After some clarification, it was established they were comparing the training speed to that of regular Transformers.
-
Alternate Jamba Solutions for Limited Hardware: A user created downsized versions of the Jamba architecture, the 8xMoE with 29B parameters and 4xMoE with 17.7B parameters, for those unable to run the full 52B model locally. These models have shown promising results and can be fine-tuned on a 4090 GPU at 4 bit.
-
Sharing Downscaled Jamba Techniques: In response to curiosity about how the reduced parameter models were created, the user mentioned using an accumulative Slerp (spherical linear interpolation) of the expert weights and promised to share an
ipynbnotebook soon. -
Inference Engine Queries: A member sought advice on the best inference engine to serve Jamba models, but no direct recommendations followed in the given messages.
-
Challenges with GPU Utilization for Jamba: A user successfully replicated the fine-tuning example from the Hugging Face Jamba model page, but had to spread the 52B model training across 8 GPUs due to its size. They are experiencing limitations due to pipeline parallelism, which is causing only 1/8th of the total GPU capacity to be utilized and inquired about training with Tensor Parallelism (TP).
Datasette - LLM (@SimonW) ▷ #ai (2 messages):
- Powering AI with QNAP NAS: A member highlighted a practical at-home setup for AI using a QNAP NAS with a GPU added to test AI capabilities. The setup in question involves the TS-h1290FX model, which boasts an AMD EPYC 7302P CPU, 256GB DRAM, and 25GbE capability.
- Storing System Prompts for Efficiency: A member inquired whether others have begun storing and retrieving system prompts for common tasks to streamline the process of setting up context in AI interactions. No further context or responses were provided in the available messages.
Link mentioned: Run a Private RAG ChatGPT on QNAP NAS: QNAP NAS platforms have the most unique and capable hardware designes in the category. We added a GPU to one and tested the AI capabilities.
Datasette - LLM (@SimonW) ▷ #llm (3 messages):
- Introducing Alter: Alter, born from the use of llm-cli, is set to launch in beta and brings AI-powered text improvement functionalities to macOS, with a demonstration video available on YouTube. The app integrates with various macOS applications, including Keynote, to generate and edit content.
- AI at Your Fingertips with Alter: Alter promises context-aware AI capabilities across all macOS applications, offering a centralized AI tool to replace multiple subscriptions and addons. Information on features, pricing, and capabilities can be found on the Alter website.
Links mentioned:
- Alter | Invisible AI for your Mac: no description found
- Alter demo - Fix typo and grammar: Improve grammar and spelling across all your apps!Alterhq.com recommends the best actions tailored to your work context.#ai #spelling #macos #chatgpt
Skunkworks AI ▷ #general (1 messages):
- Neural Network Resource Allocation Innovations: Member discussing a paper where dynamic allocation of a static compute budget is managed per token within a neural network. This strategy piqued the member’s interest for implementation in neurallambda, raising the idea that a network could discern how to distribute computational resources optimally.
- Pondering New Training Techniques: The member contemplates incorporating various methods for neurallambda, such as using pause/think tokens, implementing conditionals through reinforcement learning, and drawing inspiration from a paper where RNNs emitted their own compute usage.
- Exploring Neural Input Processing Methods: Additional considerations for neurallambda include reading input into a neural queue for flexible processing and treating input as a tape with the ability to emit tape movements on-demand, resembling a Turing machine’s operation.
Skunkworks AI ▷ #off-topic (2 messages):
- Exploring Structured Data Extraction: A video titled “Instructor, Generating Structure from LLMs” was shared, demonstrating how to extract structured data like JSON from Large Language Models including GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and GPT-4-Vision. The video aims to make it easier to get reliable structured results from LLMs. Watch the video here.
- Another Video Shared: A second YouTube video link was provided without additional context. Check out the video.
Link mentioned: Instructor, Generating Structure from LLMs: Instructor makes it easy to reliably get structured data like JSON from Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-3.5, GPT-4, GPT-4-Vision, including open source…
LLM Perf Enthusiasts AI ▷ #claude (2 messages):
-
Searching for Haiku Speed Solutions: A member inquired about ways to optimize Haiku performance, as they are experiencing unacceptable speed with the current setup.
-
Anthropic’s API Grabs the Spotlight: Results shared by a user show Anthropic’s new tool use beta API has outperformed GPT-4 Turbo in half of the scenarios on the Berkeley function calling benchmark. Full experimental outcomes are detailed in a Twitter thread.
Link mentioned: Tweet from Joschka Braun (@JoschkaBraun): I benchmarked @AnthropicAI’s new tool use beta API on the Berkeley function calling benchmark. Haiku beats GPT-4 Turbo in half of the scenarios. Results in 🧵 A huge thanks to @shishirpatil_, @fa…